Abstract
Rotavirus infections are a leading cause of severe, dehydrating gastroenteritis in children <5 years of age. Despite the global introduction of vaccinations for rotavirus over a decade ago, rotavirus infections still result in >200,000 deaths annually, mostly in low-income countries. Rotavirus primarily infects enterocytes and induces diarrhoea through the destruction of absorptive enterocytes (leading to malabsorption), intestinal secretion stimulated by rotavirus non-structural protein 4 and activation of the enteric nervous system. In addition, rotavirus infections can lead to antigenaemia (which is associated with more severe manifestations of acute gastroenteritis) and viraemia, and rotavirus can replicate in systemic sites, although this is limited. Reinfections with rotavirus are common throughout life, although the disease severity is reduced with repeat infections. The immune correlates of protection against rotavirus reinfection and recovery from infection are poorly understood, although rotavirus-specific immunoglobulin A has a role in both aspects. The management of rotavirus infection focuses on the prevention and treatment of dehydration, although the use of antiviral and anti-emetic drugs can be indicated in some cases.
Diarrhoeal diseases are one of the leading causes of illness and death in children <5 years of age, particularly those in low-income countries, and cause >500,000 deaths per year globally1. Before the 1970s, the aetiologic agent in many cases of infantile gastroenteritis was not identified, but a breakthrough occurred in 1973 with the identification of virus particles in duodenal biopsy samples from children with severe diarrhoea2 and in faecal samples from children with acute diarrhoea3. The name rotavirus (adapted from the Latin word ‘rota’, which translates to wheel) was assigned to this newly discovered virus because of its distinct morphological appearance (FIG. 1a). Rotaviruses were soon confirmed as a major cause of life-threatening diarrhoea in infants and children <5 years of age worldwide and in the young of many mammalian and avian species4.
Figure 1. Rotavirus structure.
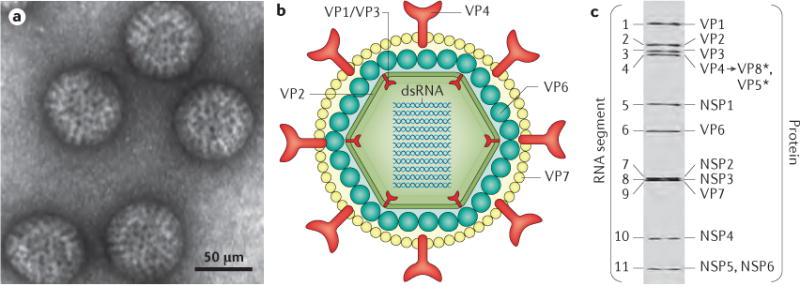
The rotavirus particle resembles a wheel with short spokes and a smooth outer rim. a | Electron micrograph of rotavirus triple-layered particles. b | Cross-sectional schematic of the rotavirus triple-layered particle. This structure consists of the inner capsid layer (viral protein (VP)2), the middle capsid layer (VP6) and the outer capsid layer (VP7 and the spike protein VP4). VP4 is proteolytically cleaved into VP8* and VP5*. The structural protein VP2, the enzymes VP1 and VP3 and the viral genome compose the virion core. The middle capsid layer protein (VP6) determines species, group and subgroup specificities. The outer capsid layer is composed of two proteins, VP7 and VP4, which elicit an immune response in infected hosts, leading to the production of rotavirus-specific antibodies. c| Electrophoretic migration profile of the 11 segments of rotavirus double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and the encoded proteins for simian rotavirus SA11 strain. NSP, non-structural protein.
Rotaviruses are non-enveloped double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) viruses that have a complex architecture of three concentric capsids that surround a genome of 11 segments of dsRNA (FIG. 1b,c). The RNA segments encode six structural viral proteins (VP1, VP2, VP3, VP4, VP6 and VP7) and six non-structural proteins (NSP1, NSP2, NSP3, NSP4, NSP5 and NSP6) (FIG. 1c). The proteins in the mature virus particle determine host specificity, cell entry and enzymatic functions necessary for the production of viral transcripts, and contain epitopes that generate immune responses (FIG. 1b,c). The non-structural proteins are involved in genome replication and antagonism of the innate immune response (a particular role for NSP1) and include the viral enterotoxin NSP4 (REF. 4).
Ten different rotavirus species (A–J) have been classified on the basis of sequence and antigenic differences of VP6 (REFS 5–7). Species A rotaviruses, which are the most common cause of infections in children, are the focus of this Primer. Species A rotaviruses are further classified into different genotypes, based on sequence differences in RNA segments 7 and 4 (encoding VP7 and VP4, respectively), which form the basis of the dual nomenclature system used for species A rotavirus strains, whereby glycoprotein (G, or VP7) and protease-cleaved protein (P, or VP4) subtypes are differentiated4. To date, 32 G genotypes and 47 P genotypes of species A rotavirus have been identified8, although globally, six G types (that is, G1, G2, G3, G4, G9 and G12) and three P types (that is, P[4], P[6] and P[8]) predominate9–11. In addition, six strains of species A rotavirus generally account for >90% of globally circulating species A rotavirus: G1P[8], G2P[4], G3P[8], G4P[8], G9P[8] and G12P[8]10–12. Geographical differences in species A rotavirus strain distribution have been observed, with more strains causing rotavirus disease in children in low-income countries than in children in high-income countries. Human species A rotavirus strains that have a high degree of genetic homology with animal strains have been identified, and direct animal-to-human transmission can occur10,13, particularly in low-income countries14. Virus evolution is driven by the accumulation of point mutations and genome reassortment, which can occur after dual infection of individual cells by different species A rotavirus strains, leading to viral progeny with combinations of the parental genomes.
In addition to diarrhoea, rotavirus infection can induce vomiting, malaise and fever. Indeed, vomiting is a hallmark of rotavirus disease15, contributes to dehydration and can hamper the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions, such as oral rehydration therapy16. Live attenuated oral vaccines against rotavirus were licensed for global use in 2006 and are used in >100 countries worldwide. Before the introduction of vaccines, rotavirus-associated gastroenteritis caused >500,000 deaths in children <5 years of age annually17. Although the introduction of vaccines has reduced the number of rotavirus-associated deaths, the effectiveness of licensed vaccines is suboptimal in low-income countries, in which, rotavirus gastroenteritis still results in >200,000 deaths annually18.
This Primer discusses the epidemiology and pathophysiology of species A rotavirus disease, including the innate and adaptive immune response to rotaviruses, clinical manifestations, disease management and prevention, and summarizes important remaining research questions.
Epidemiology
Global burden of disease
Rotaviruses are ubiquitous and infect almost every child globally by 3–5 years of age19,20. In 2003, 114 million cases of rotavirus infection were reported in children <5 years of age globally, of which 24 million cases required outpatient visits and 2.3 million cases required hospitalization21. In 2013, rotaviruses were associated with an estimated >200,000 fatalities in children <5 years of age globally18. Although the prevalence of rotavirus infection in children hospitalized with diarrhoea is similar worldwide (~30–50%), >90% of children with fatal rotavirus infections live in low-income countries18, which is likely because of limited access to health care, lack of available hydration therapy and a greater prevalence of comorbid conditions (such as malnutrition), among other factors (FIG. 2). Rotavirus disease is more frequently caused by uncommon rotavirus strains (such as G9P[6], which accounted for 9.5% of all rotaviruses identified from a multicentre collection in India22) and occurs at a younger age in low-income countries than in high-income countries18. For example, the proportion of all rotavirus hospitalizations in children <5 years of age that occur in infants by 8 months of age is 43% in Africa but only 27% in Europe23. In addition, seasonality correlates with the income level of a country, as more-seasonal disease occurs in high-income countries than in low-income countries24.
Figure 2. Rotavirus-associated mortality in children <5 years of age in 2013.
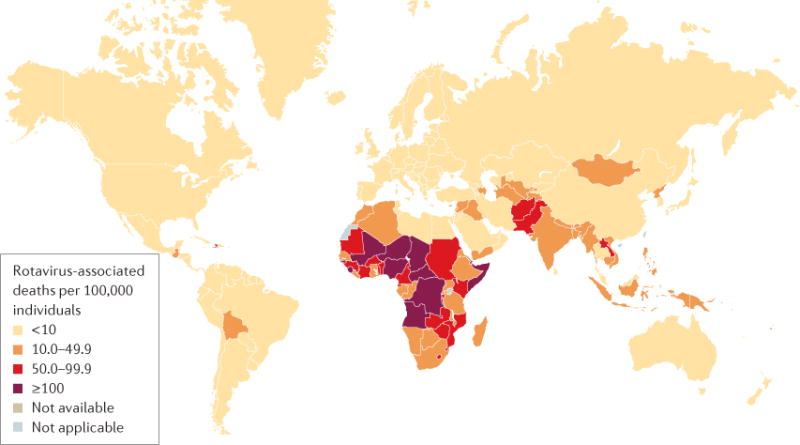
As of April 2016, the WHO estimated that worldwide, 215,000 children <5 years of age died because of rotavirus infection in 2013. Figure reproduced with permission from the World Health Organization. Rotavirus mortality rate in children younger than 5 years, 2013. http://www.who.int/immunization/monitoring_surveillance/burden/estimates/rotavirus/rotavirus_deaths_map_b.jpg?ua=1 (2017) (REF. 208).
Diarrhoea caused by rotavirus infection is of more than average severity; the proportion of diarrhoea episodes that are caused by rotavirus is lowest in patients in the community who require only home care (5–10%) compared with those who require outpatient care (15–20%) or inpatient care (30–50%)18. Indeed, before the introduction of rotavirus vaccines, global surveillance studies in several countries reported that ~40% of hospitalizations due to diarrhoea in children <5 years of age could be attributed to rotavirus infection21.
Effects of vaccination
A reduction in the burden of rotavirus disease has been observed in many countries following the introduction of rotavirus vaccines. In countries where rotavirus vaccine impact was reported during the first 10 years after introduction into the national childhood immunization schedule, all-cause hospitalizations due to diarrhoea in children <5 years of age decreased by a median of 38% (with a range of 5–63%), rotavirus disease-associated hospitalizations decreased by a median of 67% (with a range of 18–84%) and all-cause diarrhoea deaths decreased by 42% (with a range of 3–64%)21,25. Indirect protection (also known as herd immunity) of children who are age-ineligible for rotavirus vaccination has been reported in some high-income and middle-income countries, but not consistently in low-income settings, although the reasons for this are unclear25,26.
In addition, the demographics of rotavirus disease has changed since the introduction of vaccinations into national immunization schedules; for example, in Finland, rotavirus infection was most common in children <5 years of age before vaccine introduction, but after vaccine introduction, it is most common in unvaccinated children between 6 and 16 years of age and individuals >70 years of age27. Changes in the seasonal pattern of rotavirus disease have also been observed after vaccine introduction, including delays in the start of the rotavirus season, a shorter duration of seasons and blunting of seasonal peaks28. In the United States, the regular annual seasonal pattern of rotavirus disease that was observed before rotavirus vaccine introduction has shifted to biennial increases in circulating rotavirus disease (FIG. 3). This phenomenon might be due to the accumulation of unvaccinated children over two successive rotavirus seasons due to moderate levels of vaccine coverage (60–80%), leading to a larger epidemic every alternate year.
Figure 3. The number of rotavirus-positive tests in the United States before and after vaccine introduction.
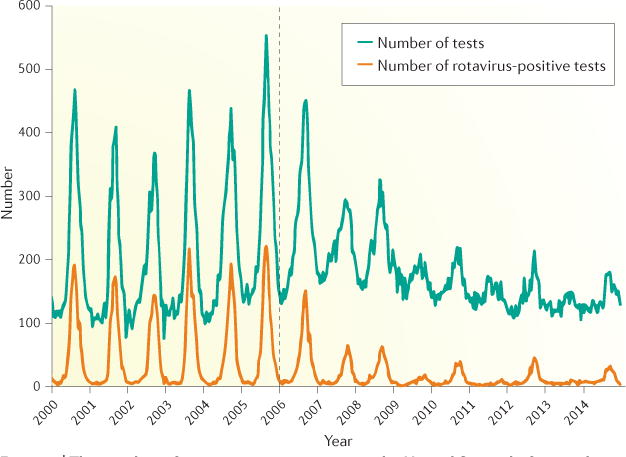
These data are from 21 continuously reporting National Respiratory and Enteric Viruses Surveillance System laboratories, collected by week of year and region, including a 3-week moving average. The number of rotavirus-positive tests has decreased, and the annual peak in rotavirus cases has been replaced by a biennial peak, following the introduction of rotavirus vaccinations (dotted line)28,209. Figure adapted with permission from REF. 209, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Although initial differences in the genotypes of circulating rotavirus strains have been described in some countries after vaccine introduction, there is little evidence that this is due to selective pressure from vaccination27,29. An increased prevalence of G2P[4] strains was observed following introduction of the monovalent G1P[8] rotavirus vaccine in several countries in South America and Europe, and Australia. However, similar increases in the prevalence of G2P[4] strains have been observed in countries that introduced the pentavalent rotavirus vaccine (which includes the G2 genotype) and in countries with low rotavirus vaccine use30. Furthermore, the monovalent G1P[8] rotavirus vaccine was effective at preventing G2P[4]-induced diarrhoea in Brazil (where this strain was initially observed)31; thus, whether the differences in rotavirus genotypes represent natural seasonal variation or vaccine-induced selection pressure is unclear. Continued surveillance is needed to monitor changes in rotavirus epidemiology following vaccine introduction. In addition to monitoring genotypes, whole genomic characterization of circulating rotavirus strains before and after vaccine introduction will help assess whether vaccines are affecting the evolution of the rotavirus genome.
