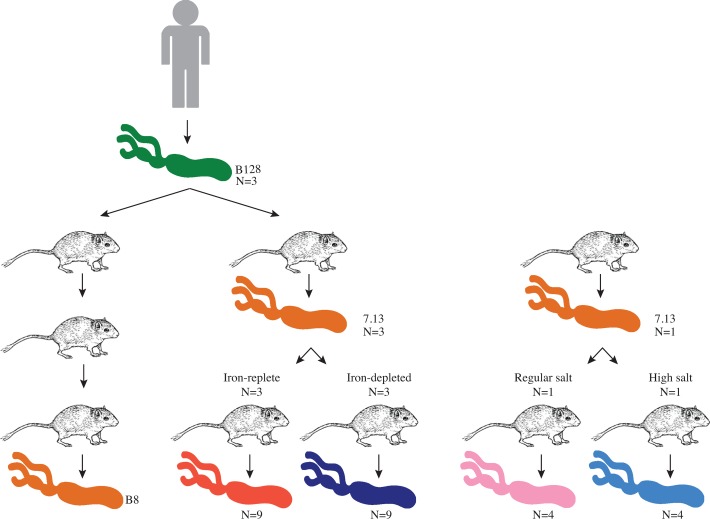
Figure 1.
Experimental design. Helicobacter pylori strain B128 was originally isolated from a human patient.54 Strain B128 (green) was used for orogastric challenge of Mongolian gerbils and was passaged three times through gerbils in a previous study.28 The in vivo-adapted output strain, designated H. pylori strain B8 (orange), was isolated from those gerbils, sequenced and used as the reference strain in this study.19 In an independent experiment, strain B128 (green) was also used for orogastric challenge of a single Mongolian gerbil, and the in vivo-adapted output strain isolated from this gerbil was designated H. pylori strain 7.13 (orange).27 Carcinogenic H. pylori strain 7.13 was then used to infect another cohort of Mongolian gerbils maintained on either iron-replete or iron-depleted diets.17 Single colonies (n=3) from three independent gerbils maintained on iron-replete diet (n=9) and three independent gerbils maintained on iron-depleted diet (n=9) were subjected to whole genome sequence analysis. In vivo-adapted strain from iron-replete (red) and iron-depleted (blue) conditions was also compared with previously described H. pylori single colonies (n=4) harvested from one gerbil maintained on a regular salt (pink) or high salt (light blue) diet.21