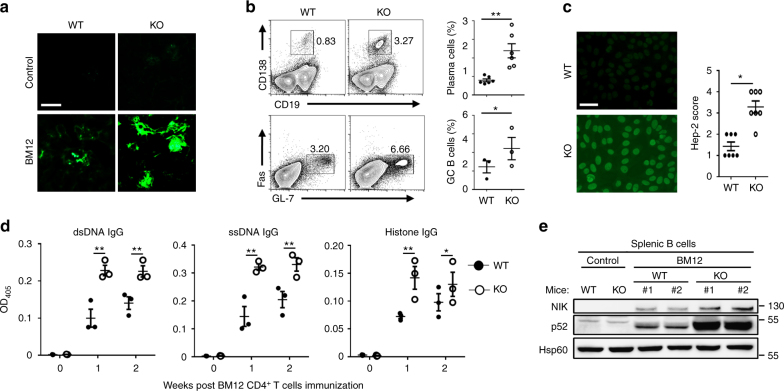
Fig. 2.
Peli1 deficiency aggravates the induction of lupus-like disease. a WT and Peli1-deficient (KO) mice were intraperitoneally injected with 7.5 million of CD4+ T cell from C57BL/6 mice (control) or from BM12 mice. Representative immunofluorescent images showing IgG deposits in kidney by staining with Alexa Fluor 488-labeled anti-mouse IgG. Scale bar, 100 μm. b Flow cytometric analysis of the percentages of CD19−CD138+ plasma cells and Fas+GL-7+ germinal center (GC) B cells in WT and KO immunized mice as described in (a). Data are presented as a representative plot (left panel) and summary graph (right panel). c Distinct anti-nuclear antibody (ANA) staining patterns of the Hep-2 cell line with serum from WT and KO mice 4 weeks after immunization as described in (a). Scale bar, 50 μm. d Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) of anti-dsDNA, anti-ssDNA, and anti-histone IgG in serum from WT and KO immunized mice as described in (a) at the indicate time point. e Immunoblot showing NIK and p52 protein levels in splenic B cells from control and BM12 CD4+ T cells immunized WT and KO mice as described in (a). Data are shown as the mean ± SEM based on three independent experiments. Two-tailed Student’s t-tests were performed. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01