Transmission
Rotavirus is shed in large quantities in stools during episodes of rotavirus-associated diarrhoea. The virus is transmitted predominantly through the faecal–oral route, mainly by close person-to-person contact4, and few virions are needed to cause disease in susceptible hosts32. Contaminated fomites (that is, objects that can enable the transmission of pathogens) also have a role in the transmission of rotavirus, especially in out-of-home care settings and hospitals33,34. Transmission of rotavirus through airborne droplets has been hypothesized to explain the rapid acquisition of anti-rotavirus antibody in the first 3 years of life, regardless of hygiene and sanitary conditions, but this has not been proved4.
Mechanisms/pathophysiology
Viral entry and replication
Rotavirus infects and replicates in the mature, non-dividing enterocytes in the middle and tip of the villi and in enteroendocrine cells in the small intestine35, suggesting that these cell types express factors that are required for efficient infection and replication15,36. The susceptibility of mature enterocytes and enteroendocrine cells to infection has been shown in mice, in a transformed human enteroendocrine cell line and in human intestinal enteroid (HIE) cultures35,36 (BOX 1). Rotavirus attachment to host cells is mediated by the outer capsid protein VP4 (through its VP8* domain37) and binding partners on the host cell surface, including sialoglycans (such as gangliosides GM1 and GD1a) and histo-blood group antigens (HBGAs)38 (FIG. 4). Rotavirus–HBGA interactions are dependent on the rotavirus P genotype, and studying these interactions has provided new insights into host range restriction and interspecies transmission of different rotavirus strains36,39. Indeed, genetic differences in HBGA expression can explain differences in rotavirus epidemiology among populations. For example, the susceptibility of neonates to some rotavirus genotypes (such as P[11]) might be due to the binding of developmentally regulated precursor HBGA, and the high prevalence of P[6] rotavirus infections in children in Africa might be due to the higher prevalence of the Lewis-negative glycan phenotype in this population40,41. The role of HBGAs in the susceptibility to rotavirus vaccine strains and the associated effect on vaccine efficacy are important emerging areas of public health research36,39,40. Following cellular uptake, rotavirus replication and assembly occur in cytoplasmic viroplasms, and newly produced rotaviruses are released from the cells through cell lysis or Golgi-independent non-classical vesicular transport (FIG. 4).
Box 1. Model systems for the study of rotavirus.
For decades, most research on the basic biology of rotaviruses was carried out using transformed cell lines infected with animal rotavirus strains that grow easily in the laboratory. However, many strain-specific differences in rotavirus pathogenesis (such as histo-blood group antigen (HBGA) binding and virus entry) exist. Understanding host–pathogen interactions and disease pathology in the healthy human gastrointestinal epithelium has been limited by the use of transformed cell line models. A major development to overcome these limitations is the use of human intestinal enteroid (HIE) cultures to model the human gastrointestinal epithelium36,192,193. HIE cultures are produced from stem cells that have been isolated from crypts of small intestinal tissues or biopsy samples donated by consenting individuals and are cultured ex vivo in 3D cultures or as monolayers. HIE cultures are multicellular and contain different cell types that are found in the intestinal epithelium including enterocytes, goblet cells, enteroendocrine cells and Paneth cells36,193. Heterogeneity in virus replication based on HBGA expression, the infection of several epithelial cell types, differences in the magnitude of intestinal innate immune responses among individuals, the production of viroplasms and their interaction with lipid droplets and visible physiological responses that can be imaged have all been observed following rotavirus infections in HIE cultures, suggesting that this system is a biologically relevant model to study human rotaviruses36,185.
Figure 4. The rotavirus replication cycle.
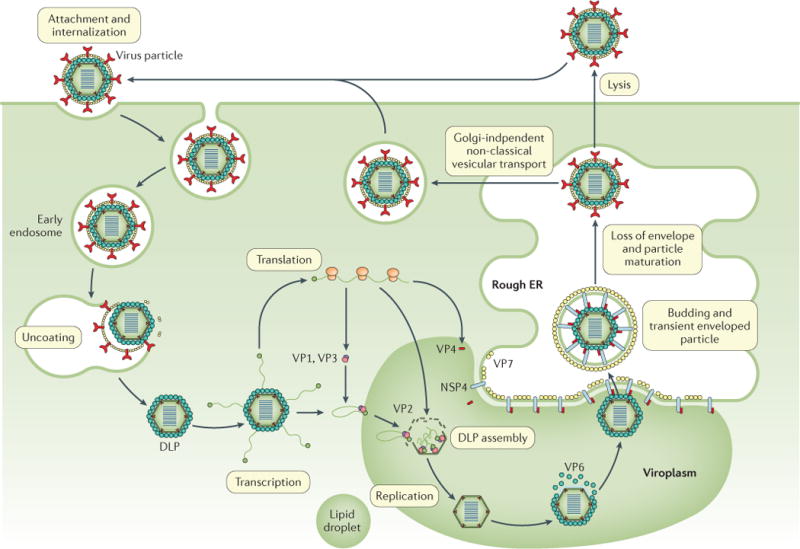
Rotaviruses attach to different glycan receptors on the host cell surface, depending on the virus strain, through interaction with the viral protein 8* (VP8*) domain of VP4. For decades, sialoglycans (for example, gangliosides such as GM1 and GD1a) were considered the key cellular glycan partner for VP8* (REF. 37). Although this remains true for animal rotavirus strains, VP8* of many human rotavirus strains binds genetically determined nonsialylated glycoconjugates, called histo-blood group antigens (HBGAs). Other proposed receptors for rotavirus cell entry include integrins210, heat shock protein 70 (REFS 211,212) and junctional proteins such as junctional adhesion molecule A, occludin and tight junction protein ZO-1 (REF. 213). After initial binding, VP7 and the VP5* domain of VP4 can interact with several of these co-receptors, which are concentrated at lipid rafts to mediate viral entry. Depending on the strain of rotavirus, the virus is internalized into cells by clathrin-dependent or clathrin-independent and caveolin-independent endocytic pathways38,214. The low calcium levels inside the endosome trigger the removal of the outer capsid layer, which releases the transcriptionally active double-layered particle (DLP) into the cytoplasm. Viral mRNA is used for translation or as a template for RNA synthesis during genome replication; the RNA is then packaged into new DLPs within viroplasms (specialized structures composed of viral and cellular proteins that require components of lipid droplets for formation179). Triple-layered particle assembly involves the binding of newly formed DLPs to non-structural protein 4 (NSP4), which serves as an intracellular receptor, followed by the budding of DLPs into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). In addition, NSP4 mediates an increase in cytoplasmic calcium levels, which is required for virus replication (not shown)50,58. In the ER, transient enveloped particles can be observed and the outer capsid proteins VP4 and VP7 are added onto the DLPs. The envelope is then lost, the virus particles mature and progeny virions are released from cells through cell lysis or by a Golgi-independent non-classical vesicular transport mechanism in polarized epithelial cells.
Gastrointestinal symptoms
In contrast to gastroenteritis caused by bacterial pathogens, rotavirus infections cause non-bloody diarrhoea that lasts for a relatively short duration and is associated with a limited inflammatory response35,42. Indeed, inflammatory markers such as serum C-reactive protein and faecal calprotectin are almost unaltered in children with rotavirus infection43,44. Thus, rotavirus-induced diarrhoea is considered non-inflammatory and has two proposed mechanisms: osmotic diarrhoea due to malabsorption (secondary to enterocyte damage or death, or to decreased epithelial absorptive function) and secretory diarrhoea due to the effects of NSP4 and activation of the enteric nervous system (ENS)45. In addition, rotavirus infection-mediated secretion of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT; also known as serotonin) can activate signalling pathways that can induce diarrhoea and vomiting15.
Enterocyte damage and death
Although few histopathological studies of samples from patients with rotavirus infection have been carried out, rotavirus infection and replication in the duodenal mucosa of infants has been shown to cause disruption to normal cellular homeostasis. This disruption results in shortening and atrophy of villi, loss of microvilli, mononuclear cell infiltration, distended endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial swelling in enterocytes46,47. Similarly to children with rotavirus infection, blunting of intestinal villi and enterocyte vacuolization and damage can be observed in rotavirus-infected piglets and calves4. By contrast, minimal loss of the intestinal epithelium has been observed in rotavirus-infected mice, although enterocyte vacuolization and ischaemia of intestinal villi have been described in rotavirus-infected mouse pups48. In addition, rotavirus infection in mice >2 weeks of age does not cause diarrhoeal disease, and infections in adult mice occur without symptoms or histopathological changes.4 As shown in studies in piglets and mice, symptoms of rotavirus infection can occur before histological changes, indicating that these changes do not solely explain clinical presentation49 (FIG. 5).
Figure 5. Duodenum histology of mice with rotavirus infection.
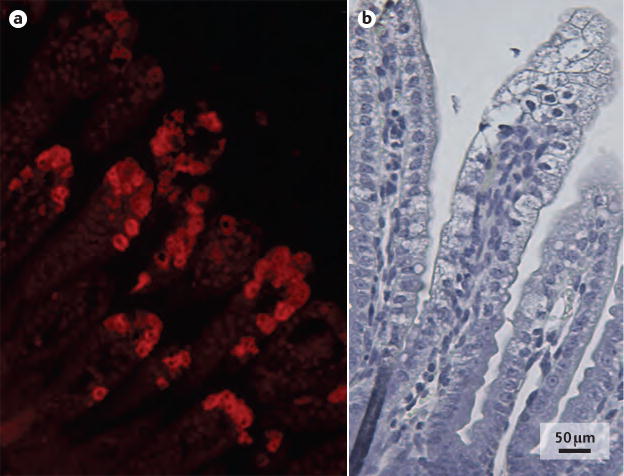
Histopathological images of the duodenum of a mouse pup infected with a murine rotavirus strain (EDIM), 48 hours after infection. a | Rotavirus predominantly infects mature enterocytes at the middle and top of intestinal villi indicated by immunofluorescent labelling of rotavirus antigen viral protein 6. b | Vacuolization of enterocytes in the top and middle of intestinal villi can be observed with rotavirus infection, but crypt cells are unaffected.
Molecular insights into the mechanisms of enterocyte damage and death have been limited owing to the lack of model systems that recapitulate the human small intestine. However, studies in cell culture and in mice have shown that the expression of NSP4 and viral replication can hijack cellular pathways that might lead to cell death or cell extrusion from the intestinal epithelium50,51. Proposed mechanisms of this include virus-mediated apoptosis51,52, NSP4-mediated mislocalization of the tight junction protein ZO-1 (REF. 53) and binding to the basement membrane extracellular matrix proteins laminin subunit-β3 and fibronectin54, as well as disruption of normal cellular homeostasis50.
Reduced epithelial absorptive function
Several mechanisms underlying the reduction of epithelial absorptive function that contributes to rotavirus-induced diarrhoea have been proposed. These mechanisms include the loss of infected enterocytes and NSP4-mediated impairment of sodium-coupled solute symporters that are involved in the reabsorption of large volumes of water under physiological conditions55. However, the contribution of the reduced epithelial absorptive function to rotavirus-induced diarrhoea is unclear, owing to the efficacy of oral rehydration therapy in rapidly correcting electrolyte and water loss in children with severe rotavirus-induced diarrhoea. This observation indicates that a sufficient number of enterocytes have intact sodium–glucose cotransporter 1 function and suggests that rotavirus does not infect all enterocytes. An alternative explanation is that rotavirus infection induces an increase in epithelial cell turnover (which has been shown in mice51) and that this might aid in the uptake of oral rehydration solution (ORS).
NSP4
The NSP4 enterotoxin was first shown to induce diarrhoea in mice45. Indeed, NSP4 secreted from cells infected with rotavirus binds to intestinal epithelial cells56 and signals through phospholipase C to increase cytoplasmic calcium levels, which activates calcium-dependent chloride channels50. Activation of these channels causes excessive secretion of chloride ions into the intestinal lumen, creating an osmotic gradient that facilitates the transport of water into the lumen, leading to secretory diarrhoea. Calcium-activated chloride channel inhibitors can prevent rotavirus-induced secretory diarrhoea in neonatal mice, supporting the role of NSP4 in the development of secretory diarrhoea57. In addition, NSP4 can induce swelling and apical fluid secretion in 3D HIE cultures, recapitulating the effect of NSP4 in the intestines of 6–10 day-old mice36,58.
