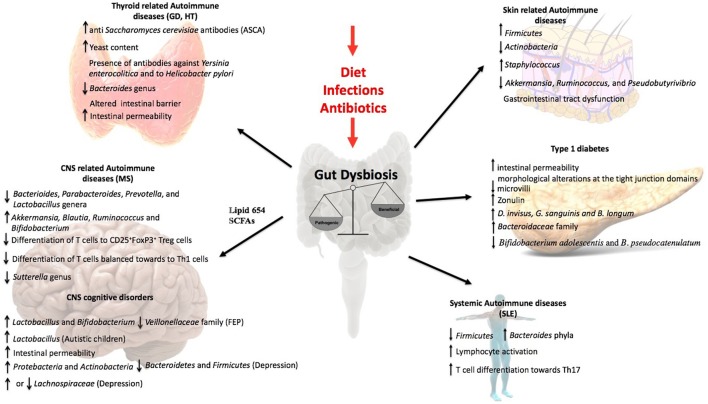
Figure 2.
Influence of the gut microbiota in non-intestinal diseases. Gut dysbiosis induced by external factors as diet, infections, or antibiotic overuse lead to an inflammatory response that influence the outcome of several autoimmune diseases as Grave's disease, Hashimoto's Thyroiditis, Multiple Sclerosis, SLE, and type1 diabetes. It has also been observed an important role in skin related autoimmune diseases as Psoriasis. Moreover, the evidences in the literature support that gut microbiota can influence CNS disorders like autism, depression, and schizophrenia.