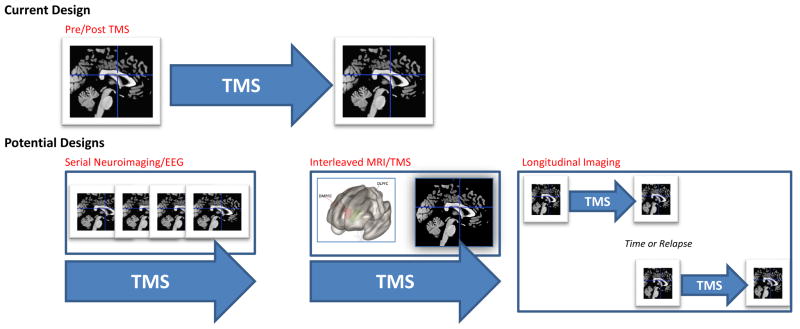
Figure 2. Current and Future Approaches to TMS Neuroimaging.
The most common approach in TMS neuroimaging research is to scan participants prior to and following TMS procedures. While this approach captures change over time, it does not provide information on what happens during the stimulation itself. Future designs may include a) serial neuroimaging, where multiple scans or other imaging modalities are performed at multiple timepoints during a course of TMS, b) causal assessments of neural network function using interleaved MRI/TMS, and c) testing the durability of neuroimaging findings across the course of depressive illness (e.g., over time or in the context of clinical relapse, etc.).
Abbreviations: TMS, transcranial magnetic stimulation; EEG, electroencephalography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging