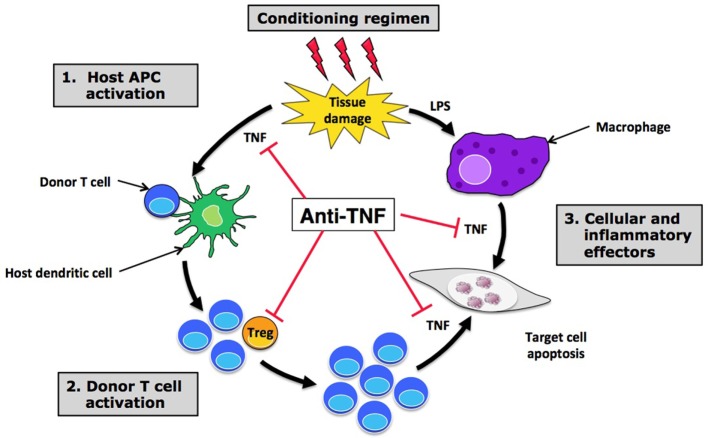
Figure 2.
Hope and disappointment in targeting tumor necrosis factor α (TNF) in graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Anti-TNF treatments are able to block the effect of TNF at different steps of acute GVHD pathophysiology, including initial host APC activation (1), effector T cell recruitment and activation in target tissues (2), and direct cell necrosis (3). By inhibiting TNF ligation to TNFR2 expressed by regulatory T cells (Tregs), anti-TNF treatments could also have a deleterious effect on these suppressive cells, leading to an increased expansion and activation of alloreactive donor T cells that may be responsible for the disappointing results observed with anti-TNF treatments in this setting. Abbreviations: APC, antigen-presenting cell; LPS, lipopolysaccharide.