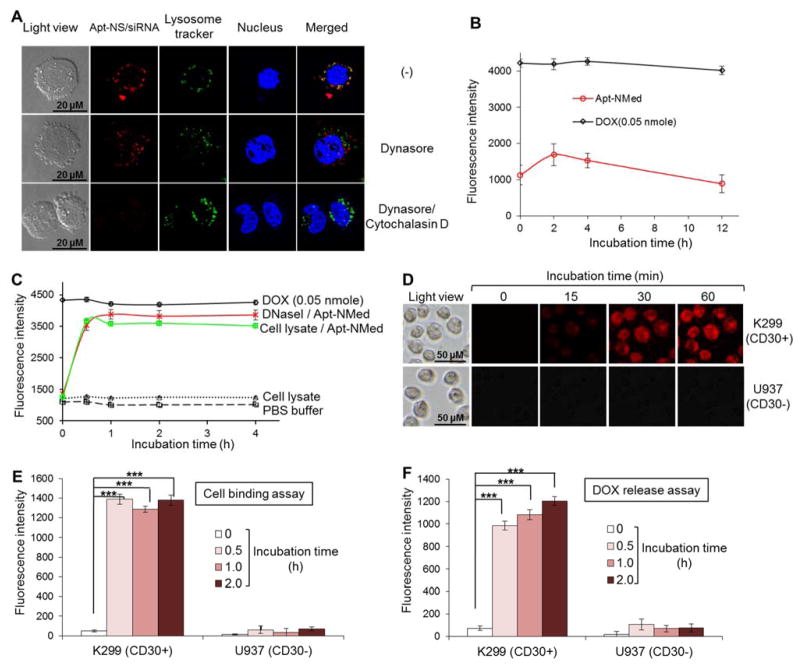
Figure 3. Intracellular delivery of Apt-NMed.
(A) Determination of internalization pathway of Cy3-labeled-Apt-NS/siRNA by confocal fluorescence microscopy. Upon treatment with endocytosis inhibitor Dynasore, Apt-NS/siRNA (red) internalization was partially blocked in K299 cells, compared to untreated cells. Apt-NS/siRNA uptake was completely blocked in the presence of both endocytosis and micropinocytosis inhibitors. (B) Stability of Apt-NMed was determined by incubating with 100% human serum. (C) Drug release from Apt-NMed was demonstrated by incubation in PBS buffer along with DNase I or cell lysate. PBS buffer and free DOX were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. Final fluorescence intensity was measured with microplate reader at excitation (470 nm) and emission (590 nm) wavelengths. (D) Fluorescence microscopy showed rapid DOX delivery and release into target cells at indicated time points. Flow cytometry analysis further confirmed specific cell binding of Apt-NMed (E) and DOX release (F) in target cells. FAM-labeled Apt-NMed and released DOX were detected with FITC and PE channels of flow cytometer, respectively. Data shown are mean ± SEM, n=3; ***p < 0.001.