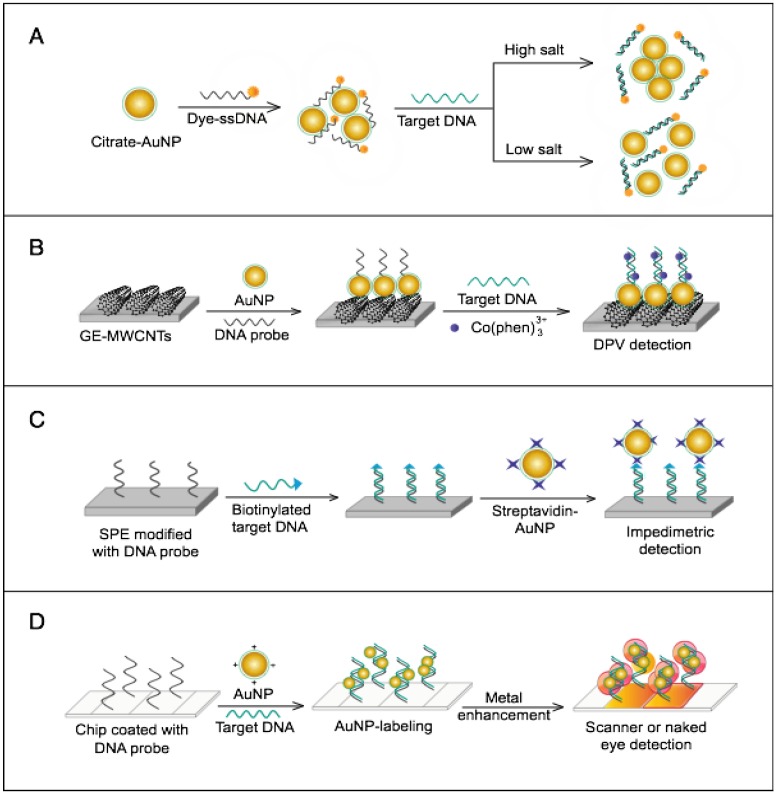
Figure 12.
AuNP-based assays for the detection of influenza A virus (IAV). (A) Fluorometric detection based on FRET-induced quenching of fluorophores by AuNPs. Single-stranded (ss)DNA probes modified with a fluorescent dye are attracted to the surface of AuNPs, resulting in quenched emission. The presence of target DNA sequences results in the formation of dsDNA in the suspension of citrate-reduced AuNPs and increases the fluorescence recovery intensities due to the desorption of the dsDNA-dye conjugates from the surface of the AuNPs 64. (B) Electrochemical assays by AuNP-enhanced differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). Specific DNA aptamers immobilized on a gold electrode (GE) modified with a layer of multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), polypyrrole nanowires (PPNWs) and AuNPs are collectively applied as an electrochemical platform for the detection of DNA hybridization using DPV 71. (C) Impedimetric electrochemical assay using streptavidin-AuNPs probes. The direct/sandwich hybridization of biotinylated target DNA with capture probes immobilized on the surface of a screen-printed electrode (SPE) and additional conjugation with streptavidin-AuNPs results in impedimetric signal enhancement 70. (D) Label-free scanometric detection using positively charged AuNPs. The electrostatic interaction between positively charged AuNPs and negatively charged DNA is utilized to visualize the double-stranded (ds)DNA formed by the hybridization of single-stranded probe DNA and complementary target DNA on the array of chips through AuNP-mediated metal staining 83, 86, 87.