Fig. 5.
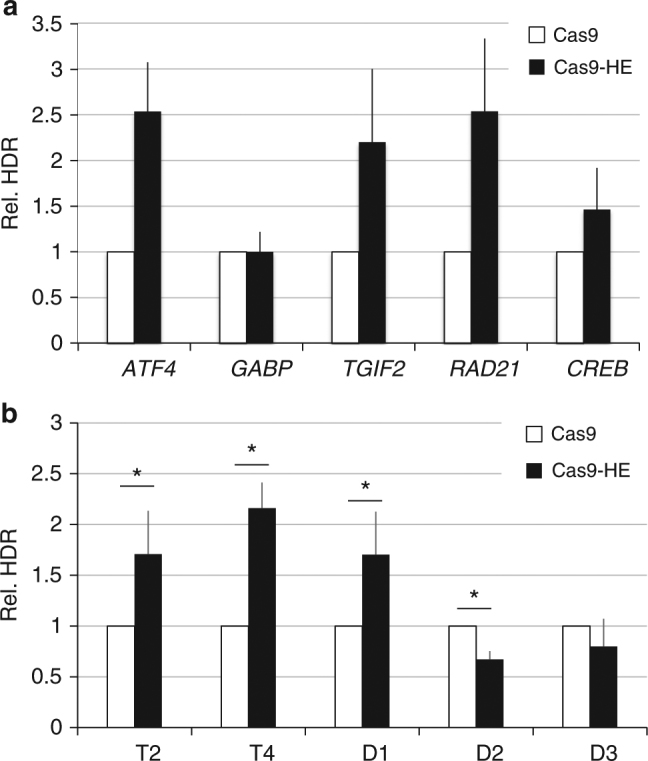
HDR stimulation by the HE domain takes place at different target genes and can depend on the guide RNA used. a Relative frequencies of HDR induced by Cas9–HE were compared to those induced by Cas9 at five different target genes in HEK293 cells using previously published guide RNAs and donor plasmids36. Targeted integration of the donor plasmid results in in-frame insertion of E2A-neoR cDNA36. G418(neomycin)-resistant colonies were counted after Cresyl violet staining to measure HDR-mediated events and normalized by the number of colonies obtained with Cas9 to give the relative HDR frequencies indicated. Data represented are from three independent experiments for TGIF2, RAD21, and CREB genes and from four experiments for ATF4 and GABP genes and are provided in Supplementary Fig. 7. Error bars indicate standard deviation. b Relative frequencies of HDR induced by Cas9–HE were compared to those induced by Cas9 with the indicated guide RNAs, which all cleave to a small 50-bp region of the AAVS1 locus, and a common p84∆ donor plasmid, harboring ~800-bp homology arms. P84∆ was derived from the p84 donor plasmid depicted in Fig. 1a by shortening the homology arms so that they would not be cleaved by any of the guide RNAs. Asterisks indicate that the difference is statistically significant when comparing Cas9–HE to Cas9 in t-test (*P<0.05). Data represented are from five independent experiments and are provided in Supplementary Fig. 7. Error bars indicate standard deviation
