FIGURE 1.
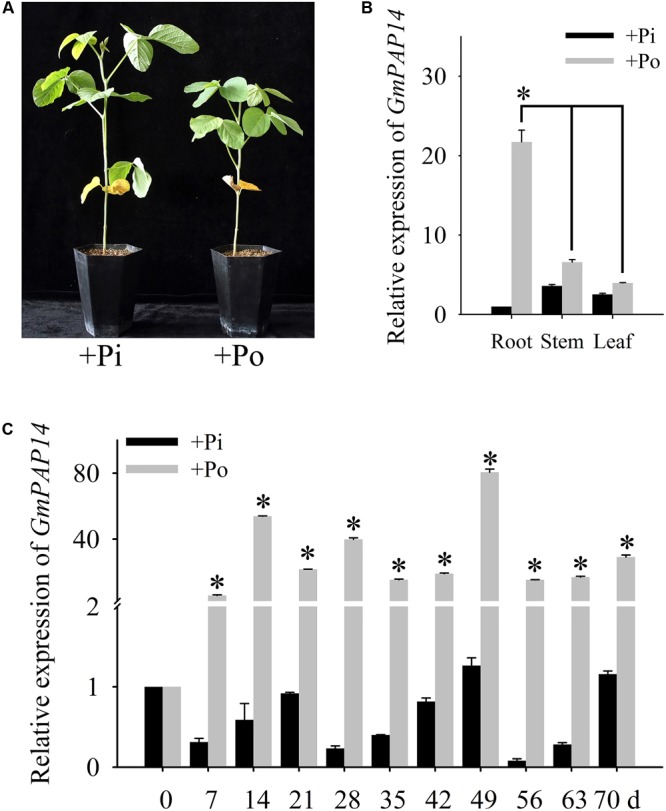
Analysis of GmPAP14 expression patterns in soybean. (A) Phenotype of zhonghuang15 (ZH15) under KH2PO4 (+Pi) and Phytate (+Po). (B) Expression analysis of GmPAP14 in different tissues of ZH15 under +Pi and +Po conditions. Seven-day-old seedlings were treated with +Pi and +Po. Seven days after treatment, roots, stems, and leaves were harvested for gene expression in different tissues. Asterisk represents significant difference of GmPAP14 expression in root compared to that in leaf and stem under +Po conditions (P < 0.05, t-test). (C) Expression of GmPAP14 in roots of ZH15. Seven-day-old seedlings were treated with +Pi and +Po (0 day was used as a control). Roots were sampled after 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, and 70 days and were used for temporal expression analysis. Asterisks represent significant differences of GmPAP14 expression at the same growth period under +Pi and +Po conditions (P < 0.05, t-test). The relative expression value was calculated by the ratio of the expression value of GmPAP14 to that of soybean housekeeping gene GmActin11 using the 2-ΔΔCt method. Each bar is the mean of three replicates with the standard error.
