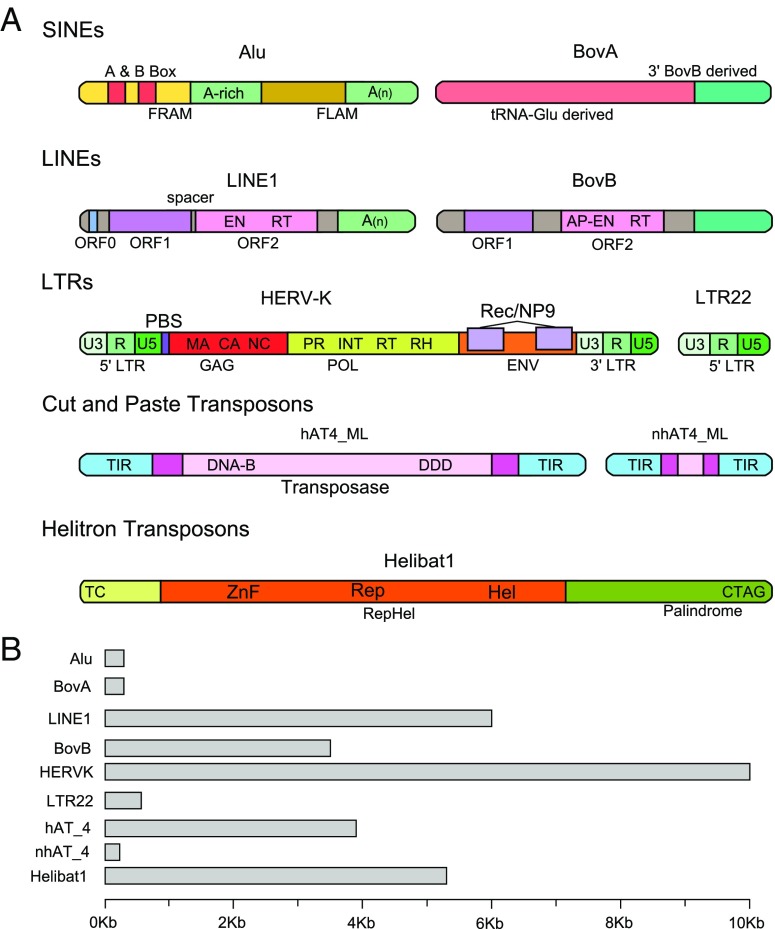
Fig. 1.
Mammalian transposable elements. a Structure of common mammalian transposable elements. A and B box, promoter regions derived from 7SL RNA; FRAM, free right Alu monomer; FLAM, free left Alu monomer; A(n) poly A repeat; UTR, untranslated region; ORF0, primate-specific open reading frame 0; ORF1, nuclear chaperone protein; ORF2 reverse transcriptase; EN, endonuclease domain; RT, reverse transcriptase domain; AP-EN, apurinic-apyrimidinic endonuclease; U3, unique 3′ sequence; R, repeated sequence; U5, unique 5′ sequence; PBS, tRNA primer binding site; GAG, GAG protein; MA, matrix domain; CA, capsid domain; NC, nucleocapsid domain; POL, polyprotein; PR, protease domain; INT, integrase domain; RH, RNAse H domain; ENV, envelope protein; Rec/NP9, Rec and NP9 proteins including possible alternative splicing events; TIR, terminal inverted repeat; DNA-B, DNA binding domain; DDD, three conserved aspartate residues; TC, TC dinucleotide sequence; ZnF, zinc-finger-containing motifs; RepHel, replicase protein; Rep, replicase domain; Hel, helicase domain; CTAG -CTAG nucleotide sequence. b Representative elements drawn to scale