Activation of the nervous system
Rotavirus infection and NSP4-mediated increase in intracellular calcium levels can induce secretion of 5-HT from enteroendocrine cells in humans and mice, which can activate enteric nerves that innervate the small intestine and ultimately lead to increased intestinal motility59 (FIG. 6). Indeed, 5-HT release from enteroendocrine cells is calcium-dependent; infection with a rotavirus strain that does not increase calcium levels, silencing of NSP4 expression or chelation of cytoplasmic calcium did not lead to 5-HT release59. In mice, rotavirus-induced diarrhoea can be attenuated by loperamide (an opioid receptor agonist) and atropine (an anti-muscarinic drug that inhibits parasympathetic nerves60) supporting the role of the nervous system in rotavirus-induced intestinal motility and diarrhoea. However, the use of anti-motility drugs such as loperamide is not recommended in children <3 years of age because of an increased risk of life-threatening adverse effects15,61.
Figure 6. Schematic model of rotavirus-induced diarrhoea and vomiting.
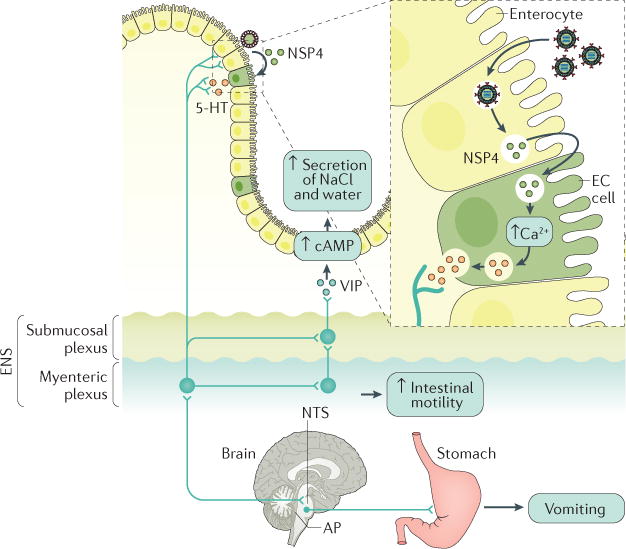
Rotavirus non-structural protein 4 (NSP4) is released from infected enterocytes and stimulates enterochromaffin cells (ECs, one type of enteroendocrine cell) to release 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)15, a neurotransmitter that regulates gastrointestinal motility and induces nausea and vomiting. 5-HT release can induce diarrhoea owing to the activation of 5-HT3 receptors on intrinsic primary afferent nerves that compose the myenteric plexus15. The activation of nerves of the myenteric plexus increases intestinal motility and activates nerves that compose the submucosal plexus, which stimulates the release of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) from nerve endings adjacent to crypt cells. These events, in turn, lead to diarrhoea by increasing cellular cAMP levels, which results in the secretion of sodium chloride (NaCl) and water into the intestinal lumen. Several lines of evidence support this model, including the attenuation of rotavirus-induced increased intestinal motility by an opioid receptor antagonist60, the attenuation of rotavirus-induced diarrhoea by a VIP receptor antagonist in mice216 and the secretion of water and electrolytes stimulated by VIP. In addition, enkephalins are endogenous morphine-like substances (opiates), which activate opioid receptors and therefore reduce the level of cAMP and might prevent this fluid secretion (not shown). Rotavirus infection can also activate the vomiting centre in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem, which comprises the reticular formation, nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) and area postrema (AP). Rotavirus or NSP4 stimulates vagal afferents to the vomiting centre by release of 5-HT from ECs in the gut15, which, in turn, stimulates the vomiting reflex. Indeed, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists are used to attenuate vomiting in children with acute gastroenteritis. ENS, enteric nervous system. Figure adapted with permission from REF. 217, Elsevier.
Rotavirus infection and NSP4-dependent 5-HT release can also activate vagal nerves that project to regions of the brain associated with nausea and vomiting15 (FIG. 6). The vagus nerve contains neurons that project from the gut to the brain and vice versa and is an important pathway in the detection of emetic stimuli and the generation of vomiting62. The anti-emetic drugs, ondansetron and granisetron (both 5-HT3 receptor antagonists), are widely used as anti-emetic drugs for children with acute gastroenteritis16,63, although direct evidence supporting the role of therapies in attenuating rotavirus-induced vomiting in children is lacking.
In addition, rotavirus infection is associated with delayed gastric emptying64. Gastric emptying is thought to be mainly a function of the pressure gradient between the stomach and the duodenum, which is influenced by poorly characterized neural and hormonal receptors in the duodenum and upper jejunum. In addition, the observed delay in gastric emptying might be mediated by increased secretion of gastrointestinal hormones (such as secretin, gastrin, glucagon and cholecystokinin) as well as activation of neural pathways that involve non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic and dopaminergic vagal neurons. However, whether rotavirus signals through these pathways or induces the secretion of these gastrointestinal hormones is unknown.
Fever and malaise
Rotavirus infection induces fever65 and is commonly associated with malaise. In general, fever is an acute-phase immune response that is regulated by the hypothalamus and is usually accompanied by inactivity, sleepiness, depression and reduced intake of food and water66. The pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and IL-6 have a role in the induction of fever, and the role of IL-1β in fever induction is dependent on IL-6 expression66,67. Although the exact mechanism of how rotavirus infection induces fever is unknown, significantly increased levels of IL-6 and TNF have been reported in the serum of children with fever following rotavirus gastroenteritis compared with levels in children who did not have gastroenteritis68. Vagal neurons that innervate the small intestine can, in theory, detect inflammatory cytokines because of the expression of appropriate receptors on the neuronal surface; these neurons relay this information to the brain, which can lead to fever and malaise. However, the exact mechanism by which rotavirus mediates this communication is unknown.
Extra-intestinal infection
Rotavirus can cause systemic infection by entering the bloodstream, although the mechanisms of extra-intestinal infection are unclear69. Detection of viral antigens (that is, antigenaemia) and infectious viruses (that is, viraemia) in serum have been reported in children with rotavirus infection, and replication of rotavirus in sites other than the intestines, although limited, is likely to occur69. One study reported antigenaemia in ≥90% of children with rotavirus infection until ~5 days after symptom onset, and some children had infectious virus in their serum69. In other studies, children with antigenaemia had more severe disease than children without antigenaemia, but the proportion of children with extra-intestinal presentations was not higher in those with antigenaemia70,71. Although it is clear that rotavirus infections can develop into systemic infections, direct evidence that this contributes to extra-intestinal disease and specific pathological findings in the infected host is lacking. However, rotavirus infection is associated with several non-gastrointestinal clinical conditions (BOX 2).
Box 2. Non-gastrointestinal conditions associated with rotavirus infection.
Rotavirus RNA has been detected in the cerebrospinal fluid in a few children with meningitis194, encephalopathy195,196 or encephalitis197, suggesting that rotavirus can reach extra-intestinal sites and cause clinical symptoms. An 18–21% reduction in the risk of seizures requiring hospitalization or emergency care in vaccinated children following the introduction of rotavirus vaccines provides more direct evidence supporting the association between rotavirus and neurological illness198.
Species C rotavirus has been detected in infants with biliary atresia199 (a neonatal cholangiopathy that results in the blocking or narrowing of the bile ducts200), which is the primary indication for liver transplantation in children200. Although rotavirus infection can lead to biliary atresia in mouse models201, the contribution of rotavirus infection to human biliary atresia is controversial.
Rotavirus infection has been implicated in the increased risk of a child developing diabetes mellitus. In a mouse model of diabetes, rotavirus infection activated plasmacytoid dendritic cells, leading to the secretion of type I interferon, which induces lymphocyte activation, including activation of islet autoreactive T cells202,203. However, contradictory findings have also been reported204,205. In addition, data from a study comparing peripheral T cell responses to rotavirus in children with or without diabetes did not support an association between development of type 1 diabetes or diabetes-associated autoantibodies in young children with rotavirus infections206. Further studies are needed to address whether rotavirus infection can contribute to the development of type 1 diabetes in a subset of children.
Immune response and clearance
Susceptibility to rotavirus infection is modulated by both non-immunological (such as the presence of gastric acid72 and differential expression of rotavirus receptors, such as HBGA, in the intestine73) and immunological factors. Most data on rotavirus-induced immune responses are from studies using animal models (mostly neonatal or adult mice and gnotobiotic piglets)74,75, although the relevance of these data to children with human rotavirus strains is unknown, and the mechanisms of immunity to rotavirus disease in humans are not completely understood.
Rotaviruses are initially recognized by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) in enterocytes or cells of the immune system (including macrophages, dendritic cells or adaptive B cells and T cells). The best characterized PRRs that have a role in rotavirus recognition are probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX58 (also known as RIG-I, which recognizes 5ʹ triphosphate uncapped RNA) and interferon (IFN)-induced helicase C domain-containing protein 1 (IFIH1; also known as MDA5, which recognizes dsRNA)76, both of which initiate type I and type III IFN responses77,78. Other PRRs include Toll-like receptors (TLRs) that were implicated in rotavirus recognition given the increased susceptibility of MYD88-knockout mice to rotavirus infection and disease79; MYD88 encodes myeloid differentiation primary response protein MYD88, an adaptor protein involved in TLR signalling. However, which, if any, MYD88-dependent TLRs directly recognize rotavirus components is unclear, as the increased susceptibility of MYD88-knockout mice to rotavirus infection could be related to the complex interaction of the microbiota with rotavirus infection. This interaction was illustrated by the report that antibiotic treatment can reduce rotavirus replication and the severity of disease in mice80. Rotavirus dsRNA can be recognized by TLR3 (a MYD88-independent TLR) and NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 9B (a component of the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor inflammasome), and these PRRs are speculated to have a role in the age-dependent resistance to rotavirus disease in mice, as both proteins are expressed at higher levels in adult animals81,82. In vitro (with multiple cell types) and in vivo experiments in mice have shown that, depending on the tissue, virus strain and age of the animal, NSP1 or possibly other rotavirus proteins can inhibit the signalling pathways activated by PRRs, which might underlie the poor innate immune response to rotaviruses78,83 (FIG. 7).
Figure 7. Rotavirus-mediated inhibition of interferon induction and amplification.
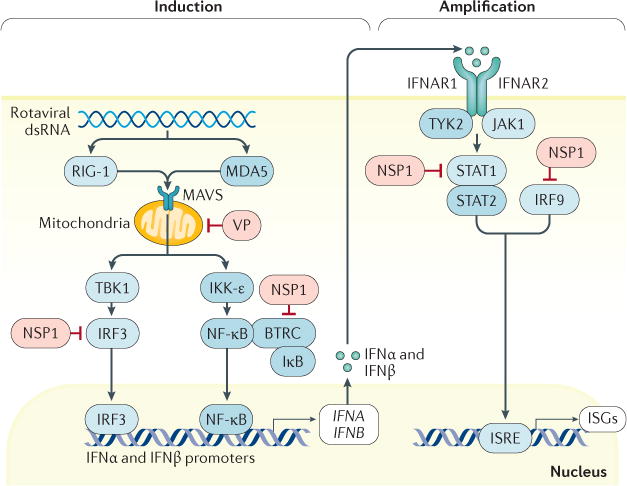
In intestinal epithelial cells, rotaviruses are recognized by the pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX58 (RIG-I) and interferon (IFN)-induced helicase C domain-containing protein 1 (MDA5). These PRRs then signal through mitochondrial antiviral-signalling protein (MAVS) to stimulate the IFN regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) pathway and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway to induce IFN type I, II or III responses. In an autocrine manner, this initially stimulates IFN signalling through the IFN receptor and then stimulates signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)1, STAT2 and IRF9 to induce transcription of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) that amplify IFN production. In human cells in vitro, evasion of the innate IFN response is mediated principally by rotavirus non-structural protein 1 (NSP1) through inhibition of NF-κB activation via degradation of F-box/WD repeat-containing protein 1A (BTRC; also known as β-TrCP)218,219. A second mechanism is mediated by NSP1 and inhibits STAT1 activation, therefore blocking type I and type III IFN responses220. Indeed, results from experiments using human rotavirus strains in human intestinal enteroid cultures185 support the findings that homologous rotavirus infection is very efficient at evading the type I and III IFN responses in mice77. Other viral proteins (VPs) might be involved in the suppression of the IFN response through inactivation of MAVS. IFNAR1, IFN-α/β receptor 1; IκB, inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB; IKK-ε, inhibitor of NF-κB kinase subunit ε; JAK1, Janus kinase 1; ISRE, IFN-stimulated response element; TBK1, TANK-binding kinase 1; TYK2, non-receptor tyrosine kinase TYK2.
