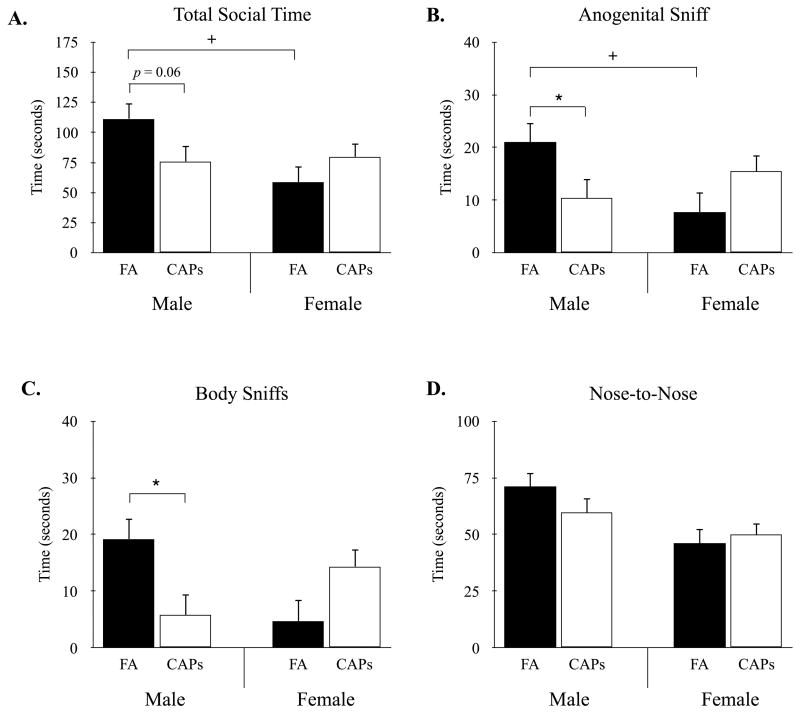
Figure 3.
CAPs exposure results in sex-dependent reductions in reciprocal social interactions. (A) Perinatal CAPs reduced social interaction time in male but not female offspring compared to FA controls. Female FA-exposed mice displayed reduced social interaction time compared to FA-treated males. (B) Male CAPs and female FA offspring displayed a significant reduction in anogenital sniffing behavior compared to FA male mice. (C) CAPs-exposure significantly decreased body sniffing in males compared to FA controls. (D) There were no differences in the total time spent in nose-to-nose sniffs between treatment conditions. Data were compared using a linear mixed-effects model with treatment and sex as fixed effects and dam as the random effect (* p < 0.05 treatment; + p < 0.05 sex). Data are means ± SEM. Sample size: FA n = 26 (13M/13F; 13 litters), CAPs n = 31 (15M/16F; 12 litters).