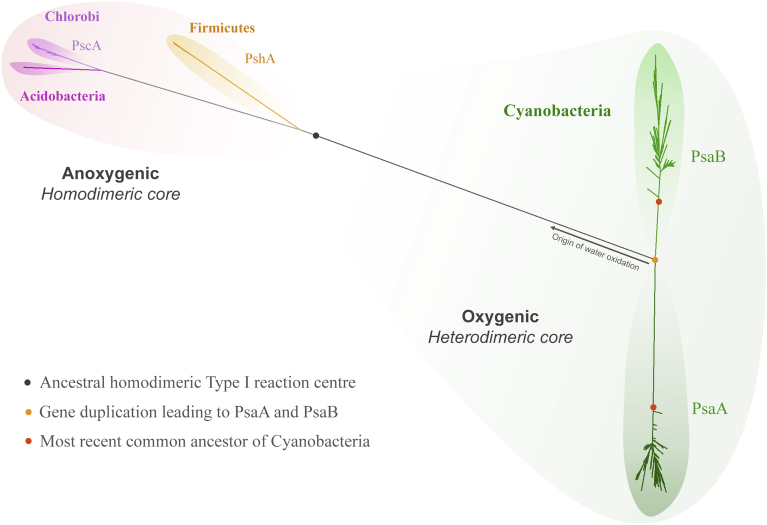
Fig. 1.
Maximum Likelihood tree of Type I reaction centre proteins. The tree is characterised by a deep split of reaction centre proteins, which separates those employed in anoxygenic phototrophy from those employed in oxygenic photosynthesis (grey spot). Cyanobacteria and photosynthetic eukaryotes are the only known phototrophs to have a heterodimeric Type I reaction centre made of two subunits known as PsaA and PsaB. All extant Cyanobacteria descended from a common ancestor that already had highly divergent PsaA and PsaB subunits (red spot). The gene duplication that led to PsaA and PsaB occurred at an earlier point in time (orange spot), which predated the most recent common ancestor of Cyanobacteria by an unknown period of time. It is hypothesised that the gene duplication that led to PsaA and PsaB occurred as a specialisation to oxygenic photosynthesis, therefore water oxidation should have originated before this gene duplication event (arrow).