Combinations of cytokines, such as IL-18 and IL-22 (REF. 84) or IL-22 and IFN85, have been proposed to mediate the clearance of rotaviruses by the innate immune system in mice77. In addition, rotavirus infection of human Caco-2 cells in vitro86,87 and in piglets88 induces transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) expression, which can downregulate the adaptive immune response to rotavirus infection (see Recurrent infections). In general, rotaviruses have several features that enable them to efficiently evade the innate immune response, leaving the adaptive immune response as a final mechanism for viral clearance. However, some T cell-deficient and B cell-deficient strains of mice clear rotavirus infection, indicating that the innate immune system has a role in viral clearance89.
In mice, cells of the adaptive immune system, such as CD8+ T cells and, to some degree, B cells, can mediate rotavirus clearance89,90. Very low levels of rotavirus-specific CD8+ T cells can be detected in the blood of children with rotavirus disease, whereas these cells are below the detection limit in most healthy children91. Rotavirus-specific CD8+ T cells can be detected in adults with or without rotavirus disease but, in general, secrete only one cytokine (IFNγ), suggesting that like CD4+ T cells, these cells are not very functionally efficient91,92. Of note, very little relevant data are available regarding the level or quality of enteric (measured in the intestine) T cell immunity to rotavirus in either children or adults.
Recurrent infections
Although children can have many recurrent rotavirus infections, they progressively diminish in severity20,93. Levels of total serum rotavirus-specific immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies, measured after infection, are currently the best marker of protection against rotavirus disease74, and the presence of anti-rotavirus IgA antibodies in serum is widely used as a marker of vaccine take, although the correlation with protection from severe gastroenteritis is not absolute.
The critical role of antibodies and T cells in protection against recurrent rotavirus infection can be observed in children with primary severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID, who have defective T cell and antibody responses), who can develop chronic rotavirus infection and intestinal and systemic disease94. Children with SCID are also susceptible to chronic rotavirus vaccine shedding, especially with the waning of maternal antibodies95. These findings form the basis for the recommendation that children with SCID should not receive rotavirus vaccines95. As monovalent G1P[8] vaccines can induce protection against other rotavirus strains with different P-types and G-types (that is, heterotypic responses)90, heterotypic neutralizing antibodies (either anti-VP4 antibodies or anti-VP7 antibodies) might have important roles in protection against rotavirus disease.
In adult mice, protection from rotavirus reinfection is almost absolute and is mostly mediated by intestinal IgA antibodies90, the production of which is largely dependent on the activation of CD4+ T cells89. These cells are not readily inducible in neonatal mice, in which protection is less efficient96. A similar situation might exist in young children in whom intestinal IgA antibodies wane90 and rotavirus-specific CD4+ T cells are found at very low levels. Indeed, children with acute rotavirus gastroenteritis have very low levels of rotavirus-specific CD4+ T cells, which almost exclusively produce IFNγ91,97. Considering the poor ability of children to develop rotavirus neutralizing antibodies and that protection against rotavirus reinfection is age-dependent, the low levels of rotavirus-specific CD4+ T cells in younger children might be a key factor in protection from severe recurrent illness and in the response to rotavirus vaccination98.
As ~50% of parents of children with rotavirus disease develop rotavirus infections, and half of these develop mild disease, levels of rotavirus-specific CD4+ T cells and neutralizing antibodies might decrease over time and become insufficient to fully prevent reinfections99. When compared directly to influenza virus CD4+ T cell responses or tetanus toxin CD4+ T cell responses, the frequencies of rotavirus-specific CD4+ T cells in healthy adults have been shown to be low97 but similar to levels of CD4+ T cells specific for other mucosal respiratory viruses91. Interestingly, in adults, rotavirus-specific CD4+ T cells have a terminal effector memory cellular phenotype, suggesting that they do not provide long-term immunity97. Collectively, these data suggest that in adults, the systemic CD4+ T cell response to rotavirus infection is poor, which might explain the absence of sterilizing immunity and the presence of moderately frequent, mild recurrent infections. The relatively poor adaptive immune response to rotavirus is most likely related to the efficient mechanisms (inhibition of IFN and secretion of TGFβ and inhibition of the IFN response.
Diagnosis, screening and prevention
In infants <1 month of age, rotavirus infections are caused by distinct strains and are often asymptomatic or mild, presumably because of protection conferred by maternal antibodies that are transferred through the placenta or through breast milk100,101. The first rotavirus infections in infants >3 months of age are likely symptomatic and accordingly the incidence of rotavirus disease peaks between 4 and 23 months of age102,103. In children, the manifestation of rotavirus disease ranges from no symptoms to mild, watery diarrhoea of short duration and to severe diarrhoea with vomiting and fever that can result in rapid dehydration with shock, electrolyte imbalance and death19,104. As previously mentioned, reinfections are common, although the severity of disease usually decreases with each repeat infection20,100. However, rotavirus can cause limited disease in older children and adults, especially parents and caretakers of children with rotavirus diarrhoea, immunocompromised individuals, travellers and elderly individuals105,106. These illnesses are generally mild to moderate in severity.
Diagnosis
Although rotavirus-induced disease is clinically indistinguishable from diarrhoeal diseases caused by other gastroenteritis-inducing infectious agents (such as noroviruses, enteric adenoviruses 40 and 41, astroviruses, Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp.), several factors can indicate rotavirus infection. For example, rotavirus infections are often more severe than diarrhoeal diseases caused by other infectious agents. In addition, the seasonality of infection can indicate rotavirus as the causative agent in some regions; for example, in non-equatorial countries, rotavirus or norovirus infection is suggested if a child presents with diarrhoea in winter.
When a laboratory-confirmed diagnosis of rotavirus infection is requested by physicians in the clinical setting, rotavirus antigen can be detected in stools using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or immunochromatography. In vaccine and epidemiological studies, these assays are often complemented by the use of reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR)-based assays, which are more sensitive and permit genotyping of virus isolates. The window for the detection of viral shedding using ELISA usually ends within 1 week after the onset of illness, but the virus can be detected for longer periods by more-sensitive assays, such as RT-PCR107. Indeed, viral shedding ranges from 4 to 57 days108, and the quantity of RNA shed directly correlates with the severity of rotavirus-associated diarrhoea in children109 but not in neonates110. Importantly, up to 29% of healthy children <1 year of age have asymptomatic rotavirus infection when detected using RT-PCR111; accordingly, the quantity of viral RNA used to confirm diagnosis should be carefully considered. In addition, abnormal enzyme levels have been observed in children with rotavirus disease, which might be related to rotavirus-associated vomiting, dehydration or nonintestinal pathology. For example, mildly increased levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in blood can sometimes be observed during rotavirus infection and might be due to rotavirus-induced mild hepatitis112,113.
Prevention
Improvements in hygiene or sanitation do not substantially reduce the burden of rotavirus disease; the incidence of hospitalizations due to diarrhoea was ~40% in high-income or low-income countries before the introduction of rotavirus vaccines114. Thus, vaccination against rotavirus is the best measure to prevent rotavirus disease.
Two rotavirus vaccines are broadly used worldwide: the RV5 vaccine, RotaTeq (Merck, USA), and the RV1 vaccine, Rotarix (GlaxoSmithKline, Belgium). The RV5 vaccine is a live attenuated, pentavalent vaccine, which is composed of five bovine–human reassortant rotaviruses that express either human VP4 or VP7 from rotavirus strains G1, G2, G3, G4 and P1A[8]115. In the United States, the RV5 vaccine is given in three doses at 2, 4 and 6 months of age. The RV1 vaccine is a monovalent, live attenuated human virus vaccine116 containing rotavirus strain 89–12, which was initially isolated from a child with G1P[8] rotavirus-induced gastroenteritis, and in the United States, this vaccine is given in two doses at 2 and 4 months of age. For both vaccines, similar dose schedules and age schedules are used in most countries worldwide, although alternative schedules have been evaluated in clinical trials. Both vaccines are highly effective in preventing severe rotavirus disease in high-income countries117 but reduce the incidence of severe rotavirus disease by ~50–60% in many low-income countries118–120. Although the factors that determine the diminished effectiveness in less developed countries are not fully understood, both vaccines save more lives in low-income countries because of the higher rotavirus disease burden and mortality in these countries90. In Ghana and Pakistan, the intestinal microbiome composition has been associated with diminished efficacy of the RV1 vaccine121,122, although the exact implications of this are unclear. Environmental enteropathy (a common disorder in children in some low-income countries that is associated with diminished gastrointestinal immunity) might also have a role in reduced vaccine effectiveness in developing countries123. Indeed, the presence of biomarkers of environmental enteropathy has been associated with diminished RV5 vaccine seroconversion in infants123. In addition, in low-income countries that administer the oral polio vaccine, co-administration of this vaccine with oral rotavirus vaccines reduces the immunogenicity of the rotavirus vaccines124. Other factors that can alter the immunogenicity of rotavirus vaccines include the presence of maternal antibodies and host genetic differences. The role of maternal antibodies in rotavirus vaccine response is unclear, with some studies reporting a reduction in vaccine immunogenicity but others reporting no effect90. In addition, although the presence of rotavirus-specific IgA antibodies in breast milk has been associated with reduced RV1 vaccine seroconversion125, withholding breastfeeding before vaccination does not consistently improve vaccine immunogencity126. Differences in genes encoding HBGA in vaccine recipients might also contribute to differences in vaccine immunogenicity127. Whether increasing the number of vaccine doses administered in low-income countries could increase vaccine immunogenicity has not been easy to examine and probably requires additional post-marketing effectiveness studies128.
The first licensed rotavirus vaccine (RotaShield, Wyeth, USA) was withdrawn by its manufacturer owing to an increased risk (1 excess case per 5,000–10,000 vaccinated children) of intussusception (in which part of the intestine enters into an adjacent part of the intestine) following immunization, which suggested a causal association between rotavirus infection and intussusception129.
Both the RV1 vaccine and the RV5 vaccine have a good safety record, although an increased risk of intussusception (~1 excess case per 50,000–100,000 vaccinated children) has been reported in many settings130. Additional studies are needed to identify how wild-type rotavirus and rotavirus vaccines induce intussusception. Although the benefits of rotavirus vaccination outweigh the low risk of intussusception, several groups are pursuing the development of non-replicating, safer and more immunogenic vaccine formulations90. A combination of oral and parenteral vaccines (inactivated or recombinant non-live vaccines) or only parenteral vaccines might be useful in this regard90. Indeed, a parenterally administered recombinant VP8* vaccine is safe and immunogenic in children131.
In addition to the RV1 and the RV5 vaccines, other live attenuated, oral rotavirus vaccines are used in some countries, and others are in development. As asymptomatic infections with specific rotavirus strains in neonates are associated with protection against disease later in life, vaccines based on these strains have been developed. These include ROTAVAC (Bharat Biotech), which is based on rotavirus strain 116E and is now licensed in India132 and RV3 (PT Bio Farma, Indonesia/Murdoch Children’s Research Institute, Australia), which was developed in Australia and is in clinical trials in neonates and infants133. Other live oral vaccines include the Lanzhou lamb rotavirus vaccine in China (Lanzhou Institute of Biological Products, China) and the Rotavin-M1 (Center for Research and Production of Vaccines and Biologicals) attenuated human vaccine in Vietnam90. To lower vaccine costs, a bovine rotavirus pentavalent vaccine (BRV-PV) developed by the NIH is in production by manufacturers in low-income countries90. Three doses of the BRV-PV vaccine reduced the incidence of severe rotavirus gastroenteritis by 66.7% in infants in Niger134.
Management
Regardless of the infecting agent, children presenting with diarrhoea are assessed for dehydration and treated accordingly. A mild case of rotavirus disease, where the child is active, shows no signs of dehydration, has had between zero and two vomiting episodes within 12 hours, has had a few loose or low output watery stools per day and has no fever or a low-grade fever, requires only observation. Symptoms can last for 1–5 days, but if they last for >1 week, medical consultation should be sought. Increasing and/or intense vomiting and repeated episodes of watery diarrhoea (for example, >1 episode per hour, especially if abundant) are the main features that indicate the need for specific treatment. In low-income countries, the goal of treatment is avoiding or rapidly treating severe dehydration and maintaining protein–calorie intake to prevent death or worsening malnutrition, whereas in middle-income and high-income countries, reducing hospitalization and the duration of diarrhoea are the main goals. Key treatment concepts including fluid and electrolyte management (including ORS and intravenous rehydration), dietary management and the use of probiotics, anti-emetics, antisecretory drugs and antiviral drugs are discussed below; comprehensive reviews of acute diarrhoea management can be found elsewhere135,136.
