Figure 1.
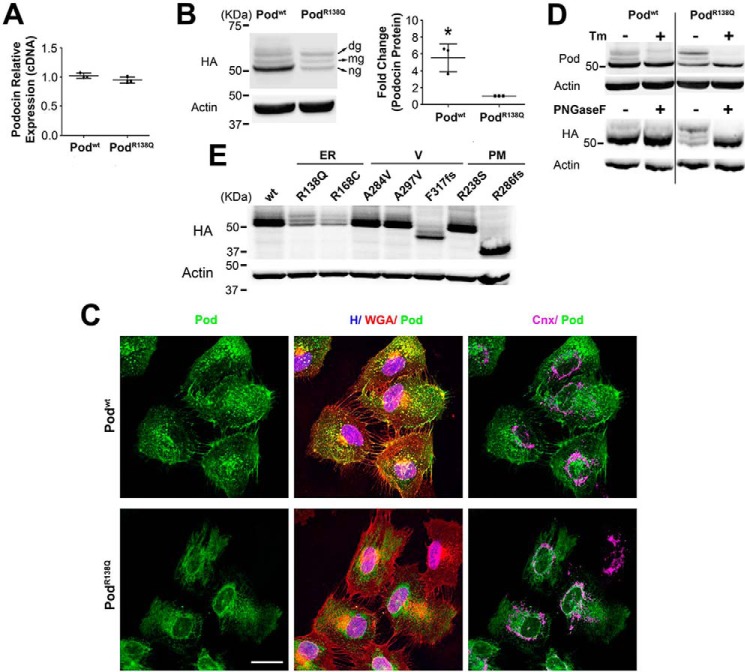
Stably over-expressed podocinR138Q is largely N-glycosylated, a feature shared only with other ER-retained podocin mutants. qRT-PCR (A), Western blot (B, D, and E), and immunofluorescence analysis (C) comparing podocin expression levels, protein band distribution, and subcellular localization, respectively, in 2HA-Podwt and 2HA-PodR138Q expressing podocyte cell lines. B, ng, non-glycosylated podocin; mg, mono-glycosylated podocin; dg, double-glycosylated podocin. Quantification of total podocin (ng, mg and dg) from three independent experiments are shown as mean ± S.D. *, p < 0.05. HA monoclonal antibody was used to identify podocin and β-actin served as loading control. C, polyclonal anti-podocin AP-P35 (Pod) and monoclonal calnexin AF18 (Cnx) were used as primary antibodies. Cell membrane and nuclei were labeled with WGA and Hoechst (H), respectively. Scale bar = 30 μm. D, cells were treated overnight with 10 μg/ml of tunicamycin (Tm) to impair N-glycosylation (upper immunoblot). Alternatively, cell lysates were treated with PNGase F, an enzyme that digests N-glycans from glycoproteins (lower immunoblot). Polyclonal AP-P35 or monoclonal anti-HA were used to immunoblot podocin. E, immunoblots of different podocin mutants known to possess different subcellular localizations. ER, endoplasmic reticulum–retained podocin mutants; V, vesicular podocin mutants; PM, plasma membrane localized podocin mutants.