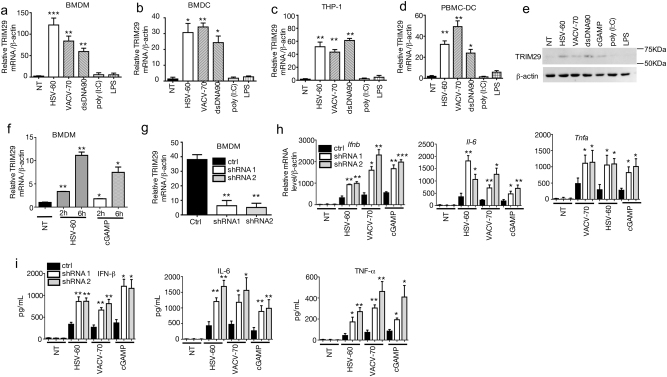
Fig. 1. TRIM29 responses to cytosolic viral DNA stimulation and negatively regulates cytosolic DNA-induced cytokine production.
Mouse BMDM a and BMDC b, human monocyte cell line THP-1 c and PBMC-derived DC d were stimulated with dsDNA90, VACV-70, HSV-60, LPS, and poly (I:C) for 12 h. The expression of TRIM29 mRNA was detected by real-time PCR and β-actin served as the reference gene. e BMDMs were treated with dsDNA90, VACV-70, HSV-60, cGAMP, LPS, and poly (I:C) for 24 h and protein level of TRIM29 was detected by IB using anti-TRIM29 antibody, β-actin served as the loading control. f BMDMs were treated with HSV-60 or cGAMP for 0, 2, or 6 h. The expression of TRIM29 mRNA was detected by real-time PCR and β-actin served as the reference gene. Two TRIM29-targeting shRNA (shRNA#1 and shRNA#2) and scramble shRNA (ctrl) were induced to mouse BMDM to knockdown TRIM29. The efficiency of knockdown was detected by real-time PCR g. BMDMs transfected with scramble shRNA or two TRIM29-targeting shRNA were stimulated with VACV-70, HSV-60, and cGAMP for 12 h, followed by real-time PCR assay h and ELISA i to detect the cytokine production. Data in all panels are representative of two to three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 (Student’s t-test). Error bars are s.d.