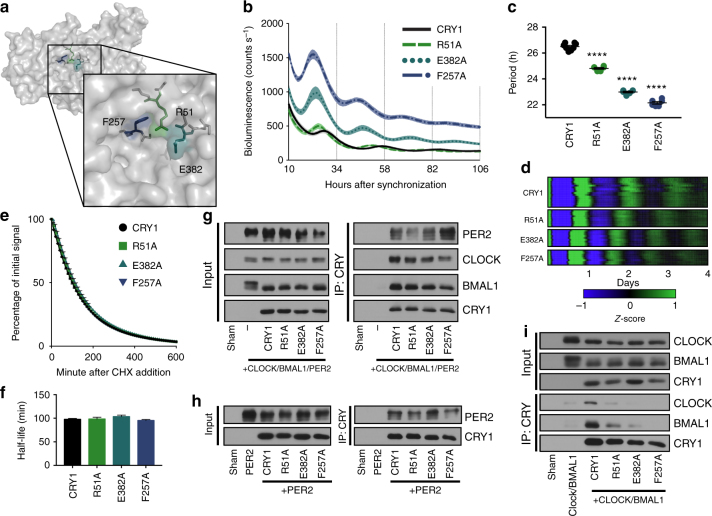
Fig. 5.
Weakened interaction between CRY1 and CLOCK/BMAL1 dramatically shortens the period in rescue assays. a Surface view of CRY1 (PDB: 5T5X) with an inset magnification of the secondary pocket. Residues R51, E382, and F257 are labeled and colored in green, teal, and navy blue. b Rescue assays performed with WT, R51A, E382A, and F257A CRY1 (n = 8, 6, 6, and 6 per condition, respectively, reflective of 9 (R51A), 15 (E382A), and 12 (F257A) plates from three to five independent experiments), shown as mean ± SEM. c Period plot for rescues shown in b. Mean ± SEM indicated by bars. Asterisks indicate significance by unpaired t test with Welch’s correction (****p < 0.0001). d Heat maps of CRY1 and mutant rescues demonstrate period and phase differences over multiple cycles. Raw data were baseline subtracted and z-scores were calculated, and then scaled to a range of −1 to 1. The data from 16 WT, 9 R51A, 9 E382A, and 8 F257A plates are shown. e Degradation assay with CRY1::LUC and mutants (n = 3 per condition). Samples were normalized to initial luminescence signal. Half-life was determined by fitting a one-phase decay curve to the data. f Half-lives from e shown as means + SEM. No significant difference between WT and mutants by unpaired t test with Welch’s correction (R51A: p = 0.8245; E382A: p = 0.0660; F257A: p = 0.2029) g Co-IP assay with PER2, CLOCK, BMAL1, and CRY1 mutants. Blot is representative of three independent experiments. h Co-IP assay with PER2 and CRY1 mutants. Blot is representative of three independent experiments. i Co-IP assay with CLOCK, BMAL1, and CRY1 mutants. Blot is representative of three independent experiments