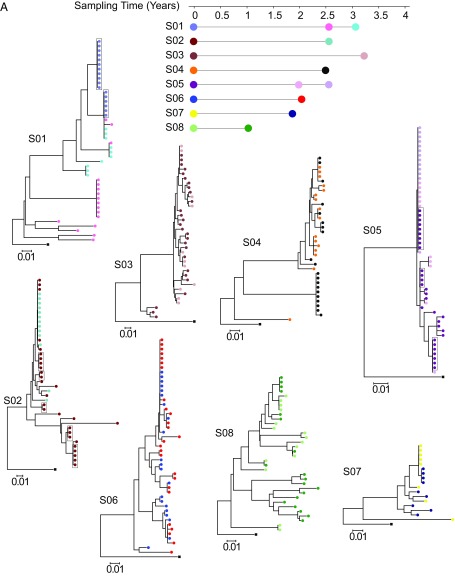
Fig. 2.
Expanded clones carrying replication-competent HIV-1 emerge and wane over time. (A) Phylogenetic trees of env sequences of independent isolates of replication-competent virus from eight subjects on ART (S01–S08) are shown. Sequencing was performed on genomic viral RNA in supernatants of p24+ wells. Different colors correspond to viruses recovered from different time points as indicated under the time line. Groups of identical sequences are indicated by symbols present on the same vertical “rake.” Sequences for the first time point were included in a previous study (18). Sequences that were previously shown to be identical by full-genome sequencing are grouped in boxes (18). The time scale indicates time in years from study entry. All patients were on suppressive ART for >6 mo before study entry. Black squares indicate the reference sequence HXB2. (B) Dynamics of expanded clones containing replication-competent HIV-1. Each pie figure shows how all of the replication-competent viruses (n) collected at a specific time point (shown on the x axis) are divided into clonal populations, with distinct colors representing different clones. Clones marked by M were identified at multiple time points. Starred lines indicate samples that are significantly different according to a test for difference in clone proportions when the null model is a random partition of the aggregated samples (Materials and Methods) (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. NS, P > 0.05).