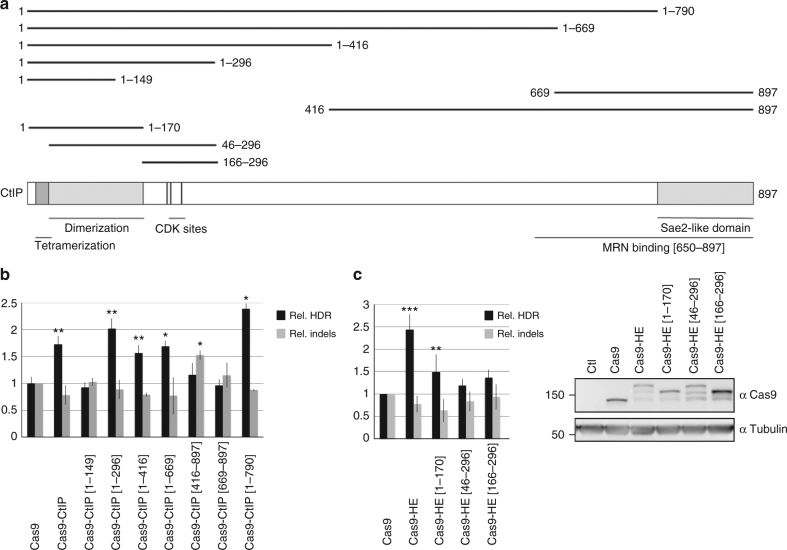
Fig. 2.
Identification of the “HDR-enhancer” (HE) domain of CtIP. a Schematic diagram of CtIP protein showing the different truncated CtIP proteins that have been fused to Cas9 and tested for their ability to stimulate HDR. Various sequence features of CtIP, including tetramerization and dimerization domains, and CDK phosphorylation sites S233, T245, and S276, are indicated. b Identification of a domain of CtIP, called HE, spanning aa 1 to 296, which is able to stimulate HDR when fused to Cas9. Human RG37 fibroblasts were transfected with the indicated plasmids expressing Cas9 or Cas9–CtIP derivatives, T2 guide RNA plasmid, and GFP transgene donor with homology arms to the targeted AAVS1 locus. Expression of fusion proteins was examined by western blot (Supplementary Fig. 1). Data are from four independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviation. c Functional analysis of HE domain. HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated Cas9 plasmids, T2 guide RNA, and GFP transgene donor with homology arms to the AAVS1 targeted locus. HDR-mediated transgene integration was measured by FACS analysis of GFP-positive cells, resulting from targeted GFP transgene integration. Indels at the cleavage site were measured by the T7E1 assay. The results are expressed as the mean of relative HDR or indel frequencies calculated by normalizing every HDR or indel frequency by that induced by Cas9, respectively. Asterisks indicate that the difference is statistically significant when comparing Cas9–CtIP or Cas9–HE derivatives to Cas9 in nonparametric t-test (*P<0.05, **P<0.005, or ***P<0.0005). Data are from four independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviation. The relative expression levels of Cas9 and Cas9–HE derivatives were analyzed by western blot using anti-Cas9 and control anti-tubulin antibodies