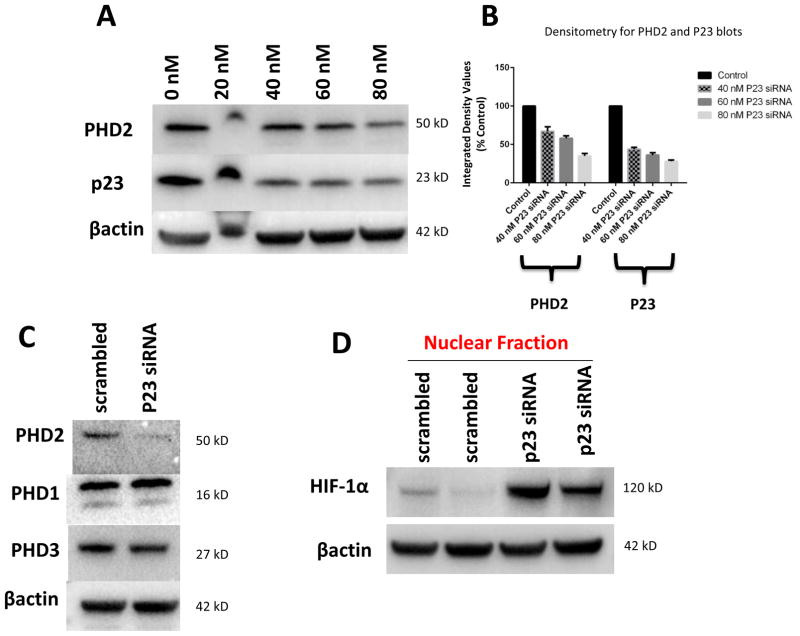
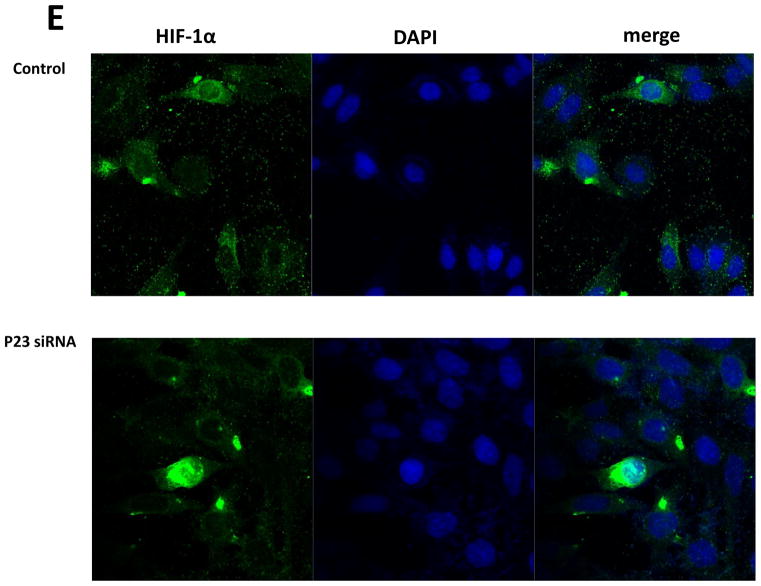
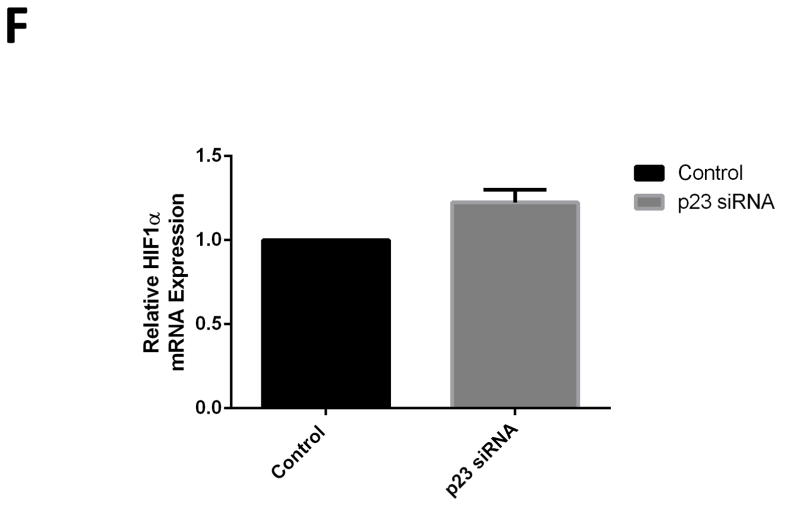
FIGURE 2.
Knockdown of p23 via siRNA results in reductions in p23 protein levels in DAergic N27 cells coinciding with select decreased in steady-state levels of PHD2 protein and activity. A, Representative western blot analyses of cells transfected with increasing dosages (0–80 nM) p23 siRNA, 24 hrs. Top panel, PHD2; middle panel, p23; lower panel, actin as loading control. B, Densitometric quantitation of PHD2 and p23 steady-state protein levels normalized to actin. C, Representative westerns of effects of 24 hr p23 siRNA transfection at 80 nM on PHD2 (top panel) versus PHD1 and PHD3 levels (middle panels); actin was used as a loading control (lower panel). D, PHD2 activity as measured by HIF1α westerns of nuclear fractions from p23 siRNA versus scrambled transfected cells. E. Representative laser confocal microcopy images show translocation of HIF-1α (green) within nuclei stained with DAPI (blue stain) in cells treated with p23 siRNA (80nM) for 24 hrs.