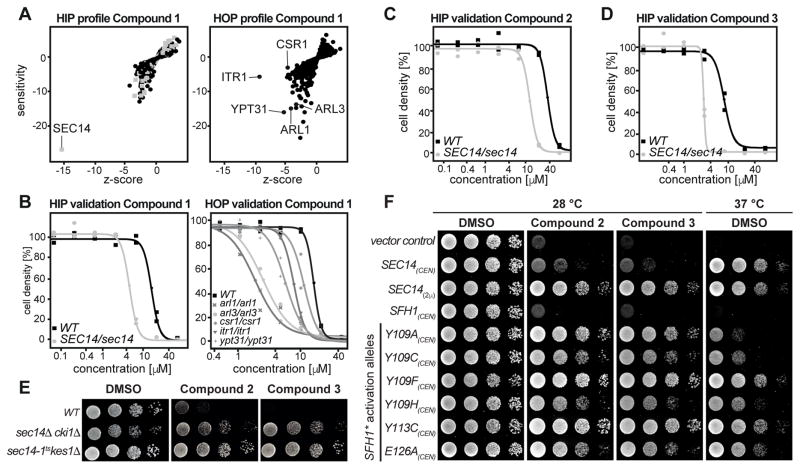
Figure 1.
Chemogenomic profiling and hypersensitivity validation. A) Calculated profiles of the chemogenomic profiling experiment. HIP outlines hits directly affected by the test compound. HOP identifies synthetic interactions with the target. Essential genes are depicted by grey boxes, non-essential genes by black dots. B) Single strain validation of hits from the chemogenomic profiling experiments as recorded in duplicates. C, D) Confirmation of hypersensitivity of the Sec14/sec14 HIP strain against compound 2 and 3 as recorded in duplicates. E) The wildtype and two “bypass Sec14p” strains were spotted on rich medium (YPD) supplemented with DMSO or 20 μM of compound 2 and 3 and incubated at 30 °C for 48 hours. F) Transformants of the temperature-sensitive sec14-1ts yeast strain harboring centromeric (CEN) plasmids carrying either SFH1 or the designated SFH1 activation alleles (SFH1*) were spotted on minimal media supplemented with 120 μM of compound 2, 30 μM of compound 3 or DMSO as indicated and incubated at permissive (left) or restrictive (right) temperature. Transformants harboring YCplac33 (empty vector), or SEC14 expressed from a centromeric (CEN) or a multi-copy plasmid (2μ) served as controls.