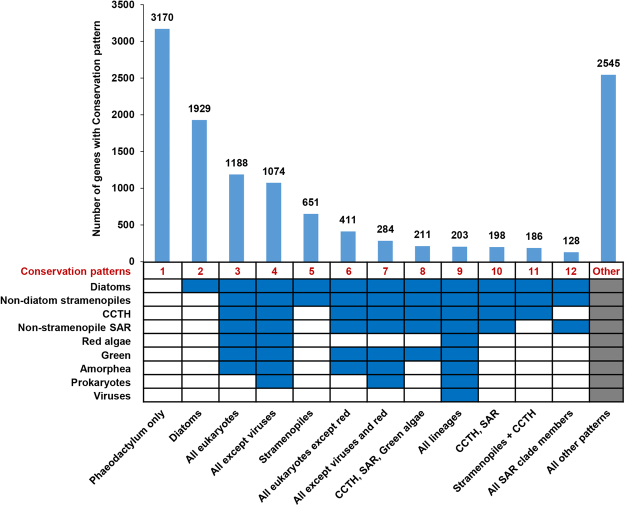
Figure 1.
Conserved and group-specific genes in P. tricornutum. The chart shows the numbers of different Phatr3 genes shared among different taxonomic groups (Diatoms, Non-diatom stramenopiles, CCTH, Non-stramenopiles SAR, Red algae, Green, Amorphea, Prokaryotes and Viruses) inferring various conservation patterns (indicated at the bottom on each column). The bar-plot shows the number of genes associated with each conservation pattern. Blue color cells, below the bar plot, indicate that orthologues are detected in the corresponding lineage. Only those conservation patterns are discretely indicated which account for at least 100 genes in the Phatr3 genome. Grey cells indicate that either conservation pattern was permitted. SAR refers to the combined clade of stramenopiles, alveolates and rhizaria; CCTH the combined clade of cryptomonads, centrohelids, haptophytes and telonemids; and amorphea refers to the combined clade of opisthokonts, amoebozoa and excavates21.