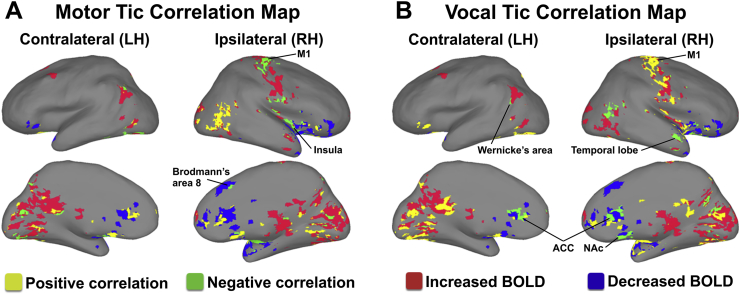
Fig. 3.
Motor and vocal tic reduction by different circuit effects. (A) Negative correlations between motor tic reduction and BOLD signals in the sensorimotor cortex, insula, and Brodmann's area 8 (IL/RH) and superior region of Wernicke's area (CL/LH). (B) Negative correlations between vocal tic reduction and BOLD signals in the ACC of both hemispheres, NAc and temporal lobe (IL/RH), and inferior region of Wernicke's area (CL/LH). In addition, in the sensorimotor strip, vocal tic reduction correlated positively with BOLD generally covering the whole strip specifically including the face area, while motor tic reduction correlated negatively with BOLD only in the hand, arm, and shoulder areas. Both positive and negative correlations were found for motor and vocal tic reduction and parietal and occipital lobe BOLD signal. Abbreviations: ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; NAc, nucleus accumbens; BOLD, blood-oxygen-level dependent; CL/LH, contralateral to the stimulation site in the left hemisphere; IL/RH, ipsilateral to the stimulation site in the right hemisphere; LH, left hemisphere; RH, right hemisphere.