Figure 6.
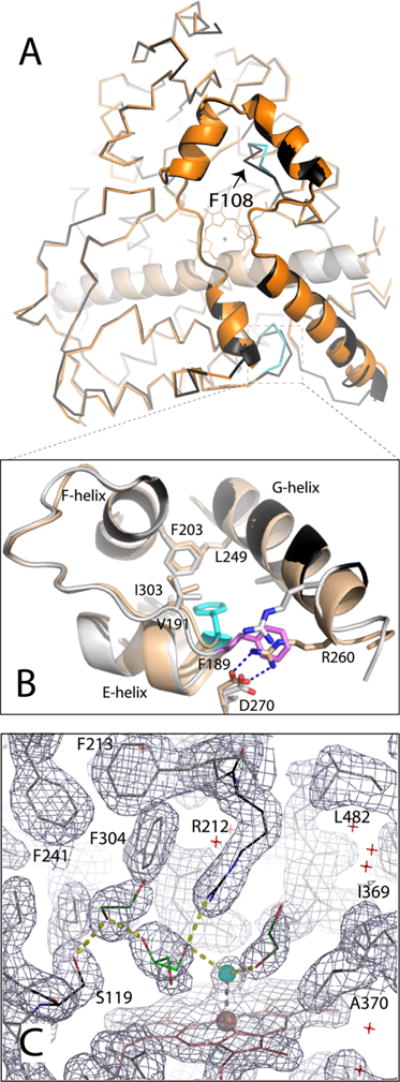
Crystal structure of opt-WT CYP3A4. (A) Structural superposition of the WT (1TQN, beige and orange) and opt-WT CYP3A4 (gray and black). The differently folded fragments in opt-WT are colored cyan; Phe108 is denoted with an arrow. (B) Magnified view of the region surrounding Phe189, whose side chain is oriented toward and away from the protein core in opt-WT and WT CYP3A4 (colored cyan and pink, respectively). The “inward” conformation allows Phe189 to interact with the hydrophobic cluster formed by Val191, Phe203, Leu249, and Ile303 and allows formation of the Arg260–Asp270 salt bridge linking the G and H helices. (C) Active site of opt-WT CYP3A4. The heme-bound water is colored cyan; other solvent molecules are depicted as red crosses. Glycerol and two ethylene glycol molecules (shown as light and dark green sticks, respectively) are interlinked with the water ligand and the Ser119 and Arg212 side chains through H-bonding interactions (shown as yellow dotted lines). The gray mesh is the 2Fo – Fc electron density map contoured at 1σ.
