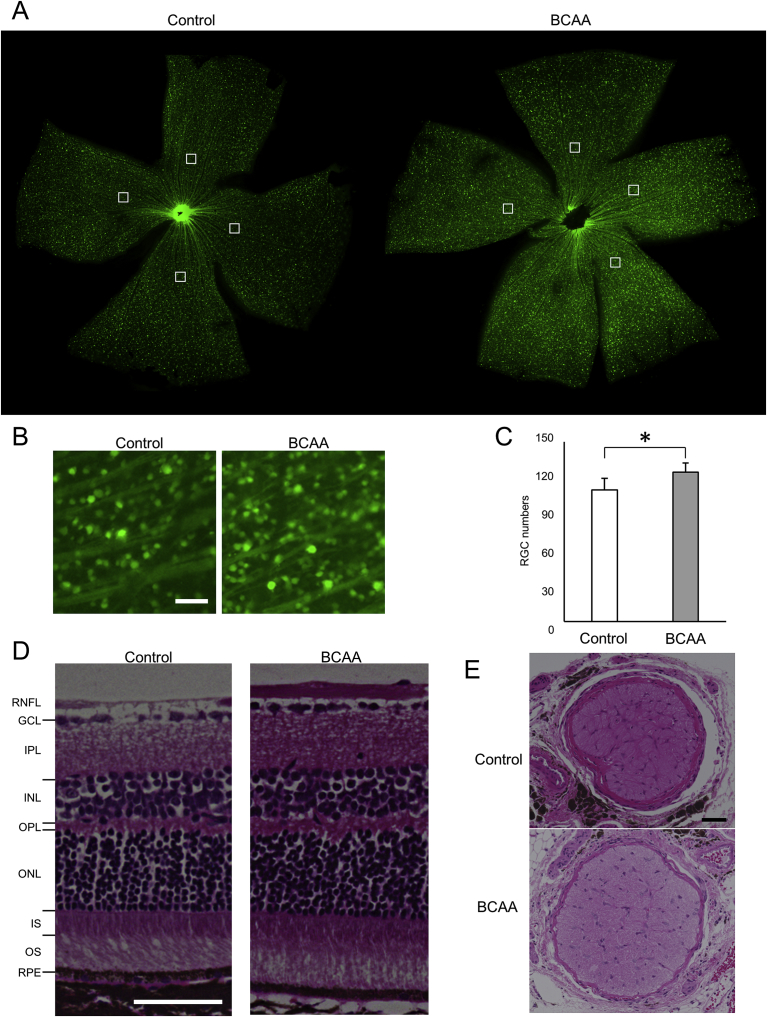
Fig. 8.
Prevention of retinal ganglion cell death in GLAST (+/−) mice by BCAAs. (A–C) Retinal flat mount of 12-month-old GLAST (+/−):Thy1-CFP mice administered BCAAs, or water as a control. (A) The CFP-positive retinal ganglion cells were counted at a distance of 1200 μm from the optic nerve head center. The white squares (250 μm squares) indicate areas in which CFP-positive retinal ganglion cells were counted. (B) Magnified images of retinal flat mounts from GLAST (+/−):Thy1-CFP mice that showed the median retinal ganglion cell counts. (C) Numbers of CFP-positive retinal ganglion cells on the retinal flat mount. N = 6 eyes of 6 mice in the BCAA group and N = 4 eyes of 4 mice in the control group, respectively, *p < 0.05, unpaired t-test. (D) Hematoxylin and eosin (HE)-stained vertical retinal sections of 12-month-old GLAST (+/−) mice administered BCAAs, or water as control. Abbreviations: RNFL, retinal nerve fiber layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, Inner plexiform layer; INL, Inner nuclear layer; OPL, Outer plexiform layer; ONL, Outer nuclear layer; IS, inner segment of the photoreceptor cell; OS, outer segment of the photoreceptor cell; and RPE, Retinal pigment epithelium. (E) HE-stained optic nerve cross-sections from 18-month-old GLAST (+/−) mice that showed the median cross-section areas. Scale bars: 50 μm in B, D and E.