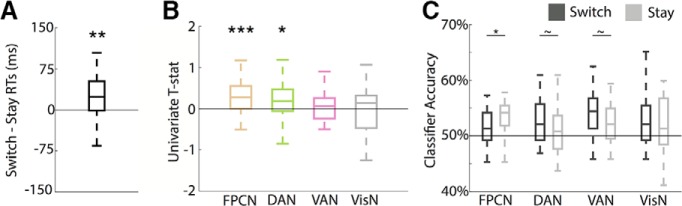
Figure 5.
Effects of task switching. A, Difference in RTs (ms) between switch and stay trials. RTs were significantly slower for switch trials than stay trials. B, Univariate contrast of switch versus stay trials. Activation was significantly greater for switch than stay trials in both FPCN and DAN. C, Goal-relevant feature decoding separated by switch and stay trials. There was a significant interaction between switch/stay and network, reflecting greater goal-relevant feature decoding on stay than switch trials in FPCN; the opposite trends were true for DAN and VAN. ∼p < 0.10, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.