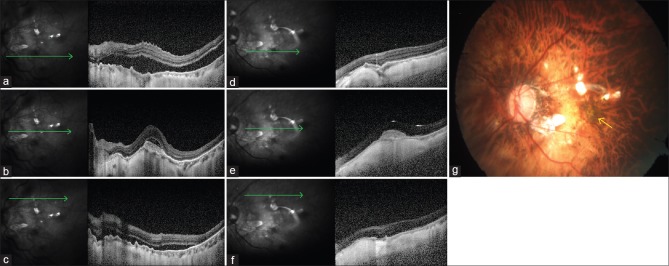
Figure 2.
(a) Preoperative line scan spectral domain optical coherence tomography image near inferior vascular arcade shows separation between retinal pigment epithelium and neurosensory retina suggestive of retinal detachment. (b) Preoperative line scan spectral domain optical coherence tomography image through the fovea shows choroidal neovascularization and overlying subretinal fluid suggestive of activity. Rest of the retina is attached. (c) Preoperative line scan spectral domain optical coherence tomography image near superior vascular arcade shows separation between retinal pigment epithelium and neurosensory retina suggestive of retinal detachment. (d) Postoperative line scan spectral domain optical coherence tomography image near inferior vascular arcade shows reattached retina. (e) Postoperative line scan spectral domain optical coherence tomography image through the fovea shows increased backscattering and reduced size of choroidal neovascularization suggestive of regression of choroidal neovascularization. Overlying subretinal fluid has resolved with regression. (f) Postoperative line scan spectral domain optical coherence tomography image near superior vascular arcade shows reattached retina. (g) Postoperative color fundus photograph of the left eye shows silicon oil-filled eye with attached retina and resolved choroidal neovascularization (yellow arrow)