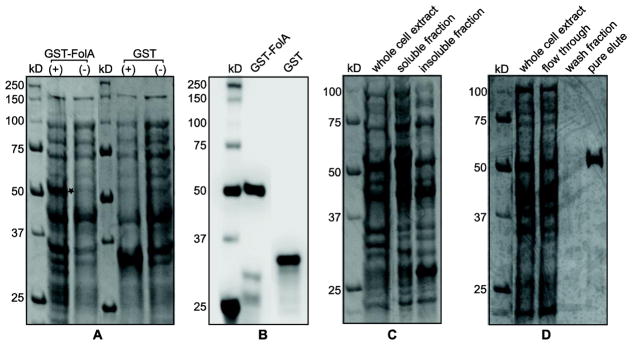
Figure 2.
Overexpression, soluble expression, and purification of recombinant GST-FolA fusion protein of Rickettsia species phylotype G021 in E. coli (DE3). 2A) Overexpression of recombinant GST-FolA fusion protein of Rickettsia species phylotype G021 in E. coli (DE3). The expression of GST proteins (GST-FolA or GST) was induced by adding 0.4 mM IPTG into E. coli cultures, which were incubated at 30°C overnight. Coomassie blue staining of total protein expression, resolved on a 12% polyacrylamide gel. The location of the overexpressed GST-FolA is labeled as a star. (+) = induced by 0.4 mM IPTG at 30°C; (−) = uninduced negative control; kDa = kilodaltons. 2B) Western blot of GST-FolA fusion protein using mouse monoclonal anti-GST antibody, visualized on a PVDF membrane with chemiluminescent detection. 2C) Soluble expression of recombinant GST-FolA of Rickettsia species phylotype G021. Recombinant GST-FolA is expressed at its correct theoretical location (53 kDa). After the induction period, cells were harvested by centrifugation and lysed by sonication. The lysate fractions were separated by centrifugation. The soluble fraction and pellet were subjected to SDS-PAGE on a 12% polyacrylamide gel, stained with Coomassie blue, and visualized using transilluminating white light. 2D) The purity analysis of the GST-FolA protein by SDS-PAGE. GST-FolA fusion protein was purified using on-column affinity chromatography. Whole cell extract after induction, flow through, wash fraction, and pure eluate were analyzed for purity by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining and transilluminating white light.