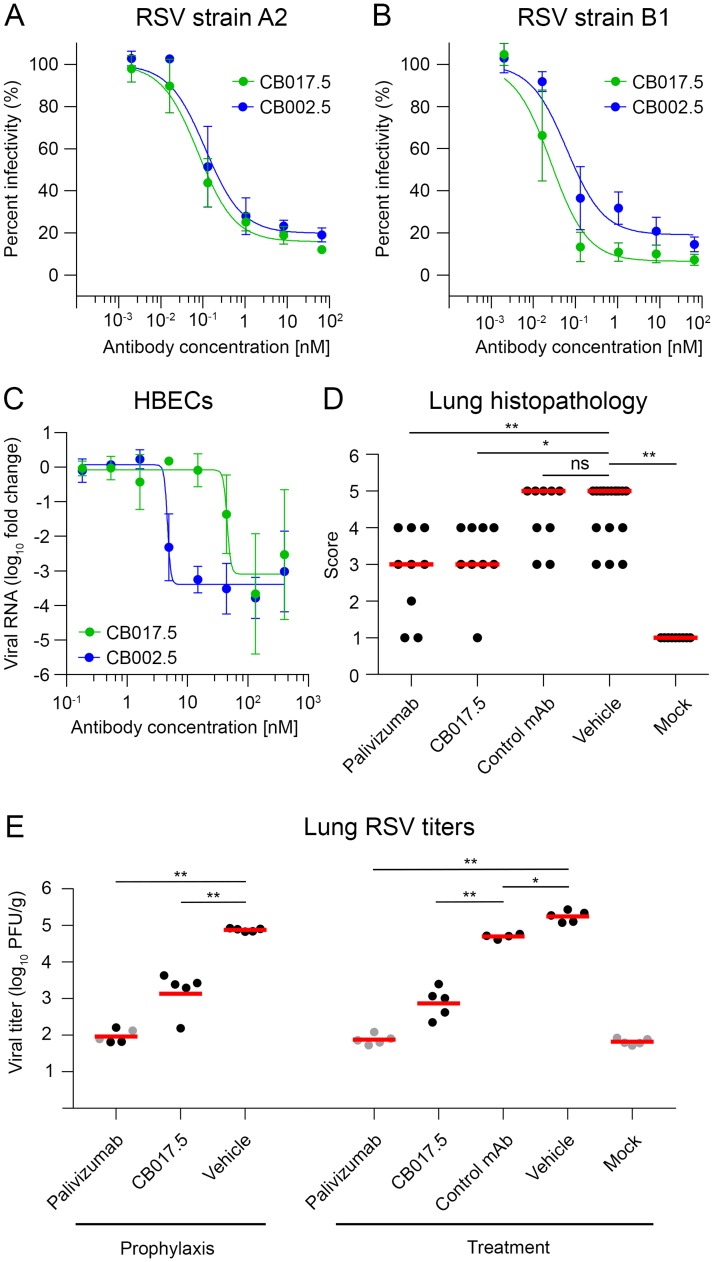
Fig 1. Virus neutralization and cotton rat protection studies.
Neutralization curves based upon a plaque-reduction assay performed in Vero cells in the presence of complement using RSV strain A2 (A) or strain B1 (B) when incubated with CB017.5 IgG (green) or CB002.5 IgG (blue). IC50 values were determined by the mean concentration required to inhibit 50% of RSV infection. (C) Neutralization curves, in the absence of complement, of an in vitro RSV cell culture model using human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) cultured at an air-liquid interface, colored as in A and B. (D) Cotton rat lung histopathology scores of each treatment group in the treatment arm of the study were evaluated six days after infection. Slides were scored blindly as described in the methods, with lower scores indicating reduced inflammation and pathology. The red line indicates the median of each group. (E) Infectious RSV titers in the lungs of cotton rats four days post-infection as determined by plaque assay. Different animal groups were injected prophylactically 24 hours prior to infection, or as a treatment one day after infection, as indicated. Animals used to determine viral titers were not included in the histopathological analysis. The red line indicates the mean viral titer. Gray dots indicate viral titers that were at the lower limit of detection. For panels (D) and (E): *p <.05, **p <.01, ns = not significant.