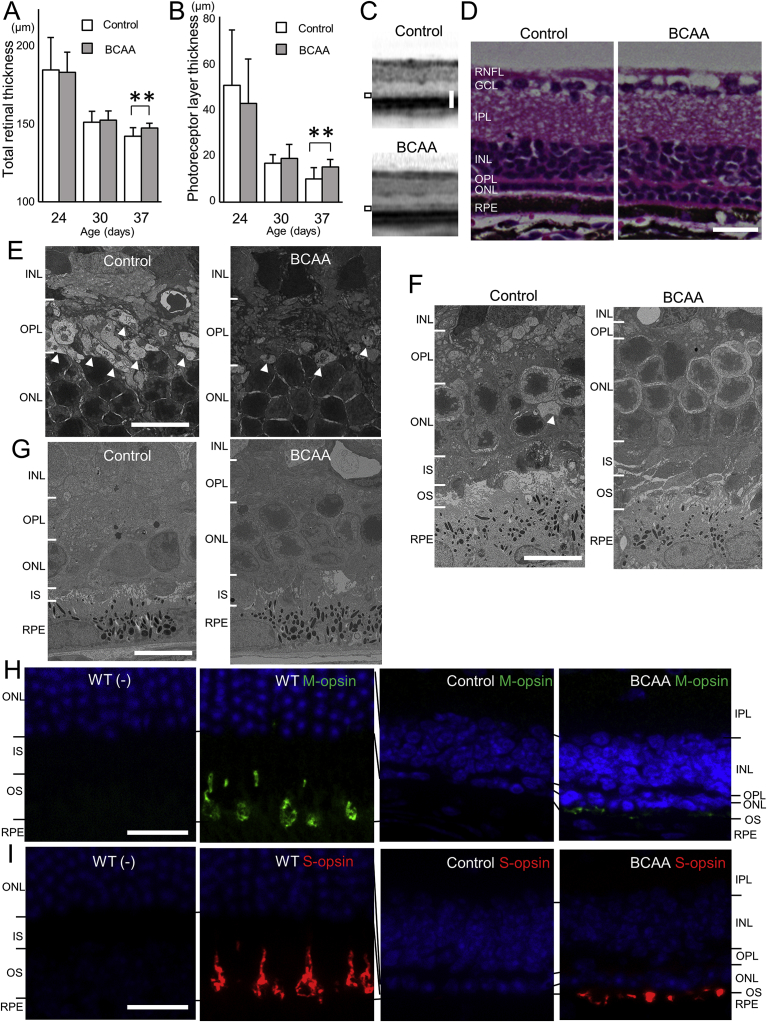
Fig. 4.
Prevention of morphological deterioration in rd10 mice by BCAAs. (A and B) Total retinal thickness (A) and the photoreceptor layer thickness (B, the sum of the outer nuclear layer thickness and photoreceptor myoid zone, ellipsoid zone, outer segment layer thickness, indicated by black rectangles in C) in rd10 mice measured on spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) images at 24, 30, and 37 days of age. **p < 0.01, unpaired t-test. N = 34 eyes of 17 mice in the BCAA group and 36 eyes of 18 mice in the control group, respectively. (C) SD-OCT images of eyes in 37-day-old rd10 mice administered supplemental BCAAs, or water as a control, which had the median photoreceptor layer thickness. (D) Vertical retinal sections of 37-day-old rd10 mice administered BCAAs, or water as a control. (E–G) Electron microscopic images of 21-day-old (E), 30-day-old (F), and 37-day-old (G) rd10 mice administered BCAAs, or water as a control. Intracellular vacuoles are seen in photoreceptors at the innermost ONL (white arrowheads). (H and I) Retinal sections from 37-day-old rd10 mice administered BCAAs, or water as a control, or age-matched wild-type (WT) mice, were stained with or without an anti-M-opsin (H, green), or anti-S-opsin antibody (I, red). Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI (blue). Abbreviations: RNFL, retinal nerve fiber layer; GCL, Ganglion cell layer; IPL, Inner plexiform layer; INL, Inner nuclear layer; OPL, Outer plexiform layer; ONL, Outer nuclear layer; IS, inner segment of the photoreceptor cell; OS, outer segment of the photoreceptor cell; and RPE, Retinal pigment epithelium. Scale bars: 50 μm in C; 20 μm in D, H and I; 10 μm in E, F and G.