Fluid and electrolyte management
One of the most important medical advancements in the past 50 years that has saved millions of infant lives was that administration of ORS resulted in glucose-coupled sodium and water absorption in the small intestine137. Oral rehydration therapy has been used safely and successfully to prevent and treat dehydration due to diarrhoeal pathogens, including rotavirus, in infants and young children138. Clinical scales that consider the presence of signs and symptoms are available to assess for dehydration139,140, and a thirsty, restless or fatigued child with a dry mouth should alert caretakers to ongoing dehydration. Prompt replacement of fluids and electrolytes, spoon by spoon if necessary, with hypo-osmolar ORS (containing 60–75 mmol per litre of sodium in addition to glucose, potassium, chloride and citrate)141 is the cornerstone of treatment for children without dehydration but with intense and repeated vomiting and/or diarrhoea episodes and for children with mild to moderate dehydration. If ORS is not available, homemade solutions can be prepared using water, sugar and salt. Plain water, soda, chicken broth and apple juice should be avoided in children with dehydration, especially in infants, as they are hyperosmolar solutions and do not sufficiently restore potassium, bicarbonate and sodium levels142. Intravenous fluids can be used in cases of severe dehydration, hyperemesis, oral rehydration therapy failure or severe electrolyte imbalances. Importantly, most children, even those with severe dehydration, can be managed effectively with ORS to prevent severe complications, including death.
Dietary management
Dietary management is an important factor in the care of children with acute diarrhoea143. Breastfeeding should be encouraged and is never contraindicated. In patients with dehydration, food withdrawal is advised for only 4–6 hours after initiating rehydration therapy136,144. The administration of repetitive, small portions of regular undiluted milk formulas is recommended for infants and children >6 months of age. The administration of lactose-free formulas might reduce the duration of treatment and the risk of treatment failure143 and can be considered for selected children, such as those requiring hospitalization136. Importantly, the maintenance of adequate protein–calorie intake during the diarrhoea episode using home-available, age-appropriate foods should be encouraged, especially in low-income settings143. In addition, zinc supplementation can improve the outcome of acute diarrhoea in low-income regions, in which malnutrition is common. Although the mechanisms of the efficacy of zinc supplementation are unclear, data from animal studies suggest zinc has anti-inflammatory properties145 and antisecretory effects146, among others. Zinc deficiency is common in low-income countries and can occur in children with acute gastroenteritis due to intestinal fluid loss. For children living in low-income regions, the WHO recommends daily zinc supplementation for infants and children for 10–14 days, starting as soon as the diarrhoea episode has been diagnosed147. However, zinc supplementation can increase vomiting after the initial dose148.
Probiotics
Commonly used probiotics for the treatment of acute diarrhoea are lactic acid-producing bacteria, such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus plantarum, several strains of Bifidobacteria and Enterococcus faecium (the SF68 strain), and yeast, such as Saccharomyces boulardii149. Most meta-analyses suggest a modest benefit of probiotics in reducing the duration of diarrhoea by ~1 day and up to 2 days for rotavirus-induced diarrhoea, although studies have been performed largely in middle-income and high-income countries3, and some studies did not report a clear benefit150,151. The mechanisms underlying this have been postulated to include the activation of antigen-presenting cells, a reduction in the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, the modulation of effector T cell and regulatory T cell immune responses, innate immune signalling (through interactions with several TLRs) and the promotion of enterocyte proliferation and/or migration152. In low-income regions, treatment with probiotics has a positive immunomodulatory effect (that is, an increased anti-rotavirus IgG response in individuals who received treatment compared with individuals who received placebo), improves intestinal function in children with rotavirus infection and might decrease repeat episodes of rotavirus diarrhoea153,154. However, probiotics are not included in the standard of care for children with rotavirus diarrhoea globally.
Other drugs
Antiviral therapy for rotavirus infection has been studied but remains mostly in preclinical stages. One exception is nitazoxanide, a broad-spectrum antiviral drug155 that has been reported to reduce the duration of diarrhoea and the duration of hospitalization of children with acute rotavirus diarrhoea155–157. Nitazoxanide inhibits the replication of rotavirus by interfering with viral morphogenesis158. One study in hospitalized children 5 months to 7 years of age reported a significant reduction in the median time to the resolution of all rotavirus-associated gastro intestinal symptoms from 75 hours in children who received placebo treatment to 31 hours in children who received a 3-day course of nitazoxanide treatment156.
Recommendations for the use of anti-emetics (such as metoclopramide, dimenhydrinate and ondansetron) for children with rotavirus disease have progressed from ‘not recommended’ to ‘possibly recommended’ owing to their effects of reducing the number of vomiting episodes and reducing the need for intravenous rehydration and hospitalization150,159. Indeed, one dose of ondansetron reduces the likelihood of needing intravenous rehydration, although this can increase diarrhoea output. Importantly, repeated doses do not provide an additional benefit over one dose. The largest benefit can be gained when ondansetron is used early in the clinical course of children with rotavirus infection and intense vomiting.
Other potential therapies for rotavirus gastroenteritis include racecadotril and smectite. Racecadotril (an intestinal enkephalinase inhibitor that reduces the secretion of water and electrolytes into the gut160) has been shown to significantly decrease diarrhoea output at 48 hours after treatment and did not increase the frequency of adverse effects161. However, treatment with racecadotril did not reduce the proportion of patients with diarrhoea 5 days after treatment161. In addition, one meta-analysis of seven clinical trials reported that racecadotril treatment is more effective than placebo or no intervention at reducing the duration of illness and stool output in children with acute diarrhoea162. However, in Kenya, racecadotril did not alter the number of stools after 48 hours, the duration of hospital stay or the duration of diarrhoea in children with severe gastroenteritis who received ORS and zinc163 and was not effective in Indian children with acute diarrhoea and vomiting164. Thus, racecadotril can be considered for the management of children with severe secretory diarrhoea, but the efficacy is variable. Smectite (a natural adsorbent that binds to endotoxins, exotoxins, bacteria and viral particles) has been reported to decrease the duration of acute diarrhoea by 18–29% in a meta-analysis of mostly open-label trials in children with acute diarrhoea. In addition, smectite has been shown to increase the cure rate at day 5, without any increase in the risk of adverse events and accordingly could be beneficial in some individuals with rotavirus disease165,166.
Combination trials evaluating the simultaneous use of several treatments are lacking99. Indeed, improvements in treatment strategies are needed, especially in regions where rotavirus-associated deaths occur and where vaccines are underutilized.
Quality of life
Health-related quality of life (HRQOL) is used to quantify how diseases affect health, but few tools are available that are applicable for acute self-limited childhood illness, are used in low-income countries and are comparable across various geographic or socio-economic settings. The WHO’s QOL assessment tool has been translated into 40 languages, although the use of this tool to complement cost of illness surveys in low-income countries, particularly for acute illness, is uncommon. This lack of use is because of methodological challenges associated with estimating HRQOL or quality-adjusted life years for short or mild illnesses, particularly in young children167,168. In addition, few studies have used multiple assessments to measure the effect of an acute illness on QOL for the entire episode, as most studies assess HRQOL only at presentation to a health-care facility. The limited number of studies assessing the association between rotavirus illness and QOL from Europe, North America and Thailand have estimated HRQOL to range from 0.604 to 0.896 in children and 0.618 to 0.875 in parents, where 1 indicates no effect of illness169,170. The differences between locations might be due to variations in the tools used, the type of health-care facility available and cultural determinants regarding when children are taken to a health-care facility. Nonetheless, the illness of a child (which lasts for ~1 week) can affect the QOL of the parents owing to missed work (of, on average, 2 days in duration, but this can be up to 3 days for parents with children who require hospitalization) and other household members developing gastroenteritis. Indeed, in the 4-week period starting 2 weeks before the baseline health-care facility visit of the index case, at least 1 other household member will develop rotavirus infection in ~50% of families, leading to worry, stress and disruption of daily activity171.
Although rotavirus infection is considered an acute, self-limiting illness of young children, children in poor environmental conditions who develop repeat infections might sustain long-term damage to the gut, which can lead to consequences on physical and cognitive development172. Whether this gut damage depends on the mode of action of a pathogen or on the number of infections is not clear, but QOL during and after infections and the long-term effects of enteropathy will need to be evaluated in the future.
Over 100 hundred studies evaluating the cost-effectiveness of rotavirus vaccination have been conducted, but nearly all studies have focused on the direct and indirect cost of illness, and very few have considered QOL173. Although providing a single global estimate of the cost-effectiveness of vaccinations is difficult, one analysis of the economic impact of rotavirus vaccination in eligible countries by Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, reported a cost-effectiveness of US$42 per disability-adjusted life year averted. Regional differences in cost-effectiveness were reported, with the highest ratios in the Western Pacific region ($231) and lowest in the Eastern Mediterranean region ($30)174. Few data are available because most information is collected at health-care facilities that manage moderate or severe disease, whereas a large proportion of disease is mild and is therefore not managed at such facilities.
Outlook
Remarkable progress in our understanding and management of rotavirus disease has been made with life-saving vaccines, but considerable gaps in our knowledge remain in terms of basic virology and practical applications to improve the effectiveness of treatment and vaccines. Rotaviruses remain powerful tools for the understanding of host–enteric virus interactions, and their investigation needs to be continued.
Virus structure and replication
Although the 3D structures of most rotavirus capsid proteins have been determined, the structure of the capping enzyme, VP3 (REFS 175–177), and most of the non-structural proteins are unknown; determining these structures would aid our understanding of their functions and could lead to the development of targeted antiviral drugs. In addition, the structure of the rotavirus dsRNA genome and the exact mechanisms of rotavirus genome assortment, packaging and particle assembly await exploration. For example, rotavirus double-layered particles acquire a transient envelope during maturation, which is lost upon completion of triple-layer particle formation by an unknown mechanism178. During rotavirus replication, rotavirus-encoded proteins interact with cellular components, and exploration of these mechanisms is a topic of ongoing research (for example, the lipid droplet formation required for viroplasm assembly179) and should reveal new mechanisms that regulate replication. Although host HBGAs have been identified as receptors for human rotaviruses, the role of genetic variation in HBGAs in susceptibility to rotavirus infection and response to vaccination is incompletely understood.
Virus evolution
Zoonotic transmission of rotaviruses is suggested to involve mutations that allow rotavirus–HBGA binding180 and, in combination with other mechanisms of inter species transmission, should be monitored to fully understand host restriction. For example, bats are hosts of rotaviruses, and some strains of rotavirus are genetically related to other mammalian rotaviruses, although other strains are bat-specific7,181. The significance of bats as a reservoir for rotavirus transmission to other mammalian species (including humans) remains to be determined.
Reverse genetics of rotavirus
After many efforts182,183, a fully tractable, plasmid only-based reverse genetics system for rotaviruses has been developed184. This system can produce rotaviruses with predetermined changes in the genome, which enables functional analysis of the rotavirus NSPs and can be used to rescue rotaviruses containing heterologous inserts in one of their genes184. The reverse genetics system is versatile and very exciting and will be developed further to permit experiments that could not be previously conducted (BOX 3) and to move the field forward.
Box 3. Studies enabled by the plasmid only-based reverse genetics system184.
Exploring the packaging signals of the rotavirus single-stranded positive RNAs to increase knowledge of rotavirus replication.
Identifying the sequences of individual RNA segments that are involved in the genome assortment process, leading to a better understanding of reassortment mechanisms and potentially the development of safer, live attenuated vaccines in which reassortment is blocked.
Investigating the compatibility of cogent proteins of different rotavirus species (for example, of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerases of rotavirus species A and C), elucidating rotavirus evolution.
Studying host range restriction, pathogenicity, virulence and attenuation, enabling various projects of translational research, which could identify new therapies.
Developing rotaviruses that have directed mutations and that express green fluorescent protein to enable live imaging and pathogenesis studies.
Developing a rotavirus with highly cross-reactive epitopes (that would induce cross-protective immunity) and has the potential to become a ‘universal rotavirus vaccine’ candidate.
Experimental models
As previously mentioned, HIE cultures can be used to study rotavirus replication36 and closely mimic the natural infection, and these cultures await further exploration. This includes studies of the innate immune response to rotavirus185 and of disease pathophysiology, including defining the molecular mechanisms of rotavirus-induced diarrhoea and vomiting, the factors determining host restriction and the mechanisms of vaccine or virus attenuation in addition to studies testing candidate antivirals. Potential targets for rotavirus-specific antivirals include cellular receptors, proteins involved in viroplasm assembly, the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, proteins involved in RNA assortment and packaging and molecules involved in particle maturation. The significance of the composition of the gut microbiome for chronic enteric diseases, in addition to the host response to acute viral infections or viral vaccinations121,186, is being increasingly recognized and merits further exploration.
Vaccine development
Although rotavirus vaccination has an 80–90% effectiveness against severe rotavirus disease in high-income countries, the levels of rotavirus-specific antibodies sufficient for virus neutralization are found in only 30–50% of vaccinees115. Accordingly, understanding the true correlates of protection to improve current vaccines and facilitate the development of more effective next-generation vaccines, is urgent187. In addition, the effectiveness of rotavirus vaccines is 30–40% lower in low-income countries than in high-income countries118–120, and the causes of this remain incompletely understood188. At present, all licensed rotavirus vaccines are live attenuated vaccines, which can revert to virulence in immunodeficient and prematurely born children95 and can reassort with co-circulating human wild-type rotaviruses189,190. Thus, safer replication-incompetent rotavirus vaccines are required. One study identified memory B cells in the submucosa of adult intestinal tissue that produced broadly cross-reactive and cross-neutralizing antibodies specific to VP5*; accordingly, recombinant VP5* might represent a broadly efficient candidate for a rotavirus vaccine191.
