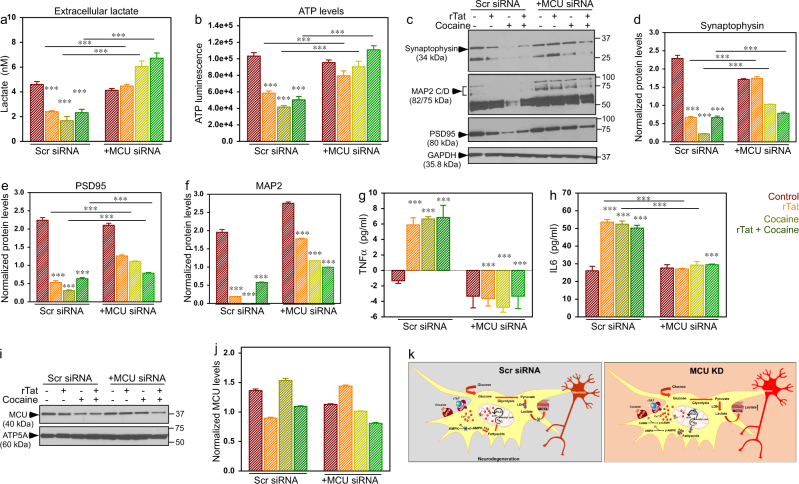
Fig. 5. Co-culturing astrocytes knocked down for MCU protects neurons from rTat/cocaine-induced toxicity.
a Quantification of extracellular lactate levels in control (Scr siRNA) and MCU KD astrocytes and neuronal co-cultured media. b Quantification of ATP levels in co-cultured neuronal lysate. c Lysates from neurons co-cultured with astrocytes were Western blotted for Synaptophysin, PSD-95 and MAP2. d–f Quantification of the normalized Synaptophysin (d), PSD-95 (e), and MAP2 (f) protein levels in neurons. g, h Quantification of cytokine levels in media from co-cultures: TNFα (g), and IL6 (h) levels. i Representative Western blot depicts unaltered MCU levels in neurons co-cultured with control (Scr siRNA) or MCU KD astrocytes. The mitochondrial membrane synthase, ATP5A was used as the loading control. j Quantification of normalized MCU levels in neurons co-cultured with control (Scr siRNA) or MCU KD astrocytes. Data represents Mean ± SEM; ***P < 0.001; n = 6–8. k Schematic representation of the proposed astrocytic metabolic switch results in neurodegeneration during rTat/cocaine treatment