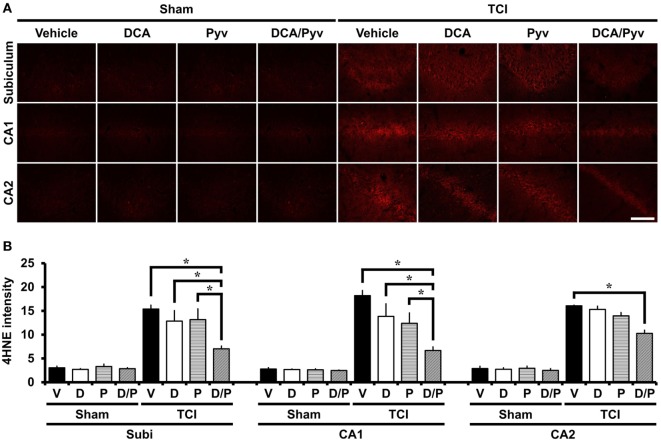
Figure 2.
Combined treatment with dichloroacetic acid (DCA) and pyruvate reduces oxidative injury after transient cerebral ischemia (TCI). Neuronal oxidative injury was measured by 4-Hydroxy-Nonenal (4HNE, red color) staining at the hippocampal cornus ammonis 1 (CA1), CA2, and subiculum areas at 7 days after TCI. (A) Sham-operated groups showed minimal 4HNE immunoreactive signal across the hippocampal regions. Combined treatment of DCA with pyruvate reduced the immunoreactive fluorescence intensity of 4HNE in the hippocampus when compared to the vehicle-treated group after TCI. Scale bar = 100 µm. (B) Bar graph represents statistically significant difference between groups (Normal-vehicle, n = 5; Normal-DCA, n = 5; Normal-pyruvate, n = 5; Normal-DCA + pyruvate, n = 5; TCI-vehicle, n = 6; TCI-DCA, n = 4; TCI-pyruvate, n = 4; TCI-DCA + pyruvate, n = 4). Data are mean ± SEM. *Significant difference from the vehicle-treated group, P < 0.05. D, DCA; P, pyruvate; D/P, DCA + pyruvate; V, vehicle.