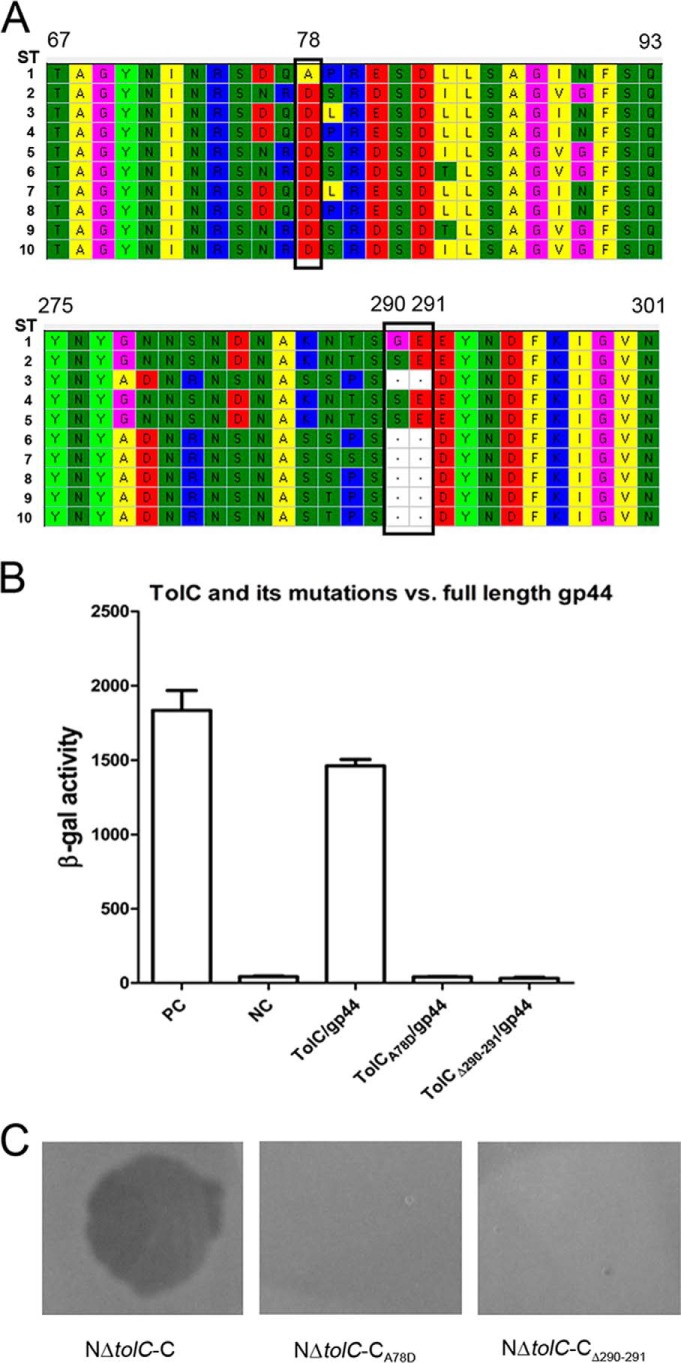
Figure 6.
Sequence alignment of TolC of the VP3-sensitive and -resistant strains and the interaction analysis between gp44 and TolC or its amino acid site mutants. A, all the TolC amino acid sequence fragments of the VP3-sensitive and VP3-resistant strains containing the mutation sites were aligned using MEGA, 10 sequence types (ST1 to ST10) were found. All the VP3-sensitive strains have one sequence type, ST1. All the VP3-resistant strains belong to ST2–ST9 with the amino acid residue mutations. The common mutant residues in the VP3-resistant strains compared with the VP3-sensitive strains are marked with black boxes. The numbers of the amino acid residue sites are shown based on the sequence of ST1. B, BACTH assays of the interactions between gp44 and TolC or its mutants, including the mutation on A78D and the deletion of Gly-290–Glu-291. C, double-layer plaque assays were performed to detect the roles of the TolC protein mutants for the VP3 infection. The lysis plaque was observed when VP3 was added in the culture layer of strain NΔtolC-C but absent in the culture layers of the strains NΔtolC-CA78D or NΔtolC-CΔ290–291.