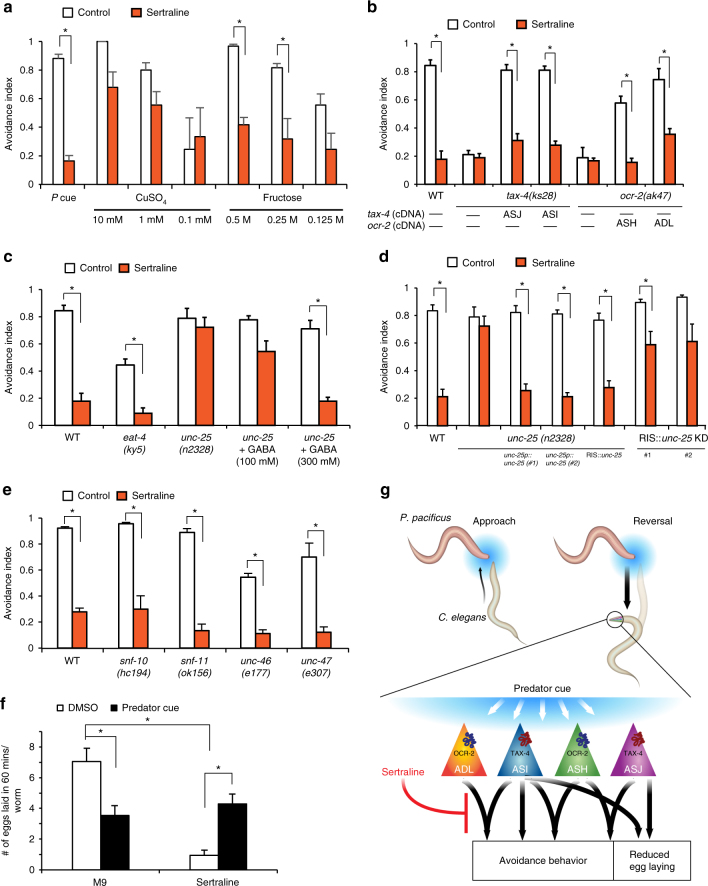
Fig. 4.
Sertraline attenuates C. elegans responses to the P. pacificus predator. a Sertraline attenuates C. elegans respnses to predator cue and fructose, whereas copper avoidance is only slightly reduced. b The effect of sertraline is lost in tax-4 and ocr-2 mutants, and modulation is restored when TAX-4 is restored to either ASI or ASJ, or when OCR-2 is restored to ASH or ADL. c Sertraline requires GABA, but not glutamate signaling. Sertraline modulates avoidance responses of eat-4 (glutamate receptor), but not unc-25 (glutamic acid decarboxylase, required for GABA synthesis) mutants. Adding GABA exogenously to plates restores sertraline modulation to unc-25 mutants. d Defective unc-25 response is rescued by expressing wild-type unc-25 cDNA under the unc-25 promoter or a RIS-selective promoter. Knocking down unc-25 specifically in RIS interneuron partially blocks sertraline modulation of predator avoidance. e Sertraline attenuates mutants in multiple GABA transporters including unc-47, snf-11, snf-10, and unc-46 (a transmembrane protein that recruits UNC-47). f Animals were treated with predator cue or predator cue and sertraline for 30 min and egg-laying was monitored for 60 min after removal of these compounds. g C. elegans detects predator cue using sensory circuits consisting of ASI, ASJ, ASH, and ADL neurons that use CNG and TRP channels and act in a redundant manner to generate rapid avoidance. In contrast, CNG channels act in ASI and ASJ neurons to reduce egg laying over many minutes. Sertraline attenuates both predator-induced avoidance behavior and egg-laying behavior downstream of these sensory neurons. Averages of either n > 30 (a–e) or n > 35 (f) and s.e.m. are shown. *p < 0.05 compared to controls obtained using Fisher’s exact t-test with Bonferroni correction (a–e) and *p < 0.05 compared to controls obtained using a two-way ANOVA (f)