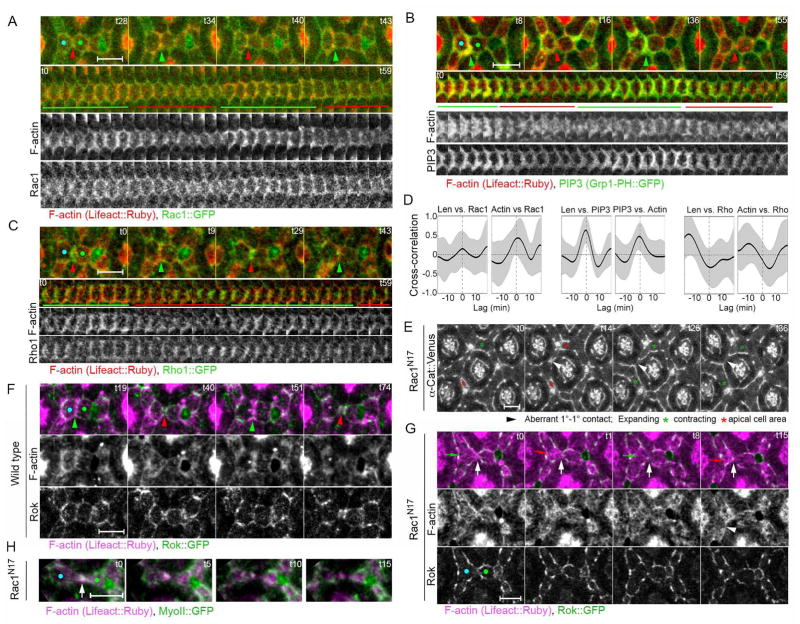
Figure 5.
Phosphoinositide PI(3,4,5)3 accumulate dynamically along LC-LC contacts, and small Rho GTPase signaling affects contractile and protrusive dynamics, cell contact length and lattice remodeling. (A–D) Live imaging of F-actin (Lifeact::Ruby, red) and upstream cytoskeletal regulators (green) in 28–30 hour APF eyes. (A) Rac1::GFP (green) and (B) GFP-tagged PI(3,4,5)3 binding PH domain of GRP1 accumulated along cell contacts and positively correlated with actin accumulation (red) (Rac1: R=.43; shift=45+/−210sec; n=8 contacts from 2 eyes; PI(3,4,5)P3: R=.47; shift=−1.4+/−3.1min n=18 contacts from 3 eyes). PI(3,4,5)P3, but not Rac1, positively correlated with contact length (R=.62; shift=−40+/−78sec). (C) Conversely, Rho correlated negatively with contact length and actin accumulation (length: R=−.32; shift=.5+/−3.7min; actin: R=−.35; shift=5.3+/−3.9min; n=12 contacts from 2 eyes). (D) Cross-correlation analysis of molecular dynamics in A–C. (E) Cell behavior in Rac1N17 expressing eyes. Stills from a time lapse of F-actin (Lifeact::Ruby, magenta) and Rok::GFP (green) in (F) control and (G) Rac1N17-expressing eyes (Movie 5). (F) Wild type eyes exhibit normal F-actin accumulation at expanded (green arrowheads) but not constricted (red arrowheads) contacts. (G) Rac1N17 expressing eyes exhibit loss of pulsed F-actin dynamics along LC-LC contact, as F-actin accumulated medioapically in constricting cells (red arrows), (H) MyoII accumulated with F-actin in separating LC-LC contacts in Rac1N17 eyes. Scale bars = 5 μm.