Acknowledgments
The findings and conclusions in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official position of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Footnotes
Author contributions
Introduction (S.E.C. and S.R.); Epidemiology (J.E.T. and U.D.P.); Mechanisms/pathophysiology (L.S. and M.H.); Diagnosis, screening and prevention (M.A.F. and H.B.G.); Management (M.O.); Quality of life (G.K.); Outlook (U.D. and M.K.E.); Overview of Primer (S.E.C., S.R. and M.K.E.).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.GBD Diarrhoeal Disease Collaborators. Estimates of global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of diarrhoeal diseases: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:909–948. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30276-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bishop RF, et al. Virus particles in epithelial cells of duodenal mucosa from children with acute non-bacterial gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1973;2:1281–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92867-5. This study shows visualization of rotavirus as the causative agent of viral gastroenteritis and the associated histopathology. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Flewett TH, et al. Letter: Virus particles in gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1973;2:1497. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92760-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Estes MK, Greenberg HB. In: Field’s Virology. Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Lippincott: Williams & Wilkins; 2013. pp. 1347–1401. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Matthijnssens J, et al. VP6-sequence-based cutoff values as a criterion for rotavirus species demarcation. Arch Virol. 2012;157:1177–1182. doi: 10.1007/s00705-012-1273-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mihalov-Kovács E, et al. Candidate new rotavirus species in sheltered dogs, Hungary. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21:660–663. doi: 10.3201/eid2104.141370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bányai K, et al. Candidate new rotavirus species in Schreiber’s bats, Serbia. Infect Genet Evol. 2017;48:19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2016.12.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Leuven KU, Rotavirus Classification Working Group: RCWG KU Leuven Laboratory of Viral Metagenomics. 2017 https://rega.kuleuven.be/cev/viralmetagenomics/virus-classification/rcwg.
- 9.Matthijnssens J, et al. Rotavirus disease and vaccination: impact on genotype diversity. Future Microbiol. 2009;4:1303–1316. doi: 10.2217/fmb.09.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gentsch JR, et al. Serotype diversity and reassortment between human and animal rotavirus strains: implications for rotavirus vaccine programs. J Infect Dis. 2005;192(Suppl. 1):S146–S159. doi: 10.1086/431499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Santos N, Hoshino Y. Global distribution of rotavirus serotypes/genotypes and its implication for the development and implementation of an effective rotavirus vaccine. Rev Med Virol. 2005;15:29–56. doi: 10.1002/rmv.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Matthijnssens J, et al. Phylodynamic analyses of rotavirus genotypes G9 and G12 underscore their potential for swift global spread. Mol Biol Evol. 2010;27:2431–2436. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nakagomi O, Nakagomi T. Genetic diversity and similarity among mammalian rotaviruses in relation to interspecies transmission of rotavirus. Arch Virol. 1991;120:43–55. doi: 10.1007/BF01310948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Martella V, et al. Zoonotic aspects of rotaviruses. Vet Microbiol. 2010;140:246–255. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2009.08.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hagbom M, et al. Rotavirus stimulates release of serotonin (5-HT) from human enterochromaffin cells and activates brain structures involved in nausea and vomiting. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1002115. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002115. This report shows that rotavirus can stimulate 5-HT release from human enterochromaffin cells and activate the vomiting centre in the central nervous system. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Leung AK, Robson WL. Acute gastroenteritis in children: role of anti-emetic medication for gastroenteritis-related vomiting. Paediatr Drugs. 2007;9:175–184. doi: 10.2165/00148581-200709030-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tate JE, et al. Estimate of worldwide rotavirus-associated mortality in children younger than 5 years before the introduction of universal rotavirus vaccination programmes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12:136–141. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70253-5. 2008. This study is the 2008 estimate of rotavirus related mortality (450,000 deaths), the benchmark by which the impact of rotavirus vaccination programmes were measured. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tate JE, et al. Global, regional, and national estimates of rotavirus mortality in children <5 years of age, 2000–2013. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62(Suppl. 2):S96–S105. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gurwith M, et al. A prospective study of rotavirus infection in infants and young children. J Infect Dis. 1981;144:218–224. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.3.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Velazquez FR, et al. Rotavirus infection in infants as protection against subsequent infections. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:1022–1028. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199610033351404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Parashar UD, et al. Global illness and deaths caused by rotavirus disease in children. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:565–572. doi: 10.3201/eid0905.020562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ramachandran M, et al. Unusual diversity of human rotavirus G and P genotypes in India. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:436–439. doi: 10.1128/jcm.34.2.436-439.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sanderson C, Clark A, Taylor D, Bolanos B. Global review of rotavirus morbidity and mortality data by age and region. WHO; 2011. http://www.who.int/immunization/sage/meetings/2012/april/Sanderson_et_al_SAGE_April_rotavirus.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Patel MM, et al. Global seasonality of rotavirus disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2013;32:e134–e147. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e31827d3b68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Burnett E, et al. Global impact of rotavirus vaccination on childhood hospitalizations and mortality from diarrhea. J Infect Dis. 2017;215:1666–1672. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix186. This study summarizes the impact of rotavirus vaccination during the first 10 years after vaccine licensure and concludes that implementation of rotavirus vaccines substantially decreased hospitalizations from rotavirus and all-cause acute gastroenteritis. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tate JE, Parashar UD. Rotavirus vaccines in routine use. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:1291–1301. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Markkula J, et al. Rotavirus epidemiology 5–6 years after universal rotavirus vaccination: persistent rotavirus activity in older children and elderly. Infect Dis. 2017;49:388–394. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2016.1275773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Aliabadi N, et al. Sustained decrease in laboratory detection of rotavirus after implementation of routine vaccination-United States, 2000–2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64:337–342. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Leshem E, et al. Distribution of rotavirus strains and strain-specific effectiveness of the rotavirus vaccine after its introduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:847–856. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70832-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Doro R, et al. Review of global rotavirus strain prevalence data from six years post vaccine licensure surveillance: is there evidence of strain selection from vaccine pressure? Infect Genet Evol. 2014;28:446–461. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2014.08.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Correia JB, et al. Effectiveness of monovalent rotavirus vaccine (Rotarix) against severe diarrhea caused by serotypically unrelated G2P[4] strains in Brazil. J Infect Dis. 2010;201:363–369. doi: 10.1086/649843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ward RL, et al. Human rotavirus studies in volunteers: determination of infectious dose and serological response to infection. J Infect Dis. 1986;154:871–880. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.5.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ansari SA, et al. Survival and vehicular spread of human rotaviruses: possible relation to seasonality of outbreaks. Rev Infect Dis. 1991;13:448–461. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.3.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Butz AM, et al. Prevalence of rotavirus on high-risk fomites in day-care facilities. Pediatrics. 1993;92:202–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lundgren O, Svensson L. Pathogenesis of rotavirus diarrhea. Microbes Infect. 2001;3:1145–1156. doi: 10.1016/S1286-4579(01)01475-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Saxena K, et al. Human intestinal enteroids: a new model to study human rotavirus infection, host restriction, and pathophysiology. J Virol. 2015;90:43–56. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01930-15. This study uses human intestinal enteroids to study rotavirus infections. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lopez S, Arias CF. Multistep entry of rotavirus into cells: a Versaillesque dance. Trends Microbiol. 2004;12:271–278. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Arias CF, et al. Rotavirus entry: a deep journey into the cell with several exits. J Virol. 2015;89:890–893. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01787-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ramani S, et al. Diversity in rotavirus-host glycan interactions: a “sweet” spectrum. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;2:263–273. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2016.03.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nordgren J, et al. Host genetic factors affect susceptibility to norovirus infections in Burkina Faso. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e69557. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ramani S, et al. The VP8* domain of neonatal rotavirus strain G10P[11] binds to type II precursor glycans. J Virol. 2013;87:7255–7264. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03518-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Morris AP, Estes MK. Microbes and microbial toxins: paradigms for microbial-mucosal interactions. VIII Pathological consequences of rotavirus infection and its enterotoxin. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001;281:G303–G310. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.2001.281.2.G303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Chen CC, et al. Fecal calprotectin as a correlative marker in clinical severity of infectious diarrhea and usefulness in evaluating bacterial or viral pathogens in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012;55:541–547. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e318262a718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wiegering V, et al. Gastroenteritis in childhood: a retrospective study of 650 hospitalized pediatric patients. Int J Infect Dis. 2011;15:e401–e407. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2011.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ball JM, et al. Age-dependent diarrhea induced by a rotaviral nonstructural glycoprotein. Science. 1996;272:101–104. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5258.101. This report identifies NSP4 as the first enterotoxin that induces diarrhoea in mouse pups. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Holmes IH, et al. Infantile enteritis viruses: morphogenesis and morphology. J Virol. 1975;16:937–943. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.937-943.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Davidson GP, Barnes GL. Structural and functional abnormalities of the small intestine in infants and young children with rotavirus enteritis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979;68:181–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb04986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Osborne MP, et al. Rotavirus-induced changes in the microcirculation of intestinal villi of neonatal mice in relation to the induction and persistence of diarrhea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1991;12:111–120. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199101000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ward LA, et al. Pathogenesis of an attenuated and a virulent strain of group A human rotavirus in neonatal gnotobiotic pigs. J Gen Virol. 1996;77:1431–1441. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-77-7-1431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hyser JM, et al. Rotavirus disrupts calcium homeostasis by NSP4 viroporin activity. mBio. 2010;1:e00265–10. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00265-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Boshuizen JA, et al. Changes in small intestinal homeostasis, morphology, and gene expression during rotavirus infection of infant mice. J Virol. 2003;77:13005–13016. doi: 10.1128/JVI.77.24.13005-13016.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Bhowmick R, et al. Rotaviral enterotoxin nonstructural protein 4 targets mitochondria for activation of apoptosis during infection. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:35004–35020. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.369595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 53.Tafazoli F, et al. NSP4 enterotoxin of rotavirus induces paracellular leakage in polarized epithelial cells. J Virol. 2001;75:1540–1546. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.3.1540-1546.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Boshuizen JA, et al. Rotavirus enterotoxin NSP4 binds to the extracellular matrix proteins laminin-β3 and fibronectin. J Virol. 2004;78:10045–10053. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.18.10045-10053.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Svensson L, Desselberger U, Greenberg HB, Estes MK. Viral gastroenteritis: molecular epidemiology and pathogenesis. Elsevier; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Seo NS, et al. Integrins α1β1 and α2β1 are receptors for the rotavirus enterotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:8811–8818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803934105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ko EA, et al. Chloride channel inhibition by a red wine extract and a synthetic small molecule prevents rotaviral secretory diarrhoea in neonatal mice. Gut. 2014;63:1120–1129. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Pham T, et al. The rotavirus NSP4 viroporin domain is a calcium-conducting ion channel. Sci Rep. 2017;7:43487. doi: 10.1038/srep43487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Bialowas S, et al. Rotavirus and serotonin cross-talk in diarrhoea. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0159660. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Istrate C, et al. Rotavirus infection increases intestinal motility but not permeability at the onset of diarrhea. J Virol. 2014;88:3161–3169. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02927-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Li ST, et al. Loperamide therapy for acute diarrhea in children: systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2007;4:e98. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Andrews PL, Horn CC. Signals for nausea and emesis: Implications for models of upper gastrointestinal diseases. Auton Neurosci. 2006;125:100–115. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2006.01.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.DeCamp LR, et al. Use of antiemetic agents in acute gastroenteritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2008;162:858–865. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.162.9.858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Bardhan PK, et al. Gastric emptying of liquid in children suffering from acute rotaviral gastroenteritis. Gut. 1992;33:26–29. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Uhnoo I, et al. Clinical features of acute gastroenteritis associated with rotavirus, enteric adenoviruses, and bacteria. Arch Dis Child. 1986;61:732–738. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.8.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Brodal P. The central nervous system: structure and function. Oxford Univ. Press; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Eskilsson A, et al. Immune-induced fever is mediated by IL-6 receptors on brain endothelial cells coupled to STAT3-dependent induction of brain endothelial prostaglandin synthesis. J Neurosci. 2014;34:15957–15961. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3520-14.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Jiang B, et al. Cytokines as mediators for or effectors against rotavirus disease in children. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003;10:995–1001. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.10.6.995-1001.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Blutt SE, et al. Rotavirus antigenemia in children is associated with viremia. PLoS Med. 2007;4:e121. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040121. This is a key study that shows infectious virus in the serum of children with rotavirus infections. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ramani S, et al. Rotavirus antigenemia in Indian children with rotavirus gastroenteritis and asymptomatic infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;51:1284–1289. doi: 10.1086/657069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Hemming M, et al. Rotavirus antigenemia in children is associated with more severe clinical manifestations of acute gastroenteritis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014;33:366–371. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000000118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Bass DM, et al. Molecular basis of age-dependent gastric inactivation of rhesus rotavirus in the mouse. J Clin Invest. 1992;89:1741–1745. doi: 10.1172/JCI115776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Venkataram Prasad BV, et al. Structural basis of glycan interaction in gastroenteric viral pathogens. Curr Opin Virol. 2014;7:119–127. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2014.05.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Franco MA, et al. Immunity and correlates of protection for rotavirus vaccines. Vaccine. 2006;24:2718–2731. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.12.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Desselberger U, Huppertz HI. Immune responses to rotavirus infection and vaccination and associated correlates of protection. J Infect Dis. 2011;203:188–195. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiq031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Broquet AH, et al. RIG-I/MDA5/MAVS are required to signal a protective IFN response in rotavirus-infected intestinal epithelium. J Immunol. 2011;186:1618–1626. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lin JD, et al. Distinct roles of type I and type III interferons in intestinal immunity to homologous and heterologous rotavirus infections. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:e1005600. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.López S, et al. Rotavirus strategies against the innate antiviral system. Annu Rev Virol. 2016;3:591–609. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-110615-042152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Uchiyama R, et al. MyD88-mediated TLR signaling protects against acute rotavirus infection while inflammasome cytokines direct Ab response. Innate Immun. 2015;21:416–428. doi: 10.1177/1753425914547435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Uchiyama R, et al. Antibiotic treatment suppresses rotavirus infection and enhances specific humoral immunity. J Infect Dis. 2014;210:171–182. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Zhu S. Nlrp9b inflammasome restricts rotavirus infection in intestinal epithelial cells. Nature. 2017;546:667–670. doi: 10.1038/nature22967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Pott J, et al. Age-dependent TLR3 expression of the intestinal epithelium contributes to rotavirus susceptibility. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8:e1002670. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Holloway G, et al. Rotavirus inhibits IFN-induced STAT nuclear translocation by a mechanism that acts after STAT binding to importin-alpha. J Gen Virol. 2014;95:1723–1733. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.064063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Zhang B, et al. Prevention and cure of rotavirus infection via TLR5/NLRC4-mediated production of IL-22 and IL-18. Science. 2014;346:861–865. doi: 10.1126/science.1256999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Hernandez PP, et al. Interferon-λ and interleukin 22 act synergistically for the induction of interferon-stimulated genes and control of rotavirus infection. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:698–707. doi: 10.1038/ni.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Chanda S, et al. Rotavirus-induced miR-142-5p elicits proviral milieu by targeting non-canonical transforming growth factor beta signalling and apoptosis in cells. Cell Microbiol. 2016;18:733–747. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Rodriguez LS, et al. Immunomodulators released during rotavirus infection of polarized caco-2 cells. Viral Immunol. 2009;22:163–172. doi: 10.1089/vim.2008.0110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Liu F, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG on rotavirus-induced injury of ileal epithelium in gnotobiotic pigs. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2013;57:750–758. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e3182a356e1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Franco MA, Greenberg HB. Immunity to rotavirus in T cell deficient mice. Virology. 1997;238:169–179. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Angel J, et al. Correlates of protection for rotavirus vaccines: possible alternative trial endpoints, opportunities, and challenges. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10:3659–3671. doi: 10.4161/hv.34361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Mesa MC, et al. A TGF-β mediated regulatory mechanism modulates the T cell immune response to rotavirus in adults but not in children. Virology. 2010;399:77–86. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Jaimes MC, et al. Frequencies of virus-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes secreting gamma interferon after acute natural rotavirus infection in children and adults. J Virol. 2002;76:4741–4749. doi: 10.1128/JVI.76.10.4741-4749.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Gladstone BP, et al. Protective effect of natural rotavirus infection in an Indian birth cohort. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:337–346. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1006261. The study by Velazquez et al. (REF. 20) formed the basis for rotavirus vaccines. However, this study suggests that natural infections (and therefore vaccines) are not likely to be as effective in some populations. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Gilger MA, et al. Extraintestinal rotavirus infections in children with immunodeficiency. J Pediatr. 1992;120:912–917. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81959-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Patel NC, et al. Vaccine-acquired rotavirus in infants with severe combined immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:314–319. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0904485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.VanCott JL, et al. Mice develop effective but delayed protective immune responses when immunized as neonates either intranasally with nonliving VP6/LT(R192G) or orally with live rhesus rotavirus vaccine candidates. J Virol. 2006;80:4949–4961. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.10.4949-4961.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Parra M, et al. Circulating rotavirus-specific T cells have a poor functional profile. Virology. 2014;468–470:340–350. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.08.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Ward RL, et al. Reductions in cross-neutralizing antibody responses in infants after attenuation of the human rotavirus vaccine candidate 89–12. J Infect Dis. 2006;194:1729–1736. doi: 10.1086/509623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Florez ID, et al. The effectiveness and safety of treatments used for acute diarrhea and acute gastroenteritis in children: protocol for a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Syst Rev. 2016;5:14. doi: 10.1186/s13643-016-0186-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Bishop RF, et al. Clinical immunity after neonatal rotavirus infection A prospective longitudinal study in young children. N Engl J Med. 1983;309:72–76. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198307143090203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Kilgore PE, et al. Neonatal rotavirus infection in Bangladesh: strain characterization and risk factors for nosocomial infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1996;15:672–677. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199608000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Payne DC, et al. Active, population-based surveillance for severe rotavirus gastroenteritis in children in the United States. Pediatrics. 2008;122:1235–1243. doi: 10.1542/peds.2007-3378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Raul VF, et al. Cohort study of rotavirus serotype patterns in symptomatic and asymptomatic infections in Mexican children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1993;12:54–61. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199301000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Glass RI, et al. The epidemiology of rotavirus diarrhea in the United States: surveillance and estimates of disease burden. J Infect Dis. 1996;174(Suppl. 1):S5–S11. doi: 10.1093/infdis/174.supplement_1.s5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Echeverria P, et al. Rotavirus as a cause of severe gastroenteritis in adults. J Clin Microbiol. 1983;18:663–667. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.663-667.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Nakajima H, et al. Winter seasonality and rotavirus diarrhoea in adults. Lancet. 2001;357:1950. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)05086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Pickering LK, et al. Asymptomatic excretion of rotavirus before and after rotavirus diarrhea in children in day care centers. J Pediatr. 1988;112:361–365. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80313-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Richardson S, et al. Extended excretion of rotavirus after severe diarrhoea in young children. Lancet. 1998;351:1844–1848. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)11257-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Kang G, et al. Quantitation of group A rotavirus by real-time reverse-transcription-polymerase chain reaction: correlation with clinical severity in children in South India. J Med Virol. 2004;73:118–122. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Ramani S, et al. Comparison of viral load and duration of virus shedding in symptomatic and asymptomatic neonatal rotavirus infections. J Med Virol. 2010;82:1803–1807. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Amar CF, et al. Detection by PCR of eight groups of enteric pathogens in 4,627 faecal samples: re-examination of the English case-control Infectious Intestinal Disease Study (1993–1996) Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007;26:311–323. doi: 10.1007/s10096-007-0290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Teitelbaum JE, Daghistani R. Rotavirus causes hepatic transaminase elevation. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52:3396–3398. doi: 10.1007/s10620-007-9743-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Akelma AZ, et al. Serum transaminase elevation in children with rotavirus gastroenteritis: seven years’ experience. Scand J Infect Dis. 2013;45:362–367. doi: 10.3109/00365548.2012.740573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Patel MM, et al. Fulfilling the promise of rotavirus vaccines: how far have we come since licensure? Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12:561–570. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Vesikari T, et al. Safety and efficacy of a pentavalent human-bovine (WC3) reassortant rotavirus vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:23–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Ruiz-Palacios GM, et al. Safety and efficacy of an attenuated vaccine against severe rotavirus gastroenteritis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:11–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Leshem E, et al. Rotavirus vaccines and health care utilization for diarrhea in the United States (2007–2011) Pediatrics. 2014;134:15–23. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-3849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Armah GE, et al. Efficacy of pentavalent rotavirus vaccine against severe rotavirus gastroenteritis in infants in developing countries in sub-Saharan Africa: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376:606–614. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60889-6. This is a key study that shows lower efficacy of RV5 vaccine in Asian children relative to previous studies in developed countries and Latin America. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Madhi SA, et al. Effect of human rotavirus vaccine on severe diarrhea in African infants. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:289–298. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0904797. This is a key study that shows lower efficacy of RV1 vaccine in African children relative to previous studies in developed countries and Latin America. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Zaman K, et al. Efficacy of pentavalent rotavirus vaccine against severe rotavirus gastroenteritis in infants in developing countries in Asia: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376:615–623. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60755-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Harris VC, et al. Significant correlation between the infant gut microbiome and rotavirus vaccine response in rural Ghana. J Infect Dis. 2017;215:34–41. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw518. This study indicates that the microbiome can impact rotavirus vaccines. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Harris V, et al. Rotavirus vaccine response correlates with the infant gut microbiota composition in Pakistan. Gut Microbes. 2017 doi: 10.1080/19490976.2017.1376162. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2017.1376162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 123.Becker-Dreps S, et al. The association between fecal biomarkers of environmental enteropathy and rotavirus vaccine response in Nicaraguan infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2017;36:412–416. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000001457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Emperador DM, et al. Interference of monovalent, bivalent, and trivalent oral poliovirus vaccines on monovalent rotavirus vaccine immunogenicity in rural Bangladesh. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62:150–156. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Chilengi R, et al. Association of maternal immunity with rotavirus vaccine immunogenicity in Zambian infants. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0150100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Ali A, et al. Impact of withholding breastfeeding at the time of vaccination on the immunogenicity of oral rotavirus vaccine-a randomized trial. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0145568. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Kazi AM, et al. Secretor and salivary ABO blood group antigen status predict rotavirus vaccine-take in infants. J Infect Dis. 2017;215:786–789. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Armah G, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of the impact of alternative dosing schedules on the immune response to human rotavirus vaccine in rural Ghanaian infants. J Infect Dis. 2016;213:1678–1685. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Murphy TV, et al. Intussusception among infants given an oral rotavirus vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:564–572. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200102223440804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Tate JE, et al. Intussusception rates before and after the introduction of rotavirus vaccine. Pediatrics. 2016;138:e20161082. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Groome MJ, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a parenteral P2VP8-P[8] subunit rotavirus vaccine in toddlers and infants in South Africa: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:843–853. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30242-6. This clinical trial reports the use of a non-replicating rotavirus vaccine. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Bhandari N, et al. Efficacy of a monovalent human-bovine (116E) rotavirus vaccine in Indian infants: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2014;383:2136–2143. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62630-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Chen MY, et al. Rotavirus specific maternal antibodies and immune response to RV3-BB neonatal rotavirus vaccine in New Zealand. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2017;13:1126–1135. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2016.1274474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Isanaka S, et al. Efficacy of a low-cost, heat-stable oral rotavirus vaccine in Niger. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1121–1130. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1609462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.O’Ryan GM, et al. Management of acute infectious diarrhea for children living in resource-limited settings. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2014;12:621–632. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2014.901168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Guarino A, et al. European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition/European Society for Pediatric Infectious Diseases evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute gastroenteritis in children in Europe: update 2014. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2014;59:132–152. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Bhattacharya SK. History of development of oral rehydration therapy. Indian J Public Health. 1994;38:39–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Kotloff KL, et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): a prospective, case-control study. Lancet. 2013;382:209–222. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60844-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.King CK, et al. Managing acute infectious gastroenteritis among children: oral rehydration, maintenance, and nutritional therapy. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2003;52:1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Ruuska T, Vesikari T. Rotavirus disease in Finnish children: use of numerical scores for clinical severity of diarrhoeal episodes. Scand J Infect Dis. 1990;22:259–267. doi: 10.3109/00365549009027046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Duggan C, et al. Scientific rationale for a change in the composition of oral rehydration solution. JAMA. 2004;291:2628–2631. doi: 10.1001/jama.291.21.2628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Churgay CA, Aftab Z. Gastroenteritis in children: Part II. Prevention and management. Am Fam Physician. 2012;85:1066–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Gaffey MF, et al. Dietary management of childhood diarrhea in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2013;13(Suppl. 3):S17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-S3-S17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Lo VA, et al. An international consensus report on a new algorithm for the management of infant diarrhoea. Acta Paediatr. 2016;105:e384–e389. doi: 10.1111/apa.13432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Bzik VA, et al. Mechanisms of action of zinc on rat intestinal epithelial electrogenic ion secretion: insights into its antidiarrhoeal actions. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012;64:644–653. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.de Queiroz CA, et al. Zinc treatment ameliorates diarrhea and intestinal inflammation in undernourished rats. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014;14:136. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-14-136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.World Health Organization. Department of Child and Adolescent Health and Development & UNICEF. Clinical management of acute diarrhoea: WHO/UNICEF joint statement. WHO; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 148.Lukacik M, et al. A meta-analysis of the effects of oral zinc in the treatment of acute and persistent diarrhea. Pediatrics. 2008;121:326–336. doi: 10.1542/peds.2007-0921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.O’Ryan M, et al. An update on management of severe acute infectious gastroenteritis in children. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010;8:671–682. doi: 10.1586/eri.10.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Freedman SB, et al. Gastroenteritis therapies in developed countries: systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0128754. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Ahmadi E, et al. Efficacy of probiotic use in acute rotavirus diarrhea in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Caspian J Intern Med. 2015;6:187–195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Vlasova AN, et al. Comparison of probiotic lactobacilli and bifidobacteria effects, immune responses and rotavirus vaccines and infection in different host species. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2016;172:72–84. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2016.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Sindhu KN, et al. Immune response and intestinal permeability in children with acute gastroenteritis treated with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;58:1107–1115. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Das S, et al. Efficacy and safety of Saccharomyces boulardii in acute rotavirus diarrhea: double blind randomized controlled trial from a developing country. J Trop Pediatr. 2016;62:464–470. doi: 10.1093/tropej/fmw032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Rossignol JF. Nitazoxanide: a first-in-class broad-spectrum antiviral agent. Antiviral Res. 2014;110:94–103. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.07.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Rossignol JF, et al. Effect of nitazoxanide for treatment of severe rotavirus diarrhoea: randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2006;368:124–129. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68852-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Mahapatro S, et al. Nitazoxanide in acute rotavirus diarrhea: a randomized control trial from a developing country. J Trop Med. 2017;2017:7942515. doi: 10.1155/2017/7942515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.La FS, et al. Thiazolides, a new class of antiviral agents effective against rotavirus infection, target viral morphogenesis, inhibiting viroplasm formation. J Virol. 2013;87:11096–11106. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01213-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Das JK, et al. The effect of antiemetics in childhood gastroenteritis. BMC Public Health. 2013;13(Suppl. 3):S9–S13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-S3-S9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Primi MP, et al. Racecadotril demonstrates intestinal antisecretory activity. in vivo Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999;13(Suppl. 6):3–7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.13.s6.3.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Emparanza Knörr JI, et al. Systematic review of the efficacy of racecadotril in the treatment of acute diarrhoea [Spanish] An Pediatr. 2008;69:432–438. doi: 10.1157/13127998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Gordon M, Akobeng A. Racecadotril for acute diarrhoea in children: systematic review and meta-analyses. Arch Dis Child. 2016;101:234–240. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2015-309676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Gharial J, et al. Racecadotril for the treatment of severe acute watery diarrhoea in children admitted to a tertiary hospital in Kenya. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2017;4:e000124. doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2016-000124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Kang G, et al. Racecadotril in the management of rotavirus and non-rotavirus diarrhea in under-five children: two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Indian Pediatr. 2016;53:595–600. doi: 10.1007/s13312-016-0894-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Das RR, et al. Efficacy and safety of diosmectite in acute childhood diarrhoea: a meta-analysis. Arch Dis Child. 2015;100:704–712. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2014-307632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Dupont C, et al. Oral diosmectite reduces stool output and diarrhea duration in children with acute watery diarrhea. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:456–462. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2008.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Beutels P, et al. Funding of drugs: do vaccines warrant a different approach? Lancet Infect Dis. 2008;8:727–733. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(08)70258-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Griebsch I, et al. Quality-adjusted life-years lack quality in pediatric care: a critical review of published cost-utility studies in child health. Pediatrics. 2005;115:e600–e614. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-2127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Diez DJ, et al. The impact of childhood acute rotavirus gastroenteritis on the parents’ quality of life: prospective observational study in European primary care medical practices. BMC Pediatr. 2012;12:58. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-12-58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Rochanathimoke O, et al. Quality of life of diarrheal children and caregivers in Thailand. Value Health. 2014;17:A368–A369. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2014.08.832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Sénécal M, et al. Measuring the Impact of Rotavirus Acute Gastroenteritis Episodes (MIRAGE): a prospective community-based study. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2008;19:397–404. doi: 10.1155/2008/451540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Kolling G, et al. Enteric pathogens through life stages. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012;2:114. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Aballea S, et al. A critical literature review of health economic evaluations of rotavirus vaccination. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013;9:1272–1288. doi: 10.4161/hv.24253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Atherly DE, et al. Projected health and economic impact of rotavirus vaccination in GAVI-eligible countries: 2011–2030. Vaccine. 2012;30(Suppl. 1):A7–A14. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.12.096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Ogden KM, et al. Predicted structure and domain organization of rotavirus capping enzyme and innate immune antagonist VP3. J Virol. 2014;88:9072–9085. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00923-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Ogden KM, et al. Structural basis for 2′-5′- oligoadenylate binding and enzyme activity of a viral RNase L antagonist. J Virol. 2015;89:6633–6645. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00701-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Brandmann T, Jinek M. Crystal structure of the C-terminal 2′,5′-phosphodiesterase domain of group A rotavirus protein VP3. Proteins. 2015;83:997–1002. doi: 10.1002/prot.24794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Suzuki H, et al. Electron microscopic evidence for budding process-independent assembly of double-shelled rotavirus particles during passage through endoplasmic reticulum membranes. J Gen Virol. 1993;74:2015–2018. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-9-2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Cheung W, et al. Rotaviruses associate with cellular lipid droplet components to replicate in viroplasms, and compounds disrupting or blocking lipid droplets inhibit viroplasm formation and viral replication. J Virol. 2010;84:6782–6798. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01757-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Hu L, et al. Cell attachment protein VP8* of a human rotavirus specifically interacts with A-type histo-blood group antigen. Nature. 2012;485:256–259. doi: 10.1038/nature10996. This paper demonstrates that the A-type HBGA is a cell attachment factor for a human rotavirus strain and structurally characterizing the HBGA binding to VP8*. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Asano KM, et al. Group A rotavirus in Brazilian bats: description of novel T15 and H15 genotypes. Arch Virol. 2016;161:3225–3230. doi: 10.1007/s00705-016-3010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Richards JE, et al. Experimental pathways towards developing a rotavirus reverse genetics system: synthetic full length rotavirus ssRNAs are neither infectious nor translated in permissive cells. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e74328. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.De LG, et al. An inhibitory motif on the 5′UTR of several rotavirus genome segments affects protein expression and reverse genetics strategies. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0166719. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Kanai Y, et al. Entirely plasmid-based reverse genetics system for rotaviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:2349–2354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1618424114. This study reports the use of a plasmid-based reverse genetics system for rotavirus. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Saxena K, et al. A paradox of transcriptional and functional innate interferon responses of human intestinal enteroids to enteric virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:E570–E579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1615422114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Kandasamy S, et al. Differential effects of Escherichia coli Nissle and Lactobacillus rhamnosus Strain GG on human rotavirus binding, infection, and B cell immunity. J Immunol. 2016;196:1780–1789. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Angel J, et al. Rotavirus immune responses and correlates of protection. Curr Opin Virol. 2012;2:419–425. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2012.05.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Kirkpatrick BD, et al. The “Performance of Rotavirus and Oral Polio Vaccines in Developing Countries” (PROVIDE) study: description of methods of an interventional study designed to explore complex biologic problems. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;92:744–751. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.14-0518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Bucardo F, et al. Vaccine-derived NSP2 segment in rotaviruses from vaccinated children with gastroenteritis in Nicaragua. Infect Genet Evol. 2012;12:1282–1294. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2012.03.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Hemming M, Vesikari T. Detection of rotateq vaccine-derived, double-reassortant rotavirus in a 7-year-old child with acute gastroenteritis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014;33:655–656. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000000221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Nair N, et al. VP4- and VP7-specific antibodies mediate heterotypic immunity to rotavirus in humans. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9:eaam5434. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aam5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Ettayebi K, et al. Replication of human noroviruses in stem cell-derived human enteroids. Science. 2016;353:1387–1393. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf5211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Sato T, Clevers H. Growing self-organizing mini-guts from a single intestinal stem cell: mechanism and applications. Science. 2013;340:1190–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.1234852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Wong CJ, et al. Aseptic meningitis in an infant with rotavirus gastroenteritis. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984;3:244–246. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198405000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Wong V. Acute gastroenteritis-related encephalopathy. J Child Neurol. 2001;16:906–910. doi: 10.1177/088307380101601208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Nakagomi T, Nakagomi O. Rotavirus antigenemia in children with encephalopathy accompanied by rotavirus gastroenteritis. Arch Virol. 2005;150:1927–1931. doi: 10.1007/s00705-005-0565-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Ushijima H, et al. Suspected rotavirus encephalitis. Arch Dis Child. 1986;61:692–694. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.7.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Payne DC, et al. Protective association between rotavirus vaccination and childhood seizures in the year following vaccination in US children. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;58:173–177. doi: 10.1093/cid/cit671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Riepenhoff-Talty M, et al. Detection of group C rotavirus in infants with extrahepatic biliary atresia. J Infect Dis. 1996;174:8–15. doi: 10.1093/infdis/174.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Hertel PM, Estes MK. Rotavirus and biliary atresia: can causation be proven? Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012;28:10–17. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e32834c7ae4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Riepenhoff-Talty M, et al. Group A rotaviruses produce extrahepatic biliary obstruction in orally inoculated newborn mice. Pediatr Res. 1993;33:394–399. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199304000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Pane JA, et al. Rotavirus acceleration of type 1 diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice depends on type I interferon signalling. Sci Rep. 2016;6:29697. doi: 10.1038/srep29697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Pane JA, et al. Rotavirus activates lymphocytes from non-obese diabetic mice by triggering toll-like receptor 7 signaling and interferon production in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. PLoS Pathog. 2014;10:e1003998. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Graham KL, et al. Rotavirus infection of infant and young adult nonobese diabetic mice involves extraintestinal spread and delays diabetes onset. J Virol. 2007;81:6446–6458. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00205-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Blomqvist M, et al. Rotavirus infections and development of diabetes-associated autoantibodies during the first 2 years of life. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002;128:511–515. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Makela M, et al. Rotavirus-specific T cell responses and cytokine mRNA expression in children with diabetes-associated autoantibodies and type 1 diabetes. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006;145:261–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Angel J, et al. Rotavirus vaccines: recent developments and future considerations. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5:529–539. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.World Health Organization. Rotavirus mortality rate in children younger than 5 years, 2013. World Health Organization; 2017. http://www.who.int/immunization/monitoring_surveillance/burden/estimates/rotavirus/rotavirus_deaths_map_b.jpg?ua=1. [Google Scholar]
- 209.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sustained decrease in laboratory detection of rotavirus after implementation of routine vaccination — United States 2004–2014. CDC; 2015. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6413a1.htm. [Google Scholar]
- 210.Fleming FE, et al. Relative roles of GM1 ganglioside, N-acylneuraminic acids, and α2β1 integrin in mediating rotavirus infection. J Virol. 2014;88:4558–4571. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03431-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Guerrero CA, et al. Heat shock cognate protein 70 is involved in rotavirus cell entry. J Virol. 2002;76:4096–4102. doi: 10.1128/JVI.76.8.4096-4102.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Zarate S, et al. Interaction of rotaviruses with Hsc70 during cell entry is mediated by VP5. J Virol. 2003;77:7254–7260. doi: 10.1128/JVI.77.13.7254-7260.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Torres-Flores JM, et al. The tight junction protein JAM-A functions as coreceptor for rotavirus entry into MA104 cells. Virology. 2015;475:172–178. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Diaz-Salinas MA, et al. The spike protein VP4 defines the endocytic pathway used by rotavirus to enter MA104 cells. J Virol. 2013;87:1658–1663. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02086-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Kordasti S, et al. Serotonin and vasoactive intestinal peptide antagonists attenuate rotavirus diarrhoea. Gut. 2004;53:952–957. doi: 10.1136/gut.2003.033563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Trask SD, McDonald SM, Patton JT. Structural insights into the coupling of virion assembly and rotavirus replication. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012;10:165–177. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Hagbom M, et al. Towards a human rotavirus disease model. Curr Opin Virol. 2012;2:408–418. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2012.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Graff JW, et al. Rotavirus NSP1 inhibits NFκB activation by inducing proteasome-dependent degradation of β-TrCP: a novel mechanism of IFN antagonism. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5:e1000280. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Ding S, et al. Comparative proteomics reveals strain-specific β-TrCP degradation via rotavirus NSP1 hijacking a host cullin-3-Rbx1 complex. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:e1005929. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Sen A, et al. Rotavirus NSP1 protein inhibits interferon-mediated STAT1 activation. J Virol. 2014;88:41–53. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01501-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


