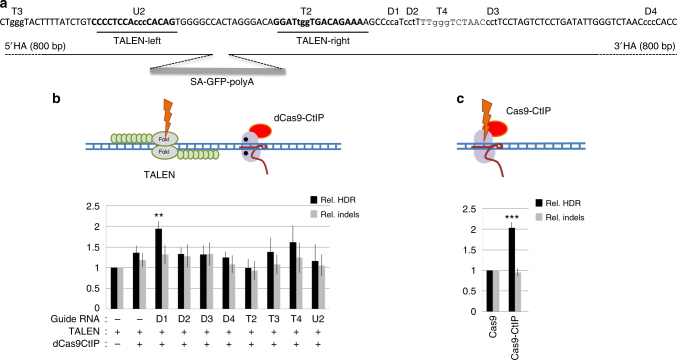
Fig. 1.
Forcing CtIP recruitment to the DNA cleavage site stimulates targeted transgene integration. a Distribution of TALEN and guide RNAs at AAVS1 safe harbor locus. gRNAs are indicated on top of their corresponding PAM motif, which is shown as lowercase in the sequence. The donor DNA used had 5′ and 3′ homology arms as indicated. b Relative HDR and indel frequencies induced by TALEN and dCas9–CtIP recruitment near the cleavage site using different guide RNAs. Human RG37 fibroblasts were transfected with the indicated plasmids and GFP transgene donor with homology arms to the targeted AAVS1 locus. HDR-mediated transgene integration was measured by FACS analysis of GFP-positive cells resulting from targeted GFP transgene integration. Indels at the cleavage site were measured by the T7E1 assay. The results are expressed as the mean of relative HDR or indel frequencies calculated by normalizing HDR or indel frequencies by that induced by TALEN transfection alone. Asterisks indicate the difference that is statistically significant when comparing cotransfection of dCas9–CtIP, guide RNA, and TALEN to TALEN-alone transfection in t-test (*P<0.05). Data are from three independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviation. c Relative HDR and indel frequencies induced by Cas9 and Cas9–CtIP at the cleavage site directed by T2 guide RNA. The results are expressed as the mean of relative HDR or indel frequencies calculated by normalizing HDR or indel frequencies by that induced by Cas9. Asterisks indicate that the difference is statistically significant when comparing Cas9–CtIP to Cas9 in t-test (**P<0.005). Data are from three independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Guide RNA T2 was used because in contrast to other guides, it did not cleave the donor DNA available