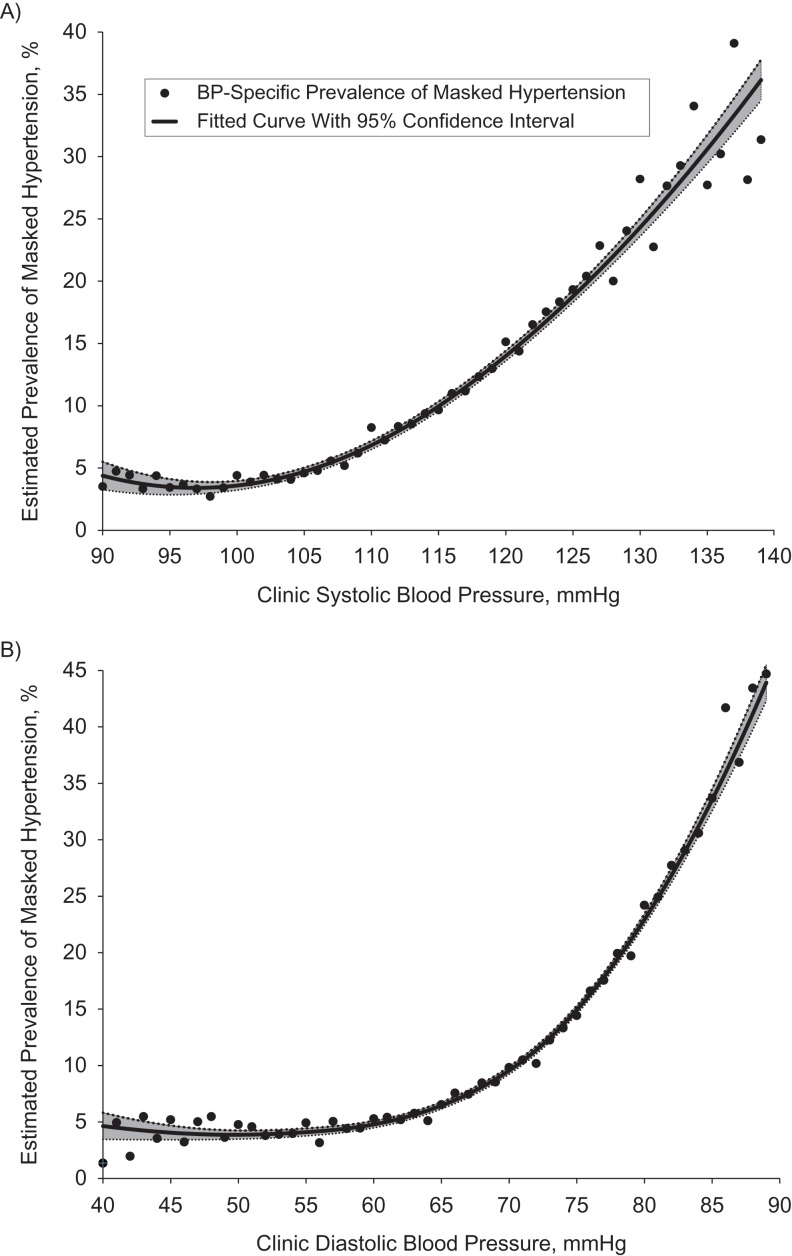
Figure 2.
Estimated prevalence of masked hypertension according to clinic blood pressure (BP) in the United States, 2005–2010. A) Systolic BP; B) diastolic BP. Estimates were based on multiple imputation (500 data sets) of hypertension status as defined by ambulatory blood pressure for 9,316 adult participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2005–2010) with nonelevated clinic BP, no history of overt cardiovascular disease, and no use of antihypertensive medication. A locally weight scatterplot smoothing (LOESS) curve using second-degree polynomials (black line) was fitted to the 50 BP-specific estimates (black circles), with weights proportional to the inverse of each estimate's squared standard error; smoothing parameters (1.00 for part A, 0.73 for part B) were selected to optimize the generalized cross-validation criterion (36). Gray area, 95% confidence interval.