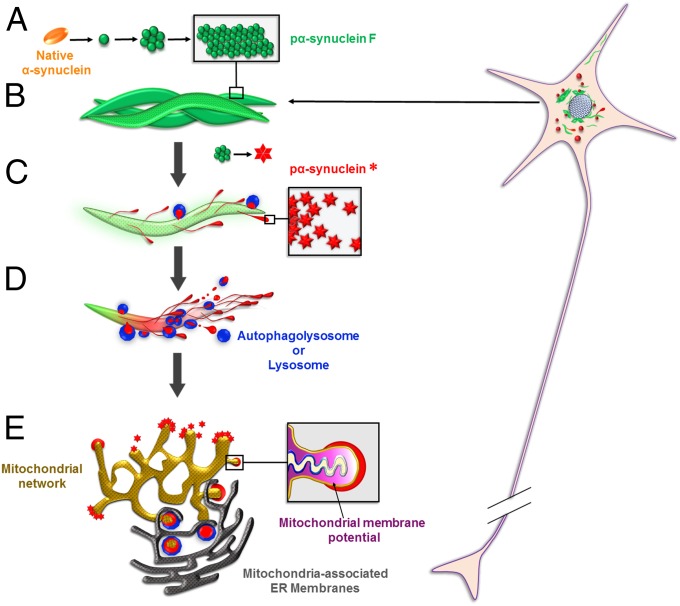
Fig. 11.
Life cycle of pα-syn*. (A) In PFF-seeded neurons, endogenous α-syn misfolds and aggregates in the pα-synF conformation (depicted in green). (B) Pα-synF forms intertwined fibrils. (C) Pα-synF fibrils undergo autophagic degradation (Figs. 3 and 4). However, this process is incomplete, generating an N- and C-terminally trimmed pα-syn species with a different conformation, pα-syn* (depicted in red). (D) Pα-syn*-containing lysosomes are found in the pα-synF fibrillar core or on the fibril surface (Figs. 3 and 5). Autophagolysosomes/lysosomes are shown in blue. (E) Pα-syn* aggregates exit the lysosomes (Fig. 5) and localize to mitochondria (Fig. 7). Pα-syn* aggregates colocalize with MAMs (33), sites of Parkin-dependent mitochondrial fission and mitophagy (34). They induce mitochondrial membrane depolarization, cytochrome C release, oxidative and energetic stress, mitochondrial fragmentation, and mitophagy (Figs. 7–10).