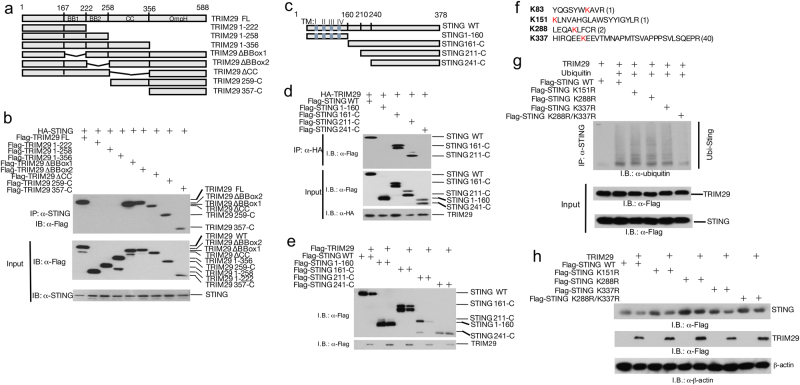
Fig. 5. Identification of critical domains mediating TRIM29–STING interaction.
a The schematic structure of TRIM29. b Full-length TRIM29 and different truncated TRIM29 mutants were co-expressed with STING in HEK 293T cells, and interaction between STING with WT or truncated TRIM29 was detected using IP and IB with indicated antibodies. c The schematic structure of STING. d The full-length STING and different truncated STING mutants were co-expressed with TRIM29, the interaction between TRIM29 with WT or truncated STING was detected by IP and IB with indicated antibodies. e The full-length STING and different truncated STING mutants were co-expressed with TRIM29 in HEK 293T cells and the protein level of STING (FL and truncated) and TRIM29 was detected with IB. f The Lys residues in STING were identified as potential targets of TRIM29 using IP-MS, highlighted in red. The number was frequency of specific peptides identified in IP product. g WT and mutated STING was co-expressed with TRIM29 and ubiquitin, the ubiquitination of STING was detected by IP and IB, and the protein level of STING was detected by IB, using indicated antibodies h