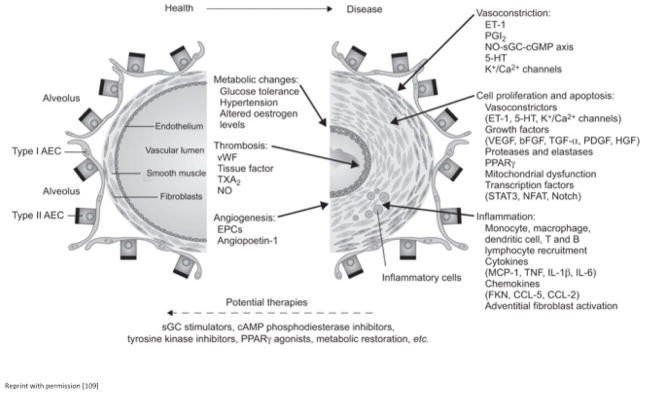
Figure 1.
The key pathological mechanisms underlying vascular changes in pulmonary hypertension (PH). Potential new therapies for PH are also indicated. AEC: Alveolar Epithelial Cell; vWF: von Willebrand Factor; TXA2: Thromboxane A2; NO: Nitric oxide; EPC: Endothelial Progenitor Cell; ET-1: Endothelin-1; PGI2: Prostaglandin I2; sGC: Soluble Guanylate Cyclase; cGMP: Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate; 5-HT: 5-hydroxytryptamine; VEGF: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor; bFGF: Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor; TGF-a: Transforming Growth Factor-a; PDGF: Platelet-derived Growth Factor; HGF: Hepatocyte Growth Factor; PPARc: Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-c;STAT3: Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3; NFAT: Nuclear Factor of Activated T-cells; MCP-1: Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1; TNF: Tumour Necrosis Factor; IL: Interleukin; FKN: Fractalkine; CCL: Chemokine Ligand; cAMP: Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate.