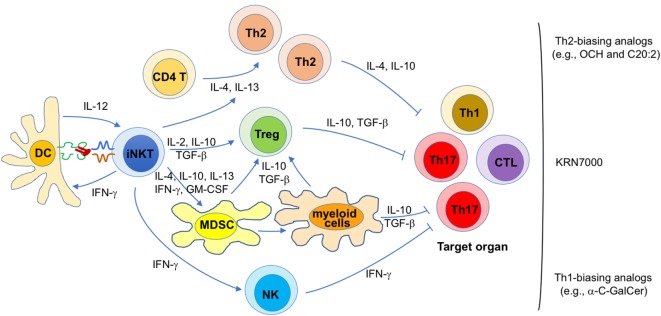
Figure 1.
Proposed mechanisms for the therapeutic potential of invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cell antigens against autoimmunity. Diverse mechanisms that may contribute to disease protection mediated by iNKT cell antigens in different autoimmune diseases are shown. Their relative contribution is likely influenced by a variety of parameters, such as the animal model (and mouse strain) employed, various treatment variables (e.g., lipid antigen, dose, timing, frequency), and the gut microbiota. Each of these proposed mechanisms likely contributes to the efficacy of KRN7000, whereas certain mechanisms are likely more dominant for KRN7000 analogs that bias iNKT cell cytokine production profiles, as indicated.