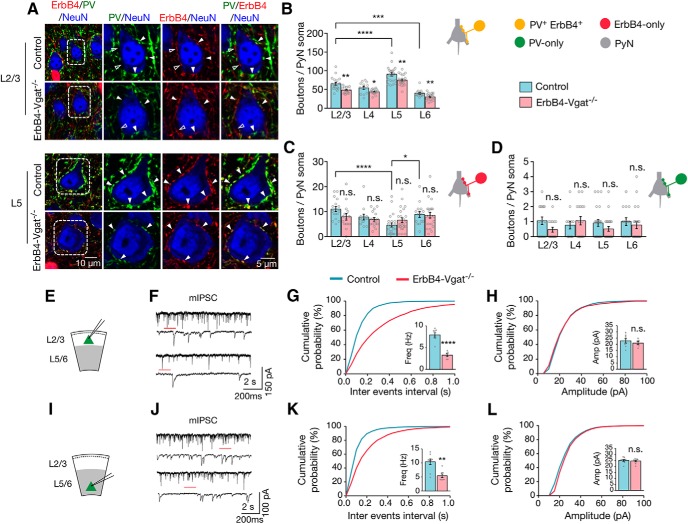
Figure 5.
Decreased axo–somatic inhibitory synapses by PV+ErbB4+ interneurons onto excitatory neurons. A, Representative Z-plane images of axo–somatic synapses onto pyramidal neurons. Cortical sections of control and ErbB4-Vgat−/− mice were stained with antibodies against PV and NeuN. Shown are L2/3 and L5 somas in which ErbB4+ boutons are labeled in red (tdTomato), PV boutons in green, and NeuN in blue. Open arrowheads indicate boutons that are either PV-only or ErbB4-only and closed arrowheads indicate PV+ErbB4+ boutons. Higher magnification images of dotted areas are shown on the right. B–D, Quantitative analysis of axo–somatic synapses that are PV+ErbB4+ (B), ErbB4-only (C), and PV-only (D). Control, n = 18, 13, 23, and 14 somas in L2/3, L4, L5, and L6, respectively, 4 mice; ErbB4-Vgat−/−, n = 15, 17, 24, and 19 somas in L 2/3, L4, L5, and L6, respectively, 4 mice. E, I, Schematics of whole-cell patch-clamp recordings of L2/3 (E) and L5/6 (I) pyramidal neurons in cortical slices. F, J, Representative traces of mIPSCs from L2/3 (F) and L5/6 (J) pyramidal neurons in control and ErbB4-Vgat−/− mice. Traces indicated by red lines are shown magnified below. G, H, Reduced mIPSC frequency (G) and no change in mIPSC amplitude (H) in L2/3 pyramidal neurons of ErbB4-Vgat−/− mice compared with controls. Control, n = 8 cells; ErbB4-Vgat−/−, n = 6 cells, 3 mice per group. K, L, Reduced mIPSC frequency (K) and no change in mIPSC amplitude (L) in L5/6 pyramidal neurons of ErbB4-Vgat−/− mice compared with controls. Control, n = 9 cells, 3 mice; ErbB4-Vgat−/−, n = 8 cells, 3 mice. Shown are cumulative probability plots for interevent intervals and amplitudes of mIPSCs. Insets, bar graphs for mIPSC frequency (Freq) and amplitude (Amp). n.s., Not significant. Error bars indicate SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.