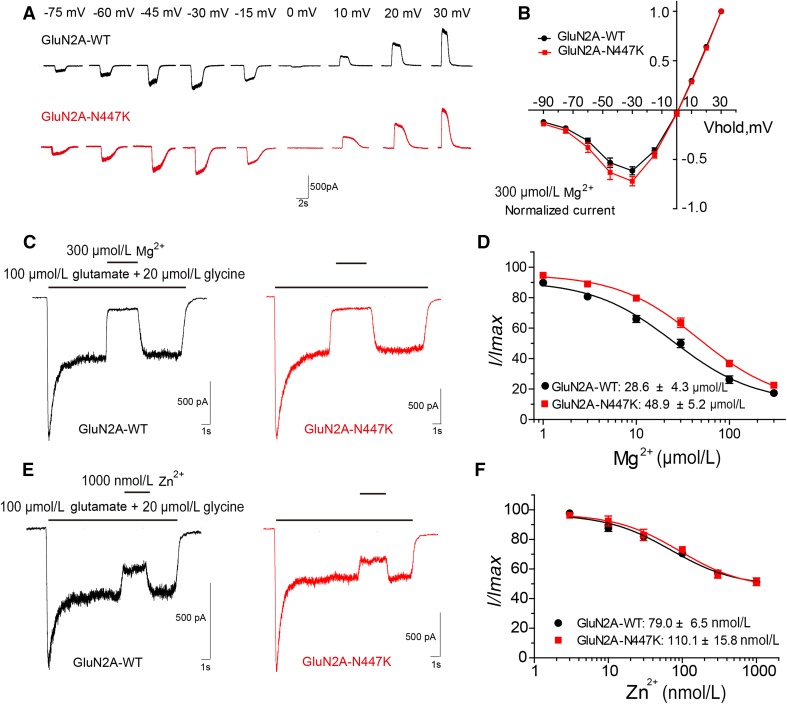
Fig. 3.
Effects of GluN2A-N447K on Mg2+ and Zn2+ sensitivity of NMDARs. A Representative evoked current traces of wild-type and mutant NMDARs at different holding potentials (current scale bar, 500 pA; time scale bar, 2 s). B Mg2+ current-voltage (I-V) relationship of GluN1/GluN2A-WT (black) and GluN1/GluN2A-N447K (red) NMDARs. C Representative current traces of wild-type and mutant NMDARs induced by co-agonists in the presence of 300 μmol/L Mg2+. Other doses of Mg2+ were applied in the same way (current scale bar, 500 pA; time scale bar, 1 s). D Mg2+ concentration-response curves reveal a decreased Mg2+ block for the GluN1/GluN2A-N447K NMDARs. E Representative evoked current traces of wild-type and mutant NMDARs inhibited by 1000 nmol/L Zn2+. Other doses of Zn2+ were applied in the same way (current scale bar, 500 pA; time scale bar, 1 s). F Zn2+ concentration-response curves show that Zn2+ inhibition of mutant NMDARs is undistinguishable from that of the WT.