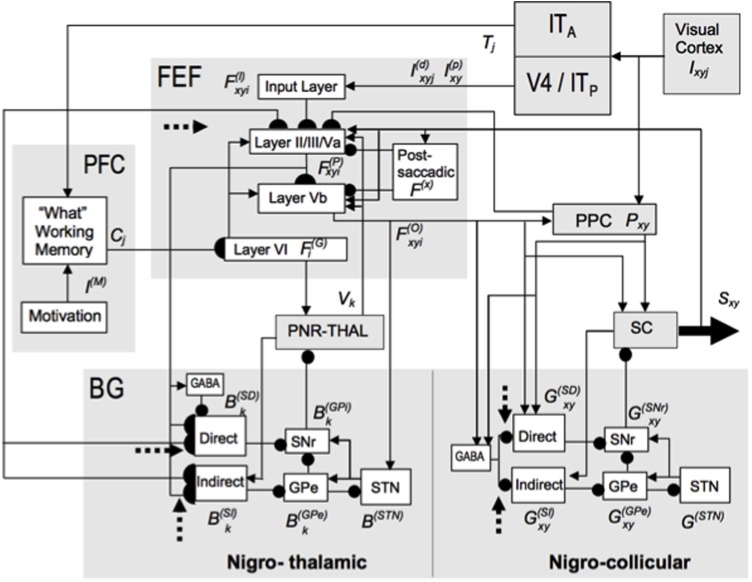
FIGURE 6.
The TELOS (TElencephalic Laminar Objective Selector) neural model of how basal ganglia (SNr) interactions gate learning of saccadic eye movement strategies. Due to the fact that parallel basal ganglia circuits regulate all aspects of cognition and behavior, similar basal ganglia dynamics may be expected in the explanations of many types of cognition and behavior. Separate gray-shaded blocks highlight the major anatomical regions whose roles in planned and reactive saccade generation are treated in the model. Excitatory links are shown as arrowheads, inhibitory as ballheads. Filled semi-circles terminate cortico-striatal and corticocortical pathways modeled as subject to learning, which is modulated by reinforcement-related dopaminergic signals (dashed arrows). See the archival article for details. [Reprinted with permission from Brown et al. (2004).]