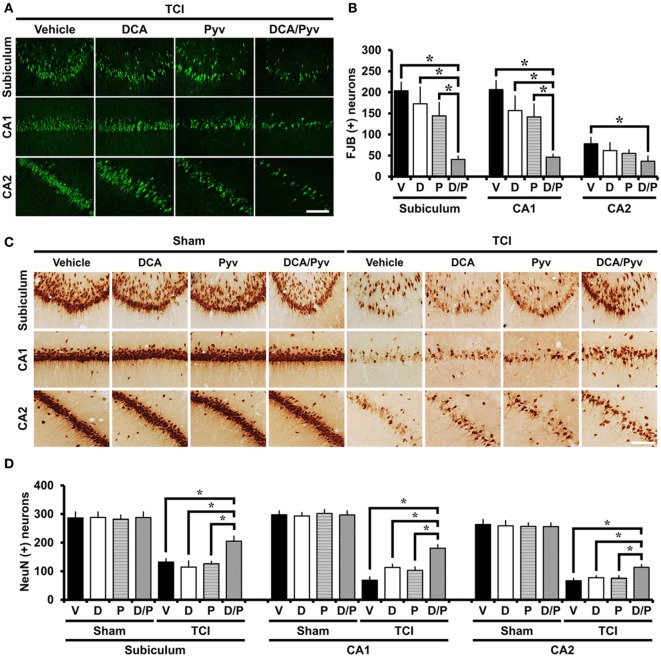
Figure 1.
Combined treatment with dichloroacetic acid (DCA) and pyruvate reduces transient cerebral ischemia (TCI)-induced neuronal death. This figure shows that the combined treatment of DCA and pyruvate demonstrated neuroprotective effects after TCI. Brain sections were stained by Fluoro-Jade B (FJB) to analyze the neurodegeneration. (A) FJB positive neurons were observed in the subiculum (Subi), cornus ammonis 1 (CA1), and CA2. Co-treatment of DCA with pyruvate once per day for 2 days inhibited neuronal death in the subiculum, CA1, and CA2 after TCI. There was no significant difference in DCA-only or pyruvate-only treatment when compared to the vehicle-treated group after TCI. Scale bar = 100 µm. (B) Bar graph represents the quantified degenerating neurons. The statistically significant difference is indicated between the DCA + pyruvate-treated groups and the vehicle-treated groups. Administration of DCA with pyruvate reduced the number of FJB (+) neurons in the subiculum, CA1, and CA2 areas when compared to the vehicle-treated group (TCI-vehicle, n = 11; TCI-DCA, n = 6; TCI-pyruvate, n = 7; TCI-DCA + pyruvate, n = 8). (C) Survival of hippocampal neurons were evaluated by NeuN staining. There was a significant difference between the TCI-vehicle, TCI-DCA, and TCI-pyruvate to the TCI-DCA + pyruvate-treated groups. The combined treatment of DCA with pyruvate improved neuronal survival in the hippocampal subiculum, CA1, and CA2 regions after TCI. Scale bar = 100 µm. (D) Bar graph represents the quantified NeuN (+) neurons. Data show that there was a statistically significant difference between the TCI control groups and the combined treatment group (DCA with pyruvate) after TCI groups (TCI-vehicle, n = 5; TCI-DCA, n = 5; TCI-pyruvate, n = 5; TCI-DCA + pyruvate, n = 5). Data are mean ± SEM. *Significant difference from the vehicle-treated group. P < 0.05. D, DCA; P, pyruvate; D/P, DCA + pyruvate; V, vehicle.