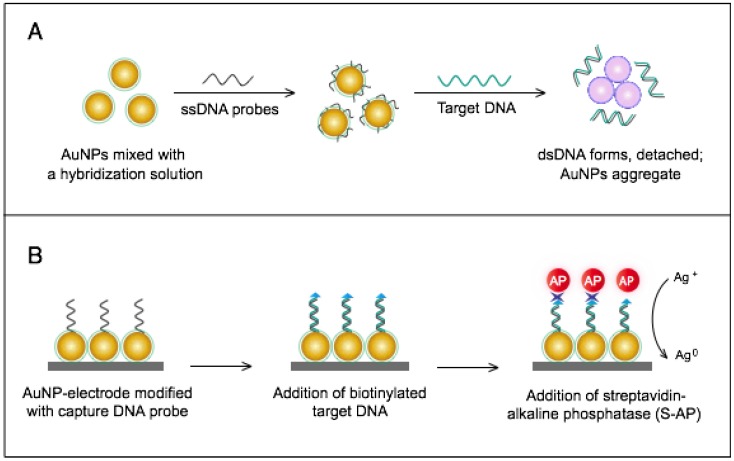
Figure 5.
AuNP-based nucleic acid assays for the detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). (A) Colorimetric detection of SARS using AuNPs stabilized by single-stranded (ss)DNA probes. In the presence of the target DNA sequence, double-stranded (ds)DNA is formed and desorbs from the surface of citrate-reduced AuNPs, leaving them to aggregate. This aggregation results in a color change from red to blue, indicating the presence of target nucleic acids 54, 56. (B) Enzymatic electrochemical detection of SARS by anodic stripping voltammetry using a AuNP-screen-printed carbon electrode. The AuNP-modified electrode is modified with capture DNA probes that are allowed to hybridize with biotinylated targets. Streptavidin-alkaline phosphatase (S-AP) is then applied for the indirect reduction of silver ions in the solution into a metallic deposit. The formed silver metals are then electrochemically measured to determine the target virus DNA concentration 72.