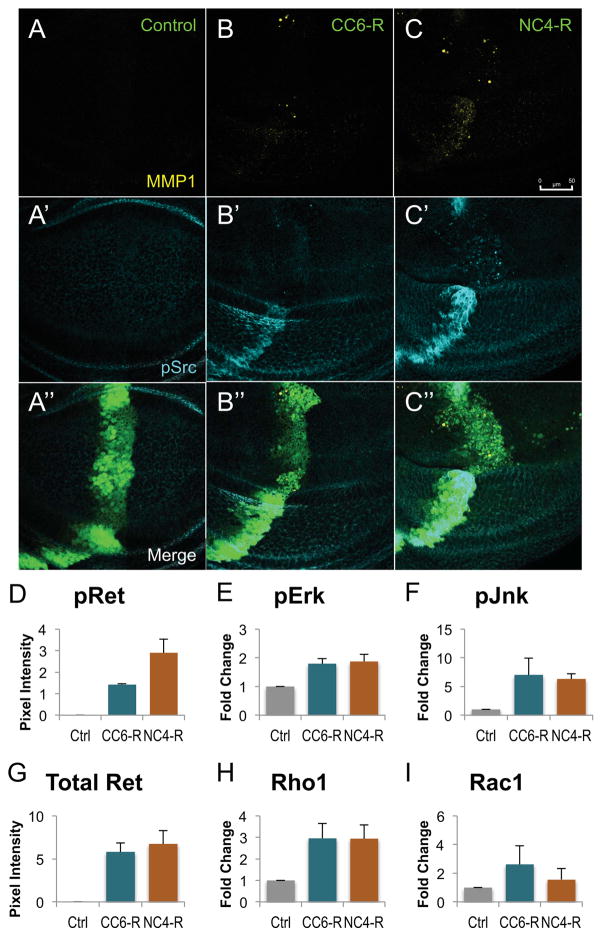
Figure 2. RET fusions directed EMT, upregulated canonical downstream targets.
A–C: Third instar larval wing discs expressing transgenes within the ptc-GAL4 expression domain. A′–C′: An antibody targeting MMP1 shows that migrating cells expressed matrix metalloproteinases, enzymes upregulated during mammalian EMT. A″–C″: An antibody against phosphorylated Src shows that expression of either RET fusion led to upregulation of activated Src, another marker of EMT. Note that ptc>NCOA4-RET displayed more cells expressing MMP1 and p-Src, correlating with its more severe cell migration phenotype. Scale bar in C represents 50 μm in A–C″.
D–I: Histograms quantifying western blots from third instar wing discs expressing either 765-Gal4 (control), 765>CCDC6-RET, or 765>NCOA4-RET. Lysates were from 20 wings discs from each genotype, and two biological replicates were averaged. All animals were raised at 25°C to ensure similar levels of Gal4 expression; Fig. S1 provides a representative blot confirming similar levels of RET fusion proteins in panel G. A phospho-RET antibody demonstrating that NCOA4-RET has a higher level of kinase activity as assessed by autophosphorylation (panel D). Downstream signaling factors showed elevated activation (phospho-Erk and phospho-Jnk) or expression (Rho1). Data are represented as mean +/− SEM.
See also Figures S1, S3, and S4