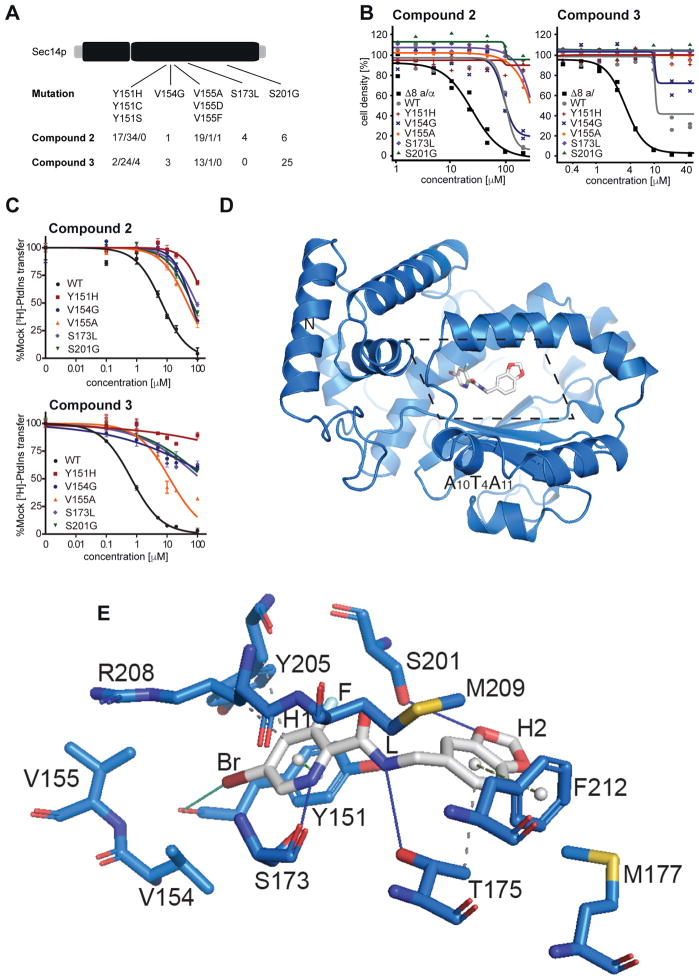
Figure 4.
Structural and functional analysis of Sec14p-compound interactions. A) SNPs and mutation frequency as identified by functional variomics for both tested compounds. B) Validation of identified mutations by integrative transformation of indicated SEC14 allele into cells. C) Validation of identified mutations by in vitro testing on recombinant protein. D) Overview of the structure of Sec14p (as cartoon, in marine) in complex with compound 2 (in sticks representation, in grey). The section displayed in detail in panel e is outlined by dotted lines. e) Detailed view (rotated 45° along the x-axis for clarity) of the binding pocket of Sec14p bound to compound 2 as identified by co-crystallization at 2.6 Å resolution. Interacting residues and relevant secondary structure elements of Sec14p are labeled; side chains are colored in marine and shown as sticks. H- and halogen-bonding are visualized as solid lines in blue and green, respectively while hydrophobic interactions are shown as grey dashed lines. p-p stackings are depicted as green dashed lines (light green for parallel stacking; smudge green for perpendicular stacking) with aromatic ring centers as grey spheres. Functional groups of compound 2 are indicated.