Fig. 1.
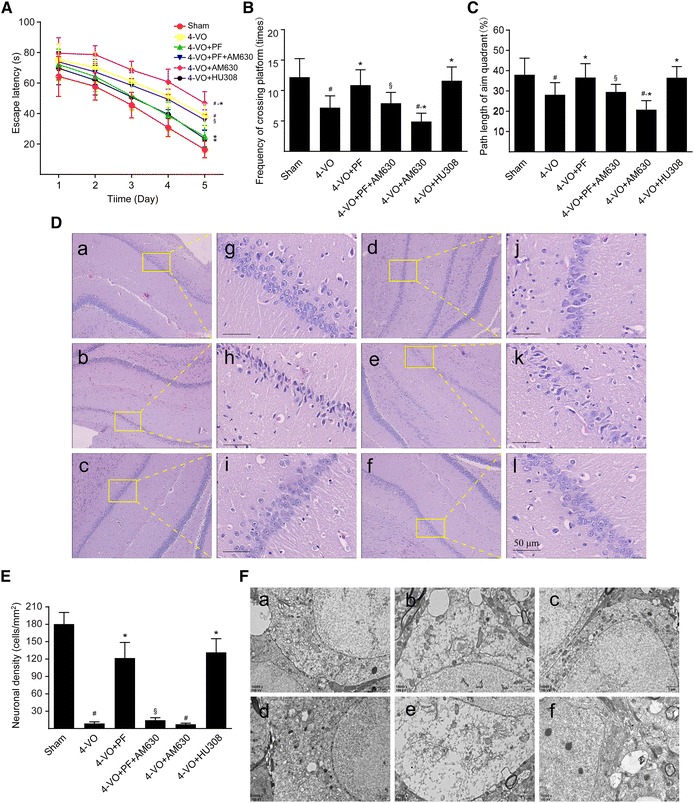
Effects of paeoniflorin on learning and memory abilities, histopathology and ultrastructure of the hippocampal CA1 area of rats after cerebral ischemia. One week after four-vessel occlusion (4-VO) surgery, rats were intraperitoneally administered saline (4-VO), paeoniflorin (4-VO+PF; 40 mg/kg/day), paeoniflorin+AM630 (4-VO+PF+AM630; 40 + 3 mg/kg/day), AM630 (4-VO+AM630; 3 mg/kg/day) or HU308 (4-VO+HU308; 3 mg/kg/day) for consecutive 28 days. Sham-operated group (Sham) was performed using the same surgical procedures, except that vertebral artery and bilateral common carotid arteries were not occluded. A Mean escape latency of rats in the water maze task was recorded during the last 5 days (23–28 days) of treatment. The spatial probe trial was performed on the last day (day 28) of water maze training, and the parameters measured included (B) the number of times rats crossed the platform and (C) relative path length in the target quadrant/path length in the whole pool within 120 s. D Rats were sacrificed after 28 days consecutive drug treatment. Representative photomicrographs of hematoxylin–eosin-stained hippocampal regions of rats are shown in different groups: (a, g) sham-operated group, (b, h) 4-VO-operated group, (c, i) 4-VO+PF group, (d, j) 4-VO+PF+AM630 group, (e, k) 4-VO+AM630 group or (f, l) 4-VO+HU308 group. Boxed regions in a–f are shown in j–l, respectively. Scale bar: 50 µm. E Neuronal cell density in CA1 region was measured by hematoxylin–eosin staining and cell counting. F Representative photomicrographs with a transmission electron microscope showing ultrastructural changes in hippocampus CA1 regions of rats in each group. Scale bar: 1 µm. Each bar represents mean ± SD of three independent experiments. n = 6 or 10 rats per group. #P < 0.05 versus sham group, *P < 0.05 versus 4-VO model group, §P < 0.05 versus 4-VO+PF group
