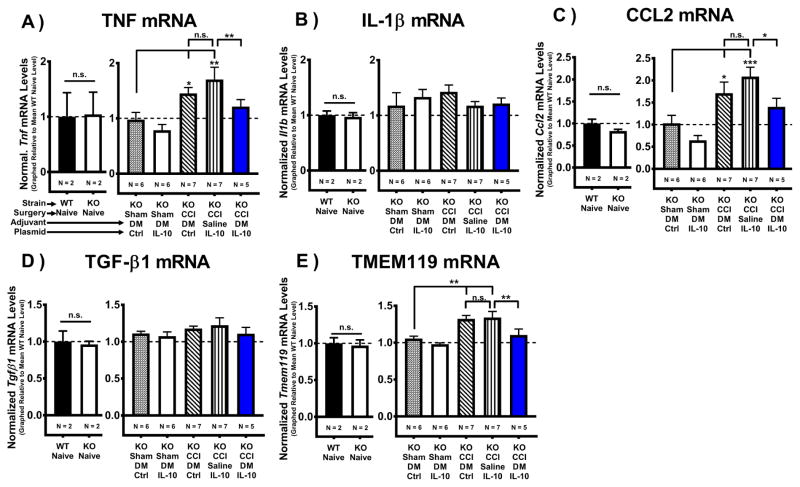
Figure 5. Intrathecal non-viral IL-10 gene therapy alters lumbar cytokines and decreases microglial activation.
Characterization of isolated cytokines and microglial-specific mRNA from the lumbar spinal cord collected on Day 12 after i.t. IL-10 gene therapy injection (Day 17 post-surgery). (A–F) Baseline transcription levels are not significantly different between WT Naïve and IL-10 KO Naïve groups (N = 2 mice/group) for all targets (P > 0.05): Tmem119, Tnf, Il1b, Ccl2, and Tgfb1. (A) mRNA transcript levels for the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF (Tnf) and (C) the pro-inflammatory chemokine CCL2 (Ccl2) were elevated only in allodynic controls, with significantly less TNF and CCL2 mRNA expression observed in pain-relieved CCI+DM/pDNA-IL-10 vs. allodynic CCI+Saline/pDNA-IL-10 mice (TNF: F(4, 26) = 6.18, P < 0.01) (CCL2: F(4, 26) = 8.10, P < 0.0001). (B) No significant differences in mRNA transcript levels for the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β (Il1b) were detected (F(4, 24) = 0.6927, P > 0.05). (D) No significant differences in mRNA levels for anti-inflammatory cytokine TGF-β1 (Tgfb1) were detected for any condition (F(4, 25) = 0.77, P > 0.05). (E) mRNA transcript levels for the microglial marker TMEM119 (Tmem119) were elevated in allodynic CCI controls, but not in pain-relieved CCI+DM/pDNA-IL-10 mice. Additionally, TMEM119 mRNA levels in pain-relieved CCI+DM/IL-10 treated mice were significantly less than for allodynic CCI+Saline/IL-10 mice (F(4, 26) = 8.24, P < 0.001). mRNA levels (mean ± SEM) are normalized to 18S rRNA and graphically presented relative to mean WT Naïve levels. Post-hoc multiple comparisons via Fisher’s LSD (α = 0.05; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001).