FIGURE 5.
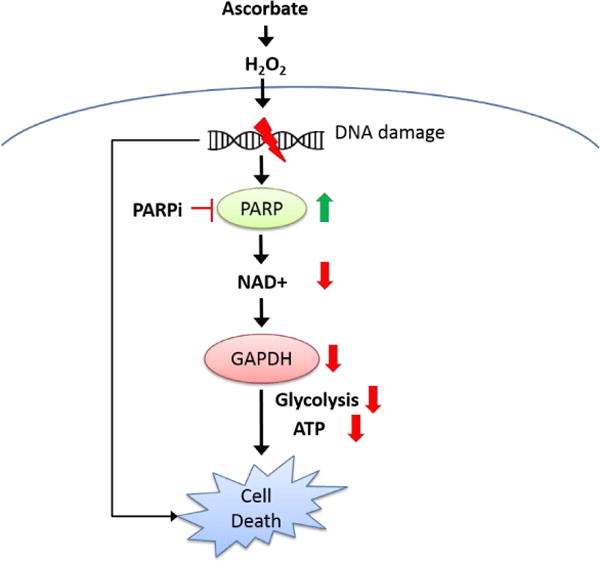
A simplified scheme for the mechanisms of pharmacologic ascorbate-induced cell death. Through oxidative stress, ascorbate damages DNA and activates PARP. Activated PARP depletes NAD+, therefore GAPDH activity is inhibited, and ATP is depleted in neuroblastoma cells, leading to cell death. In the absence of PARP activation, fatal DNA damage accumulates and leads to cell death. PARPi, PARP inhibitor.
